Why did the air -rail transport in Germany just started in China?
Author:Global Travel News Time:2022.07.29

The differences in systems in Europe and East Asia determine the differences in the development of air -rail transportation.
Recently, a relatively large news in the global tourism industry is the German Railway (Deutsche Bahn) officially announced that it has joined the Star Alliance as the Intermodal Partner. Subsequently, KLM Royal Dutch Airlines also began to cooperate with Thalys to provide air -rail transportation services for Amsterdam Airport. This incident has also aroused some discussions in China. It can be seen that the industry is also interested in the development of China's air -rail transportation.
The multi -type transportation cooperation between the German railway and the Star Alliance is the natural extension of its multi -type transportation cooperation with Luthansa. This extension is based on the transportation mode of Germany itself. When discussing air -rail transportation, we must pay attention to the differences between China and Germany. We will explain the examples of Germany, Japan and China here.
01
As an EU country, German statistics can be found in the European Bureau of Statistics. According to statistics reported in Germany in 2019, German routes can be divided into three categories:
Domestic routes (no border inspection), about 23 million passengers in 2019 (11.35%);
International routes in the Schengen Zone (also do not require border inspections), about 96.76 million passengers in 2019 (47.76%);; 47.76%);
International routes outside the Schengen area (need to pass the border inspection), and about 82.83 million passengers (40.89%) in 2019.
Germany is a small country with a slightly smaller area of 360,000 square kilometers than Yunnan (390,000 square kilometers). From the southern Munich to the northernmost big city Burger, it is less than 800 kilometers; from the western western big city, Dusseldorf, to the easiest capital Berlin, it is only 600 kilometers.
Therefore, as far as Germany is concerned, domestic flights are not far away. Less than 500 kilometers means that civil aviation passenger transport is strongly compete by ICE and even highway self -driving (German highway in principle unlimited speed). For example, from Frankfurt from Germany to the capital Berlin, it takes 1 hour and 10 minutes by plane, the train takes about 4.5 hours, and it takes 5.5 hours to drive. Considering that the high -speed rail stations in Frankfurt and Berlin are in the city center, many airplanes have no obvious advantages.
Taking the Frankfurt City Hall to the Brandonburg Gate of Berlin as an example, although the aircraft saves 1 hour and 50 minutes than the high -speed railway, more than three times the fare, the longer ground traffic time and fewer flights make most business travel The person choose to take the ICE train.
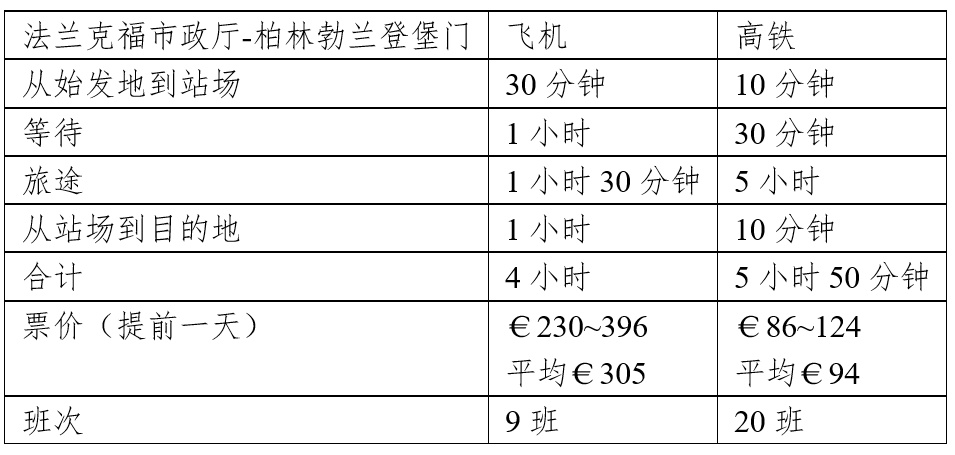
Under such circumstances, the weakness of civil aviation in Germany's domestic transportation is obvious. According to the statistics of the German official report to the European Union, there are only 23 million passengers in German flights in 2019, while Germany has a population of 83 million, which is equivalent to only 1/8 of domestic flights per year. Compared with the German railway, the German railway The daily number of passengers is 6.5 million, and the number of domestic civil aviation passengers of 23 million people is just four days of railway services.
Therefore, the current domestic routes in Germany have been squeezed to a general four routes. Taking 2019 data as an example:
1. The route connecting the second largest aviation hub Munich has an average distance of 412 kilometers, and 9.55 million passenger flow accounts for 42%(8%of 1.93 million people in Berlin and 5%of Frankfurt's 1.15 million people repeated calculations);
2. The route connecting the capital Berlin with an average distance of 495 kilometers, and 8.23 million passenger flow accounts for 36%(8%of 1.93 million people in Munich and 10%of Frankfurt 2.25 million people are repeated calculations);
3. The route connecting the largest aviation hub Frankfurt, with an average distance of 283 kilometers, 7.36 million passenger flow accounts for 32%(10%of 2.25 million people in Berlin, 5%of Munich 1.15 million people repeated calculations);
4. Other routes, the average distance is 439 kilometers, and the passenger flow of 3.2 million people accounts for 14%.
It can be seen that because Munich is in the southernmost part of Germany, its domestic passenger flow has both international line connection and point -to -point demand, so the number of passenger flows in the city is the most; Insufficient, there is a certain point of point -to -point demand; Frankfurt is an international hub, but it is located in the middle of western Germany, so the point -to -point demand is less. Under such a foundation, German domestic routes have allowed a high -speed railway to be a natural trend.
Even the routes in the Schengen area are not optimistic. For historical reasons, the German economic center is located near the west (Frankfurt) and the south (Munich), near its European neighbor. Therefore, it takes only 3 hours to take the ICE train from Frankfurt to Brussels, and only 4 hours to Amsterdam, the Netherlands, and Paris, France, are within the powerful coverage of high -speed railways.
Therefore, the routes in the Schengen zone in Germany are mainly long -distance passengers and high -speed rail. For example, the destination in Germany's largest Schengen area is Spain (26.12 million passengers are carried out in 2019, accounting for 27%of the number of routes in the Schengen area), with an average distance of 1740 kilometers, and the shortest distance is 800 kilometers. Although the two major destinations Italy (12.58 million person -times in 2019, accounting for 13%), the average distance is only 805 kilometers, but because the Alps are crossing between the two countries and the railway traffic is inconvenient, it is highly dependent on civil aviation. In countries with high -speed railways, such as France, the decline of German civil aviation is very obvious. The German railway and the French railway cooperate with each other to provide high -speed railway services with the fastest 320km/h between the two countries. The high -speed railway trains can reach Paris from Frankfurt for about 4 hours. This enabled the number of civil aviation to take the two countries (average 679 kilometers away) in 2019, which was only 7.23 million, and the international line was absolutely the main force.
In fact, for Hansha Airlines, a short -term connection flight is a tasteless and unfortunate chicken rib. Because these flights need to serve the long -distance international line, it is necessary to maintain the appropriate frequency of the class; however, due to the lack of point -to -point guests, these flights often need to use small regional passenger planes (such as CRJ or ERJ) At the same time, it also brings the society's imposition on greenhouse gas emissions.
Therefore, when the German railway just released ICE intercity motorcycle services in 1997, Hansha Airlines helped the German railway apply for IAATA code (2A) and began to sell the train passenger tickets issued by Frankfurt on the international line. Later, in 1999, the long -distance train station (Fernbahnhof), a German railway construction under the cooperation of Frankfurt Airport, improved the train reception capacity of Frankfurt Airport, allowing more trains to enter Frankfurt Airport.
This is significantly different from China and Japan. Japan Airport (Tokyo Narita, Tokyo Haneda and Osaka Kansai) and China's major international airports (Beijing Capital, Shanghai Pudong and Guangzhou Baiyun) have not access to high -speed railway services, so they lack the support for air railway transportation. Therefore, most of China's current air -rail transportation is either lacking shifts or needs to be connected.
So, is Shanghai Hongqiao? The main problem of Shanghai Hongqiao is that it is a domestic airport, and passengers do not have a reason to "go to Hongqiao". At the same time, Hongqiao Airport is located at the eastern end of the China Civil Aviation Network -from Suzhou, Hangzhou and other cities in the west to Shanghai Hongqiao. For example, take the high -speed rail from Suzhou to Shanghai Hongqiao and then transfer to Beijing. It is likely that it may not take the high -speed railway directly from Suzhou to Beijing.
02
In addition to the influence of geographical location and infrastructure, another problem faced by air -rail transportation is ticketing.
In the example of the German railway, the German railway, as a monopoly state -owned enterprise that monopolizes the entire German railway, naturally wants to cooperate with any international airline company on the international connection issue of the international line. Therefore, in addition to cooperating with Hansha Airlines, the German railway also sells train passenger tickets on the distribution systems such as Amadeus with the 2A code. However, there is a problem with this model of driving train tickets independently on GDS -the German railway requires a handling fee for each joint ticket to GDS. Because the GDS fee standard has a minimum lower limit, the German railway that is far lower than the ticket price of tickets is high, and the proportion of handling fees for selling train tickets through GDS is highly outrageous.
This issue is also applicable to the railway of Japan and China -the rules for setting the minimum handling fee for the distribution system for international ticket design, which is not appropriate to sell short -range rail tickets. The average distance of Chinese high -speed rail travel is only 400 kilometers, while civil aviation is 1,600 kilometers. Even if the high -speed rail and civil aviation use the same passenger kilometers, the total price of a railway ticket is 1/4 of the civil aviation.
However, due to the existence of the minimum fee system, the sales cost of railway tickets on the civil aviation distribution system will rise suddenly. At the same time, because the number of ticket processing of railway companies is much higher than that of civil aviation, railway companies' self -built sales systems, such as China's 12306, Japan's Mars, or DB Connect in Germany, single -customer sales costs are far lower than airlines.
In the case of Liancheng tickets, the German railway is also facing a problem. In the Liancheng ticket rules, the carrier who has an abnormal transportation (delay or cancellation) appears to be responsible for compensating the passengers to provide passengers with the cost of replacing the transportation mode (change, signing or refund). This makes railway companies with a shorter transport distance and less joint division into a small number of risks to compensate the transportation distance. The entire fare is divided into higher airlines. ten times. Therefore, Japanese JR companies do not want to cooperate with airlines, while the existing air -rail transport products of China Railway stated that they "do not bear the responsibility for delays."
Because of this, under the leadership of the German railway, the joint venture between Hansha Airlines and the German railway has developed a set of business rules and its supporting IT systems. This set of rules is called RAIL & Fly on one side of the German railway, and it is called LuffThansa Express Rail on the side of Hansha Air. In this set of rules, interested airlines need to bear sales fees for railway companies, and under the premise of railway companies to ensure that their delay control is controlled at a certain level, the change fee for delays is undertaken. Hansha Airlines founded the Star Alliance in 1997 that the service began to be promoted in the Star League member airline. Among them, the Sky Sky began using the Express Rail system in 2004 to provide trains in Germany for passengers on the Tokyo -Frankfurt flight.
As the Star Alliance began digital transformation in 2018, the system of LUFTHANSA Express Rail has also been upgraded again in digital transformation, becoming the Intermodal Partner program of the Star Alliance today. The traditional members of the Internet PARTNER and Star League apply for different cooperation clauses, so that operators responsible for connectivity do not need to bear transportation responsibilities in the way of traditional airlines.
03
Let's return to Asia. The main obstacle to the development of air -rail transportation in Japan was that after the Japanese railway was privately private, the passenger railway was composed of six companies. Therefore, airlines need to negotiate one by one, and the procedures are very complicated. Nowadays, the air -rail transportation provided by Japanese Airlines and all Japanese air inbound passengers is mainly based on the form of sales tickets. There is only one product of tickets, and the inventory management and control are very simple.
In China, we need to pay attention to the role of the Railway Corporation. As the only railway ticket system operator in China, the railway always has an undoubted right to formulate the right to formulate. At the same time, considering the large scale of the Chinese railway network, it is unrealistic to move the entire China railway network into the civil aviation ticket system.
But referring to the intermodal partner approach is to allow partners to selectively manage inventory. For example, partners can sell "tickets" tickets, and then handle ticket matters in their own systems; or can also open some major stations to sell traditional one -way and round -trip tickets.
However, considering that China does not have so many international passenger flow, and China International passenger flow is concentrated in four first -tier cities in Beijing and Shanghai, in China, the role of air -rail transportation as a "international line of international lines" is obviously limited. of.
So, what about domestic transportation? There are several airports with Guo Railway Station: Shanghai Hongqiao, Changchun, Haikou, Shijiazhuang, Turpan, Chengdu Shuangliu, Guiyang, Lanzhou, Sanya, Zhengzhou, Wuhan, Beijing Daxing, Shantou, Shenzhen, Xuzhou, Yinchuan and Qingdao. We take Chengdu as an example of "Air Fourth City".
Chengdu is a very typical example. In 2021, Chengdu GDP accounted for 37%of Sichuan GDP, and the output value of the tertiary industry accounted for 47%of Sichuan Province, ranking one -third of China's richest GDP for 95,100 yuan; Suining, Aba, etc. have less than 70,000 yuan per capita, and Ziyang is only 40,000 yuan, ranking one -third of China's poverty.
In other words, the total economic development and per capita level of cities next to Chengdu are not as good as Chengdu. Therefore, most passengers at the Chengdu Shuangliu Airport Station come from the areas where Chengdu can be covered by Chengdu Metro. This can be seen from the timetable of train services: Chengdu Metro provides 8 minutes a shift at dual -flow airport, frequent train services for 7.5 flights per hour, but only less than 30 high -speed rail trains in Chengdu and Shuangliu Airport between.
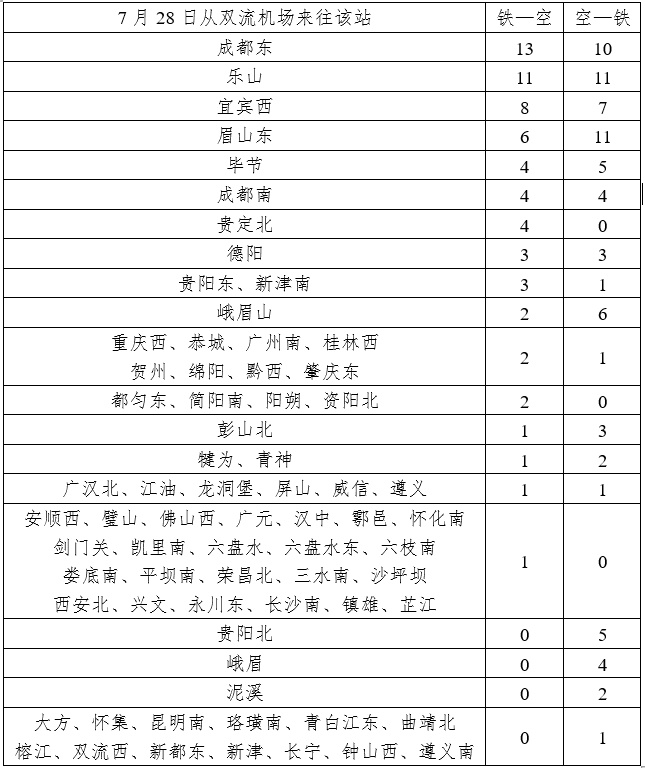
Guiyang's Longdongbao Airport went to Guiyang City. On July 28, the actual driving train was not in the first class. In fact, most of the airports with air -rail transportation services are located in larger cities. The economic development level of its city is better than the surrounding cities. Therefore, most of the civil aviation customer bases of these airports are concentrated in a single large city and covered by urban rail transit. It is limited to truly need to be covered by long -distance railway services to the airport.
For China, the largest continuous "rich island" is the Yangtze River Delta area -but Shanghai Hongqiao is already the easternmost side of the Yangtze River Delta. Jiangsu and cities on the west side of Jiangsu and Zhejiang take the high -speed rail to Shanghai Hongqiao, and then take a plane to go to Domestic cities are bound to have a detour problem. At the same time, the Yangtze River Delta is one of the most dense areas of my country's airports. The most important thing is the airport that can perform domestic and short -distance international routes. Therefore, for the residents of the Yangtze River Delta, the air -rail transportation passing through Hongqiao may not be convenient and fast at the airport at the door of the house.
This is similar to Japan: Tokyo is also a "island". From Tokyo to the west to Osaka and Nagoya, it is found that Nagoya and Osaka can also serve domestic and short -range international routes. Therefore, only when the long -range intercontinental route is performed, Shanghai Pudong, Tokyo Haneda and Tokyo Narita Airport will have some attractiveness.
Even so, for second -tier cities in Japan and China, they are facing strong competition between the remote intercontinental routes: it is also a destination to the intercontinental destination, and via the air of the foreign hub to the "air rail joint transport" through the national hub. It is obviously much more convenient -passengers can check their luggage at the starting station and enjoy the journey guaranteed by the same carrier. In contrast, Germany is different. The 500 kilometers from Frankfurt and Munich are the most prosperous continuous regions of Europe -a large number of small and medium cities in it and civil aviation demand. Considering that the per capita GDP of Germany is four times that of us, it is not unusual in Germany to have such a prosperous demand.
At the same time, the three major airports in the European Union belong to the Schengen Zone. From small cities to three cities, overseas is the same as "domestic transfer international". The domestic and international departure system is implemented. Therefore, all passengers need to forcibly extract their baggage and accept entry inspections before they can continue to take flights). Therefore, passengers in small and medium -sized cities in Europe, whether via Frankfurt, Paris, or Amsterdam, etc. In intercontinental destinations, the process of "air -to -air transit" is basically the same as "air -rail transportation".
Therefore, we need to pay attention to the subtle system of Europe and East Asia that determines the development differences between air -rail transportation in these countries:
The basis of air rail transportation is that route resources are concentrated at the hub airport, so it is more common on domestic routes than domestic routes;
The proportion of domestic domestic routes is much higher than intercontinental routes, and route resources are scattered on small and medium airports;
For most cities, the level of economic development of its province is not enough to support other prefectures and cities to use long -distance train services to the airport to fly;
Even airports such as Shanghai Hongqiao, such as Shanghai Hongqiao, do not have the advantage due to the detouring problem with the domestic route competition with other airports in the Yangtze River Delta;
Different competition conditions similar to European airports on intercontinental routes, intercontinental routes in China and Japan facing fierce competition in air -to -air transit of foreign hubs.
Therefore, the development of air -rail transportation in China is bound to be a long and time -required process.
*This article only represents the author's point of view, and does not represent the position of Global Brigade.
- END -
Integrate resources, create a "ten -scenic line" coastal tourist belt

In the midsummer season, the lakeside is lush, the blue water in the lake, and the...
Why did the Xinjiang Duku Highway, which turned into a "crying highway", made a circle of fire?

Jimu Journalist Ding PengHomestay and B B 17,000 yuan, The Highway becomes a Cryi...