Why don't woodpeckers afraid of brain shock?The previous answers were wrong!| One week technology
Author:Shell net Time:2022.07.16
Welcome to technology for a week. This week you will see: ① Human began to ponder why woodpeckers can not be elastic; ② Let men eat more in summer; ③ Deep sea squid precious images; ④ living "crystals"; ⑤ octopus suction cup gloves.
No fear of brain shock
Woodpecker is so hard topert, why do they have no brain shock? In the past, a common explanation was that their skulls could absorb impacts to protect their brains -but new studies published in "Contemporary Biology" pointed out that this statement is actually not established [1].

North American Black Standard (DRYOCOPUS PILEATUS) | Current Biology/Van Wassenbergh et al
In the past, people speculated that the "sponge -shaped" bone behind the beak of the woodpecker had the effect of absorbing impact. However, high -speed photography analysis shows that this structure has always performed very hard in the process of woodpecker, and there is almost no shock absorption effect. Researchers also pointed out that evolving and impacting skulls will reduce the efficiency of woodpeckers, which will not be conducive to the survival of woodpeckers.
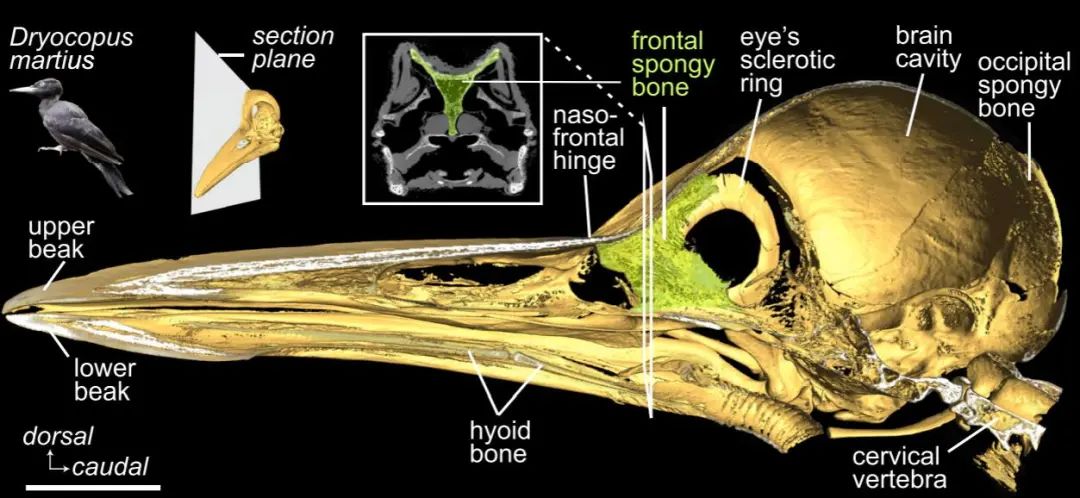
In the past, people guessing the bones of the green part in the picture can help the woodpecker to absorb the impact, but it does not actually have this effect | Van Wassenbergh et al
Although the skull is not protected, the brain of the woodpecker is still safe -this is mainly because their brains are relatively small, and they will not bear the large pressure changes like the human brain at the same acceleration. According to the calculations of researchers, these woodpeckers should increase the speed of woodpecker to twice it to cause brain fluctuations.
Summer appetite
Summer sunshine will have an unexpected effect: it will make men eat more [2].

Sunshine can affect appetite -but this seems to only be established for men | stocksnap/pixabay
By analyzing the survey data of about 3,000 people, Israeli researchers have found that seasonal light changes will affect the food intake of human men: Compared with winter, the average energy intake of men in March to September in the sun is increased. 17%. In women, this phenomenon does not exist.
Further studies have shown that this effect is related to hormones called "Elein release peptides". Growth release peptide has the effect of promoting appetite, and ultraviolet rays (UVB) in the sun can stimulate the skin's adipose tissue to produce more hormones -and this process will be suppressed by estrogen. Therefore, the appetite of human men and male experimental mice is affected by ultraviolet rays, but women and female mice will not have obvious appetite changes.
Squid mother
On the bottom of the 1390 meters deep, the remote control equipment was taken very rare pictures -a squid mother drifted in the deep sea with eggs. This squid's wrist is a gel -like substance on the feet, and densely densely like pearl -shaped eggs [3].
Video: Deep sea gun squid carrys eggs like beads | mbari
This is a squid of a deep sea rifle squid, with a body length of about 7.5 cm, and the specific species is unknown. The behavior of carrying eggs with you is more common in the berth, but in squid, only 3 kinds of squids are observed. In 2005, the agency observed another squid with eggs in the deep sea. It was a B. Berryi, which came from the same genus as the protagonist. Generally speaking, squid will produce eggs on the bottom of the sea. Although it can give the eggs better and improve the survival rate of offspring, it consumes very consuming mother's energy and makes it easier for mothers to be prey. This video was shot by the Montrey Bay Aquarium Research Institute. They took many precious pictures through deep -sea remote control equipment.
Live "Crystal"
In this week's "Nature", researchers at MIT reported an interesting phenomenon: In a diner, the living starfish embryo will spontaneously form a "crystallization" structure [4].
Video: Spontaneous gathering of starfish embryos to form "Crystal" | Massachusetts Institute of Technology
In the process of studying the development of Patiria MINITE, people inadvertently discovered this kind of self -assembly phenomenon similar to crystals. In the early days of fertilization, the surface of these starfish embryos grew ciliac hair and started to rotate in the water. When the rotating starfish embryo approaches each other, they will stick together under the action of the water flow, and gradually gather on the water surface to form a tightly accumulated plane hexagonal structure. Before the final disintegration, this "living body crystallization" structure can last for several days.
The rotating starfish embryo is close to each other, and the small particles around show the water flow vortex | Nature Video
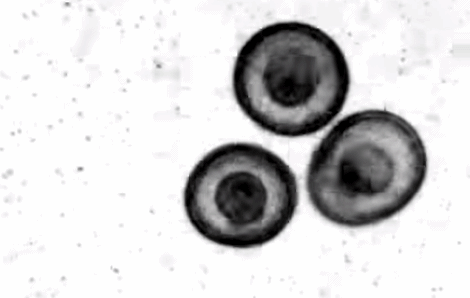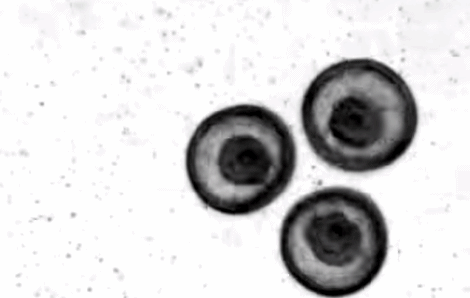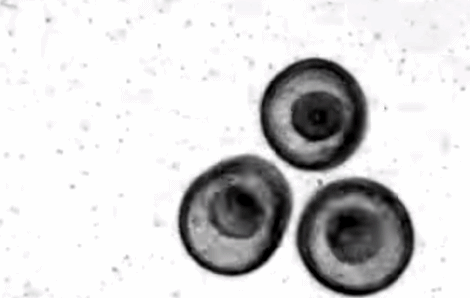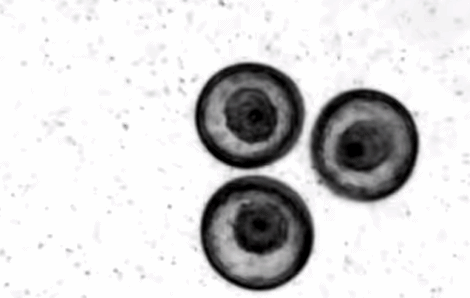
Researchers conducted actual observation and computer simulation of this phenomenon. They hope that such a self -assembly structure can be inspired by designing robot systems.
Octopus glove
Inspired by octopus, researchers of Virginia University of Technology designed a suction cup that can automatically adhere to objects, and made it into a suction glove to help people grasp underwater objects [5].
Inspired by octopus as a suction cup glove | Michael Bartlett

This suction cup is a hollow conical structure covered with elastic film. By extracting the air in the cone -shaped cavity, the film can be depressed inward and the contact surface of the object can be formed to suck the object. The suction cup system is attached to the micro -lidar sensor, which can automatically detect the distance from the object, and automatically start working when it is close to the surface of the object, and complete high -intensity adsorption within 50 milliseconds. In the demonstration, the "octopus gloves" successfully absorbed various surface shapes and hardness of toy cars, metal disks, and hydrogel balls underwater. Users do not need to grab or control buttons.
Automatically absorbing objects | Michael Bartlett Lab

The current "octopus gloves" still look relatively simple, but researchers say that this design idea is expected to be applied to medical and underwater rescue scenes in the future.
references
[1] https://www.cell.com/current-biology/FullText/s0960-9822 (2)00855-777
[2] https://www.nature.com/articleS/s42255-022-00587-9-9
[3] https://www.mbari.org/products/creature- Feature/deep---squid/
[4] https://www.nature.com/articleS/S41586-022-04889-6
[5] https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/sciadv.abq1905
Author: Mai Mai, the window knocks on the rain
Edit: Window knocking rain
- END -
"Epidemic Prevention and Control · Authoritative Answers" What is the standard for setting up a risk zone in Lanzhou?When is it lifted?
New Gansu Client July 15th (New Gansu · Daily Gansu.com reporter Wang Ziyi Wang Yuchen) After the epidemic in this round, the general public is paying attention to how many risk areas have set up in
"Multi -noodles", he played a healthy "gatekeeper" in the community

Zhang Jinrong, chief physician of the Pingliang Community Health Service Center, h...