Once the gallbladder cancer is discovered, the early diagnosis pay attention to the following 4 points!
Author:Cancer Channel of the Medical Time:2022.07.07
*For medical professionals for reading reference
The preferred imaging examination of biliary disease is ultrasound
Gallbladder cancer is the most common biliary malignant tumor. Bilebal carcinoma has a typical characteristics of malignant tumors such as hidden, fast development, and poor prognosis. Most of them have been advanced or progressive. Only 25%of patients have surgical opportunities. 5 years The survival rate is about 15%, which has not improved significantly in recent years. The key to improving its prognosis is early diagnosis and treatment.
The preferred imaging test of the biliary disease is ultrasound. Next, we can learn the precautions of ultrasonic diagnosis of gallbladder cancer through a case!
Introduction:
57 -year -old woman has no cause of abdominal pain ...
Patient, female, 57 years old, admitted to our hospital clinic because of "repeated abdominal pain with poor abdominal pain and disgusting March".
The patient had no obvious causes of upper abdomen pain before March, and there was a defamination colic, no obvious radiation pain, accompanied by loss of appetite, nausea and vomiting, fearless cold fever, no vomiting, and black. In the past six months, he has lost more than 10 kilograms.
The outpatient clinic applies for ultrasound examination with "abdominal pain".
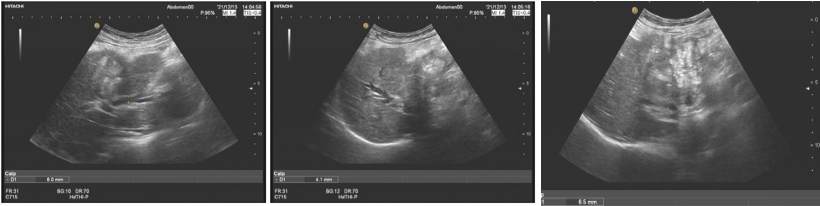
Figure 1: Liver's general view: Liver morphology is abnormal, the envelope is not only rectified, the liver's substantial echo is thickened, the left and right bile duct expansion of the liver, and no significant expansion of the external bile ducts of the liver.
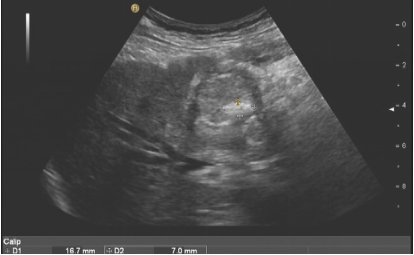
Figure 2: The gallbladder cut surface, the gallbladder shape is abnormal, the gallbladder wall is diffused and thickened, the pulp and mucous membrane layer is not only rectified. The gallbladder cavity changes in the medium echo group in the gallbladder cavity. The bile duct of the rear hepatic door was compressed.
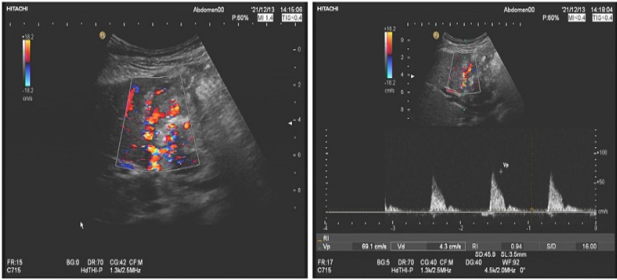
Figure 3: The gallbladder can be explored and enriched the blood flow signal. It can be seen that the rough nourishing the arterial blood flow is obtained.
Based on the patient history of patients and the above ultrasound image, diagnosis is given:
Main diagnosis: The lesion of the gallbladder cavity in the gallbladder cavity, considering the gallbladder CA, it is recommended to check further.
Secondary diagnosis: 1. Pulti -stones of gallbladder; 2. Internal biliary ducts; 3. liver cirrhosis.
Improve relevant examinations and diagnose gallbladder cancer!
After the results of the ultrasonic examination came out, the outpatient clinic was "gallbladder occupied lesions: CA?" Improved relevant inspections after admission:
Laboratory related inspection: CA-199 69.09U/ml,
Film degree exam:
MRCP: 1. Occupation of gallbladder area, considering the possibility of gallbladder CA. 2. The intestinal wall of the colon and the intestinal wall is thickened, and the boundary of the gallbladder is not clear. 3. Light expansion of the intrahepatic, biliary tube and left and right hepatosculus, narrowing the hepatic pipes in the liver door area: the possibility of cholecoscopic lesions invading the bile duct.
CT: gallbladder occupies, consider gallbladder CA.
PET-CT: The gallbladder mass is abnormally increased. Considering the gallbladder CA and invading the substance of the liver, cumulative duodenal descending section, colon liver curvature and liver door bile ducts, follow-up colon, backbone intestinal tube and intrahepatic bile duct expansion.
In order to further clarify the cause, gastric and colonoscopy examinations were found to invade the duodenum, lift the colon, and sampling for pathological examination.
Pathological returns: medium differentiated adenocarcinoma. In the end, the patient suffers from gallbladder cancer.
After the examination results were perfected, they communicated with the patient's family members. The family members were asked to be discharged back to the local area because they learned that the patient's condition had reached the late stage.
Summary induction: Pay attention to the following 4 points for the diagnosis of gallbladder cancer!
Conventional ultrasound can clearly show the thickness, integrity, inner wall blood flow situation of the gallbladder wall, the size of the tumor, internal echo, internal blood flow, or the size of the cavity and its size, and the active relationship, the stones and the tissue of the gallbladder wall peripheral tissue and other relationships Tumor and peripheral liver relationship.
One: 4 types of gallbladder cancer ultrasound type:
Typical gallbladder cancer can be divided into 4 types according to its different ultrasound performance:
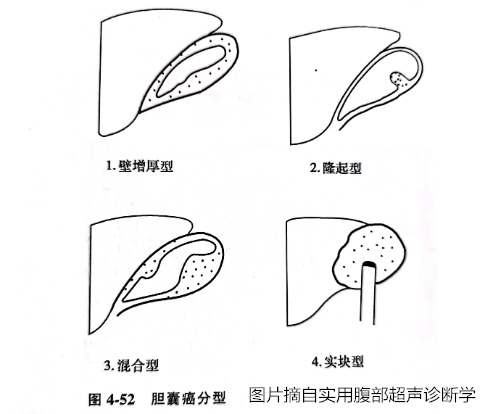
Thick wall type: The limitation of the gallbladder wall or is not uniform and thickened, showing high echo (common) or low echo, the entire gallbladder is stiff, deformed, rough, irregular, echo is interrupted, often the neck or body is more more than the body. It is significant.
Break -up type: The inner knot of the gallbladder cavity, the base is wide, the edges are irregular, and the internal echo is uneven. It can be seen that the central abnormal echo caused by stones, air or necrosis, most of them occur in the neck.
Real type: Most of them are late cases. The entire gallbladder is a messy low echo or a medium echo solid mass. There is no echo area in the gallbladder cavity disappear, often accompanied by gallbladder stones. Cancer infiltrates and grows around, allowing the normal interface between gallbladder and liver to interrupt or disappear, and sometimes the liver infiltrates the lesion.
Hybrid: thick wall type and nodule type exist at the same time. (At present, some literatures are deleted in this type).
2. 5 Big ultrasound diagnosis points:
Patients over 50 years of age (especially women) will have the following performance:
1. Oxibly gallbladder morphology;
2. The wall limitations are thickened and irregular;
3. A substantive group block that appears in the cavity with the relationship between the gallbladder wall, and the gallbladder wall at the base is continuously interrupted;
4. There are high -speed high -resistance blood flow spectrum inside;
5. The indirect signs of early metastasis, such as internal liver metastases and enlarged lymph nodes.
3. Ultrasound differentiation diagnosis:
1. Chronic cholecystitis, gallbladder genital hyperplasia
2. Gallbladder polyps and adenoma
Often manifested the cholecyscopic neck or body high echo or waiting for echo nodules, protruding towards the cholecoscopic cavity. The differentiated adenoma and early gallbladder cancer are difficult to identify. Generally, those with the following manifestations should be actively dealt with: (1) the size exceeds 10 mm; Bladed gallbladder stones and gallbladder wall thickened.
3. Yellow granulomatous cholecystitis
Almost all of the ultrasonic doctors were misdiagnosed as gallbladder cancer before this disease. It is difficult to identify the sound image diagram alone. Pedting biopsy is the most effective way to identify diagnosis. 4. Imaging examination of gallbladder cancer
Ultrasonic: Ultrasonic is the first choice for early diagnosis and follow -up of gallbladder cancer or even gallbladder disease, because the ultrasonic operation is simple, the price is relatively low, and the diagnosis rate of gallbladder cancer is close to 80%. In addition, color Doppler ultrasound has a certain effect on helping to judge the venous vein and hepatic arteries, and then evaluate the resection of the tumor. However, the abdominal wall is thick, the intestinal tube accumulation, the strong echo interference of the stones, and the coverage of the large sound shadow will affect the ultrasonic image, making the tumor easily missed.
Although the patient we introduced today, although the ultrasound found in the gallbladder, because the patient's intestinal qi and gallbladder stones were obscured, the degree of the gallbladder occupied by the surrounding organs was not good. Essence
CT: In addition to better display the shape, size, location, and differential and malignant nature of the tumor, CT has an advantage in judging the liver and lymph node metastasis of the tumor, which can make up for the defect of ultrasound.
The accuracy of CT's diagnosis of gallbladder cancer is about 85%, and it can help judge the staging of gallbladder cancer. However, CT still cannot replace the position of ultrasound in the early diagnosis of gallbladder cancer, and its sensitivity is not as sensitive as ultrasound. The spiral CT under the intravenous blood vessels can judge whether there are vascular violations and peripheral tissue infiltration, combined with early arterial phase and advanced door venous phase to determine the progress of lesions, which are expected to be widely used in clinical practice.
MRI: MRI can achieve multi -directional imaging, and the resolution of soft tissue can clearly show the relationship between gallbladder and surrounding soft tissues. Compared with CT, MRI can better diagnose the metastasis of tumors and the invasion of nearby organs. However, its disadvantages such as long scanning time, expensive costs, and pseudo -shadows are prone to sports.
Magnetic Resonance Cholangiopancream, Magnetic Resonance CHOLANANCREA-TOGRAPHY (MRCP) technology can intuitively reflect the dissection of pancreatic bile ducts, which has a unique advantage in the diagnosis of gallbladder carcinating bile duct. The MRI combined with MRCP has a good diagnosis of gallbladder cancer, has a high degree of specificity and sensitivity, and can accurately evaluate the local infiltration range of the tumor and judge the clinical staging. It can be widely used in clinical and gradually attracted attention.
Positive Electronics Event Fleece Imaging Technology (PET): PET has developed rapidly in recent years. At present, more applications are 18F-FDGPET/CT. The gallbladder malignant tumor tissue has a high closeness of 18F-FDG, which can be diagnosed according to the level of 18F-FDG metabolism and lesions, tumor markers, etc., especially for the good and malignant judgment of gallbladder polyps.
Compared with the above-mentioned imaging methods, 18F-FDG PET/CT has a high sensitivity and accuracy of the diagnosis of gallbladder cancer, but it is still not specific. There are also false positive reports. In terms of the identification of inflammation, it has the value of diagnosis for the distant metastases of the uncertainty of gallbladder cancer. The combined application of several other imaging methods can further increase the diagnosis rate of gallbladder cancer.
references:
[1] Yu Zhiyuan, Sun Yan. The diagnosis and treatment of gallbladder cancer [J]. China Popular foundation and clinical magazine, 2019,26 (03): 282-287.
[2] Cao Haigen, Wang Jinrui. Practical abdominal ultrasound diagnosis.
The tumor information you want
Please pay attention to the doctor station 注
1. Scan the QR code below
2. Click to download the app

3. Open the doctor station app and click on the upper right corner
4. Find the tumor in the channel
And follow
Download the doctor's station app and subscribe anytime, anywhere ~
The first release in this article: The digestive liver disease channel in the medical community

Author of this article: Ivan
Review of this article: Deputy Chief Physician of the Second People's Hospital of Jingdezhen City, Yang Health
Editor in charge: Sweet
- END -
Science and Technology Board Stocks are published in the city trading business rules, and the service application adopts the filing system
Zhongxin Jingwei, July 15th. On the 15th news of the official WeChat signal of the Shanghai Stock Exchange, the Shanghai Stock Exchange issued the science and technology board stocks as the city tradi
The State CPPCC helps Li Changshun County Agricultural Modernization Industrial Park Development Special Consultation Association held in Changshun

On July 18, the State Political Consultative Conference to help Changshun County A...