Elimination of Helicobacter pylori can effectively prevent gastric cancer -different stages, benefit differently
Author:Digestive liver disease channe Time:2022.07.10
For medical professionals for reading reference
Before the bowelization, it can prevent intestinal gastric cancer 100%!
The infection rate of Helicobacter pylori (HP) in my country is as high as 40%-60%, and the infection rate of population in most areas is more than 50%. The infection rate of people under 20 years of age is as high as 37.1%. A variety of stomach problems.
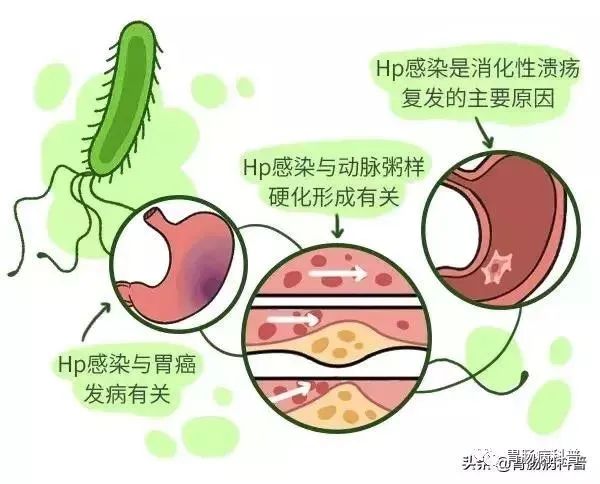
It is currently believed that Helicobacter pylori is one of the most important culprits of gastric cancer.
According to authoritative figures, my country reached 498,000 people who died of gastric cancer in 2015, almost one in almost one minute on average.
Elimination of HP is undoubtedly the most important and controllable factor in preventing gastric cancer.
Studies have shown that about 1%of infected people will eventually suffer from gastric cancer. Don't underestimate these 1%. If 50%of the infected people in my country are 700 million people;
Even if 1%of the infected people are unfortunately suffering from gastric cancer, it is the horror figure of 7 million people! Intersection Intersection
Therefore, the people's attention to HP has become increasingly urgent, and it can even be said to be urgent.
So, when is the best time to get rid of Helicobacter pylori?
Different stages of eradication, benefit differently
The bacteria are mainly spread through the mouth. Once the infection can hardly heal itself, it has been identified as infectious diseases.
research shows:
After infection of Helicobacter pylori:
All patients may experience chronic activity gastritis,
About 15%-20%of infected people may experience digestive ulcers,
About 5%-10%of patients may experience indigestion,
Less than 1%of patients may experience gastric cancer and gastric mucosa -related tissue lymphoma.
The occurrence of gastric cancer is the result of multi -factor common effects. In addition to the infection of Helicobacter pylori, there are also factors such as genetic, lifestyle, and environment.
Studies have shown that Helicobacter pylori infection is the most important and controllable risk factor that reduces the risk of gastric cancer. Elimination of Helicobacter pylori can significantly reduce the risk of gastric cancer, especially for high -risk people who occur in gastric cancer (such as living in high incidence of gastric cancer, family cancer families with gastric cancer families History, bad life hobbies, etc.).
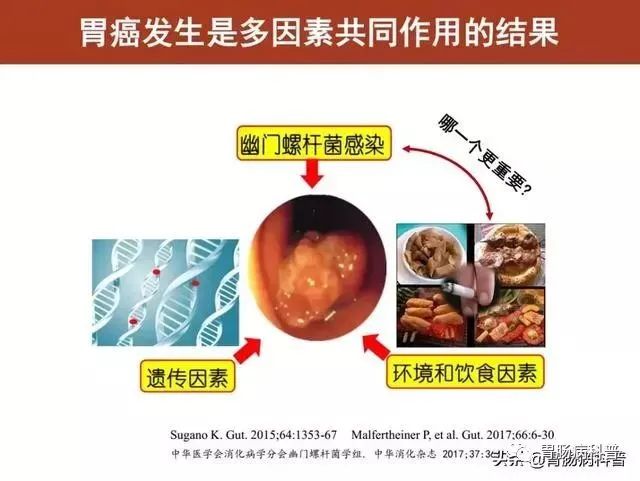
Although HP infection is not the only pathogenic factor in gastric cancer, it is the most important and controllable pathogenic factor.
According to the "intestinal" gastric cancer mode proposed by Professor Correa, the evolution of gastric cancer is normal gastric mucosa -superficial gastritis -atrophic gastritis -intestinal hyperplasia -intestinal gastric cancer.
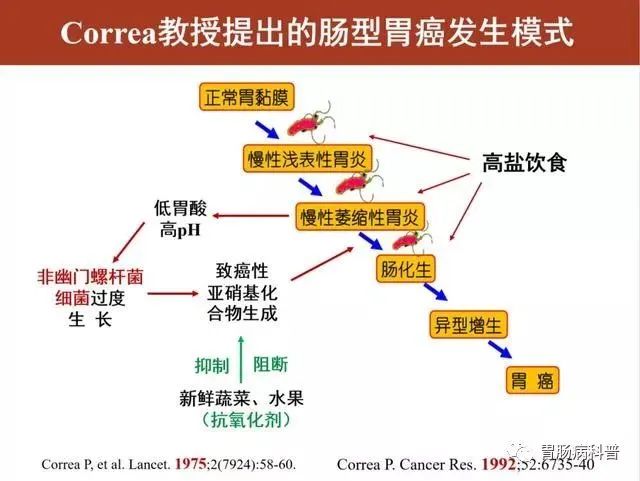
Helicobacter pylori has gastric cancer from the gastric mucosa to the gastric mucosa. Those who infection of Helicobacter pylori will go through five stages. By eliminating Helicobacter pylori, the first four stages have the opportunity to eliminate or reduce the risk of gastric cancer.
The first stage is superficial gastritis (non -atrophic gastritis).
Helicobacter pylori is settled in the gastric mucosa, causing gastric mucosa damage through ammonia -producing toxin, inflammatory response, and immune response. At the beginning of the disease, gastric mucosa damage was located at a shallow layer, called superficial gastritis.
Patients with superficial gastritis can eliminate almost 100%gastric cancer risk by eradicating Helicobacter pylori.

The second stage is atrophic gastritis.
The lesions of patients with superficial gastritis expand from shallow to deep, which affects the inherent glands, resulting in a decrease in the number of inherent glands, and the atrophy of gastric mucosa will become thinner. About 5%of Helicobacter pylori infection may cause gastric mucosa atrophy.
At this stage, eliminates the progress of gastric mucosa atrophy at this stage of eliminates of pylori.
To a certain extent, the risk of gastric cancer can be reduced, but the corresponding risk cannot be eliminated.
The third stage is intestinal epithelium.
On the basis of gastric mucosal atrophy lesions, when the gastric mucosal epithelial cells appear similar to that of intestinal mucosa, this pathological change is called intestinal epithelium, which is closely related to the occurrence of intestinal gastric cancer.
Earlier, it was believed that once the bowelization was almost irreversible, at this time, only the progress of intestinalization was delayed through anti -Helicobacter pylori treatment, reducing the risk of gastric cancer.
However, the latest research believes that most of the mild and moderate bowelization can be reversed through symptomatic treatment and eliminating the cause of the symptomatic treatment and removing the cause of the disease.

The fourth stage is heteroid hyperplasia.
Heteroid hyperplasia, also known as typical hyperplasia and intraplate tumor, belongs to pre -cancer lesions, and there are three degrees of light, medium and heavy.
The mild chance of reversing is normal, the probability of moderate and later reversal gradually decreases, and the risk of cancer is gradually rising.
Patients with high alien hyperplasia, even if they are cut off, gastric mucosa in other parts may evolve into gastric cancer. This is a heterogeneous gastric cancer. However, it can reduce the risk of heterosexual gastric cancer through anti -Helicobacter pylori.
The fifth stage is gastric cancer.
Patients with pylori infection, from normal gastric mucosa-superficial gastritis-atrophic gastritis-intestinal hyperplasia-gastric cancer-gastric cancer, which occurs, is the vast majority of gastric cancer.
Due to the lack of specific symptoms in the early stages of gastric cancer, it is not easy to find that when related symptoms or signs occur, it usually progresss to the middle and late stages, and the prognosis is poor.
Even if gastric cancer occurs, many factors are still recommended to eradicate HP treatment to improve gastric mucosa inflammation, prevent and treat heterogeneous gastric cancer, or recur on gastric cancer.
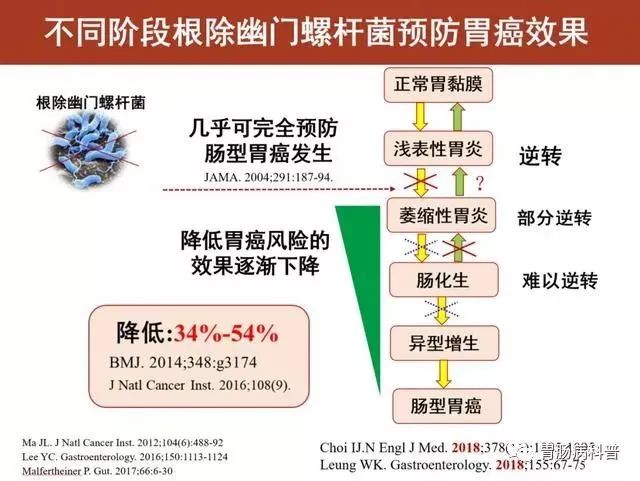
Before the atrophy and bowel, the root cause is the largest
After infection of Helicobacter pylori, whether it is progressing to gastric cancer is related to various factors. The toxicity of Helicobacter strain, genetic genes in the infected person, other environmental factors (such as high -salt diet, pickled food, grill, water pollution), etc., can all be possible. Affects the return of the disease.
However, among the pathogenic factors of gastric cancer, Helicobacter pylori is the most important environmental factors. After eliminating Helicobacter pylori, gastric cancer risk can be reduced. Therefore, even if less than 1%of patients may have gastric cancer, in principle, those infected infected are all infected. Treatment should be eliminated. Among the patients infected with Helicobacter pylori, the people who have the greatest benefit of the treatment are patients with atrophic gastritis and bowelization. After that, although pylori can reduce the risk of gastric cancer, although the risk of gastric cancer can be eliminated.
In the past, it was believed that eliminates of pylori can bring adverse reactions such as antibiotic abuse, obesity, and intestinal excitement syndrome, but recent research found that standardized root causes will not bring these adverse reactions.
Elimination of Helicobacter pylori,

It can be described as one stone and three birds, which is greater than the disadvantages
Professor Liu Wenzhong believes that eradicating HP can play a role in "one stone and three birds", that is, not only can prevent gastric cancer, but also effectively prevent and treat HP-related digestive disorders and digestive ulcers; , Mainly reflected in three aspects:
The first is to eliminate or reduce the risk of gastric cancer;
The second is to reduce the cost of treating diseases such as indigestion;
The third is to reduce the risk of infection of the surrounding people.
summary:
In summary, Helicobacter pylori infections can cause various stomach -related diseases such as chronic activity gastritis, digestive ulcers, digestive disorders, gastric cancer, and other stomach -related diseases. Elimination of Helicobacter pylori can eliminate almost the risk of gastric cancer. In principle, all H. pylori infections of Helicobacter pylori should be treated with treatment. Four couplet therapy for eradication schemes is over 90%.
1. Elimination of Helicobacter pylori is the most important controllable means to prevent gastric cancer;
2. According to Japan's experience, between 18-40 years old, the root cause is the greatest;
3. Eliminate at the superficial gastritis or asymptomatic stage, which benefits the greatest, which can prevent intestinal gastric cancer almost 100%;
4. Elimination of HP profits is greater than the disadvantages, and there is no direct evidence to indicate that it is positively correlated with certain diseases;
5. In the selection of the eradication scheme, abandon the previous standard three -combined therapy, and recommend the use of four -combined therapy containing a tadpole;
6. It is recommended that all adults with non -competing factors check and eradicate.
Do you want to know more about HP infection diagnosis and treatment?

The academic zone of "double no" has been officially opened. Here are the latest information, guidelines, consensus consensus, industry big coffee visits, diagnosis and treatment experience sharing, dry goods, waiting for you to see!
Source of this article: gastrointestinal disease
Editor in charge: xu
- END -
Shunfeng Time Bureau | Three keywords, look at 92 square kilometers charm Beijiu's new trends

Pearl water is leisurely, and the flow of flowing is hundreds of; the hot soil is ...
"Leshan Good Police" caused hot discussion among netizens in the country: full energy is full

Leshan News Network (Reporter Xu Zisheng) Persistence, persistence, persistence .....