"Spots": The strap -like induction area inside the liver of the liver
Author:Bioart biological art Time:2022.07.02

Written article 丨 November
Former David M. Sabatini Research Group, Andrew L. Cangelosi (the first author is also the correspondent), and colleagues issued an article entitled Zonated Leucine Sensing by Sestrin-MTORC1 in the Liver Controls THE DIETARY Leucine, where In the mice, the SeSTRIN-MTORC1 band-shaped distribution area of sensitine in the diet was found, and the mechanism of amino acids and the impact on related physiological function in mammalian inductive foods.
"The Speckled Band" is one of the famous works of Conan Doru. The "spots strap" that appeared in the bedroom in the middle of the night was the trained weapon -poisonous snake. The bright picinosamine induction area found in this work is reminiscent of the "spots band" in this novel. It has a specific mode and has important functions. At a critical moment, I will be like Holmes in the novel. The ins and outs of the "spots" for you and unveil this "spots band".

Brightening is a kind of amino acid necessary for protein and metabolic products. Its biological functions include promoting skeletal muscle growth, insulin secretion, immune function, and regulating life. One of the key biological functions of brightein is the target of MTORC1 protein kinase. MTORC1 is the main regulatory factor for growth and metabolism, but how MTORC1 senses brightened pH is still unsolved.
SABATINI Laboratory has previously discovered that brightened aminopamin SESTRIN1 and SeSTRIN2 will be used as the brighterine sensor of the MTORC1 signal pathway (Nature | Liu Ying's research group reported SAR1B to perceive the brightened aluminate concentration MTORC1 activity) [MTORC1 activity) [ 1-2], but it is unknown to whether there is a brightine perception function in mammals, which organizations play, and how to play as a brightine sensor.
In order to solve these problems, the author first hopes to detect whether MTORC1 can sense the changes in brightening pinine in the body in the body. Therefore, the authors have only changed the content of glitine in mouse standard foods, and the content of brightened acid is 100%, 10%, and 0%, respectively. After fasting, the feeding was resumed. After the feeding, the author detected the concentration changes of brightein picots in the cells and the changes of the MTORC1 substrate in the liver. As a result, the brighterine in the diet would indeed control the activity of MTORC1 in the body (Figure 1). Essence
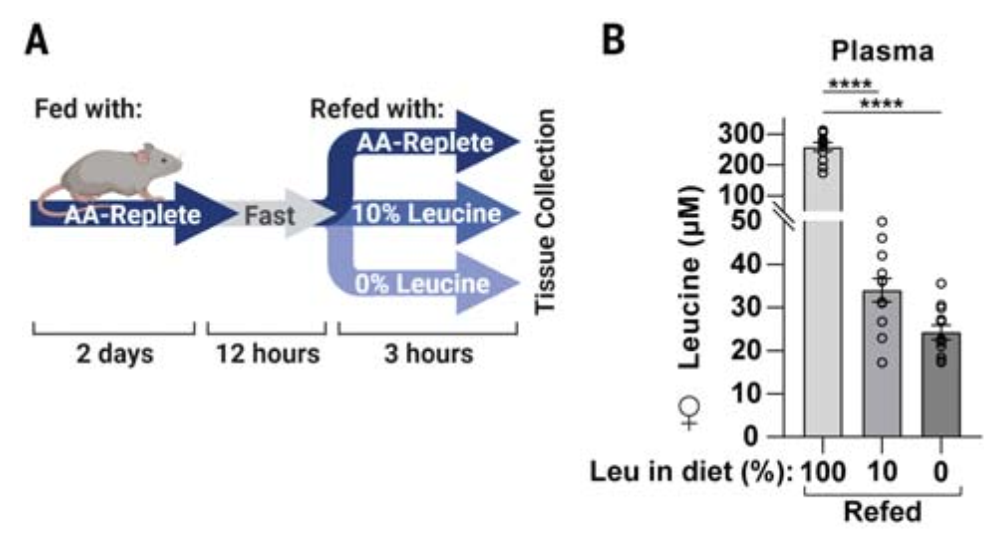

Figure 1 The glitterine content in the food affects the activity of MTORC1
The authors of biochemical experiments have proved that the changes in mice in vitro sensitine are implemented by affecting the GATOR2 complex in the MTORC1 signaling pathway by affecting the combination of Sestrin1 and SeStrin2. In order to further detect the glitterine of SESTRIN1 and SSTRIN2 in the body in the body, the authors constructed the double knocking mice of SeStrin1 and SeSTRIN2. The sensitivity of SESTRIN1 or SESTRIN2 has no significant effect on the sensitivity that does not feel the changes in bright pH, which does not have a significant effect. The result is consistent with the consequences of the cultivation of the cells, indicating that the two factors have functional redundancy. In Sestrin1 and SESTRIN2 double -knocking mice, the authors found that the MTORC1 activity was adjusted in a white adipose tissue in the white adipose tissue in mice.
In order to detect the important physiological role of brightein sensitization, the authors continuously continuously tap the food for mice to feed the lack of brightened picinosine for wild types and SESTRIN1 and Sestrin2, respectively. Analyze. The authors found that double -knocking mice has a more obvious reduction due to severe lack of white fat, and the skeletal muscle volume has also decreased significantly.
In order to find the factors participating in brightein sensitization in the liver, the authors put their attention on FGF21, fibroblast growth factor FGF21, which is related to the metabolic process of amino acid hunger and white fat. The authors found that glitterine hunger can lead to significantly improved the expression of FGF21 protein and mRNA in the liver of Seastrin1 and Sestrin2. By comparing the transcription group of wild mice, the expression of transcription regulation related factors expressed in mice and FGF21 has been significantly improved.
Different areas in the liver have different functions and transcription programs, so authors speculate that the expression of SeStrin1 and Sestrin2 may also have certain space characteristics. Through a single -molecule fluorescent in situ hybrid experiment, the author found that the mRNAS of Seastrin1 and Sestrin2 appeared in a belt distribution. At the same time, through the analysis of MTORC1 active markers, the author found that the activity of MTORC1 was not evenly distributed, and the expression of FGF21 was also affected by the spatial characteristics expressed by SeStrin1 and SeSTRIN2 (Figure 2).
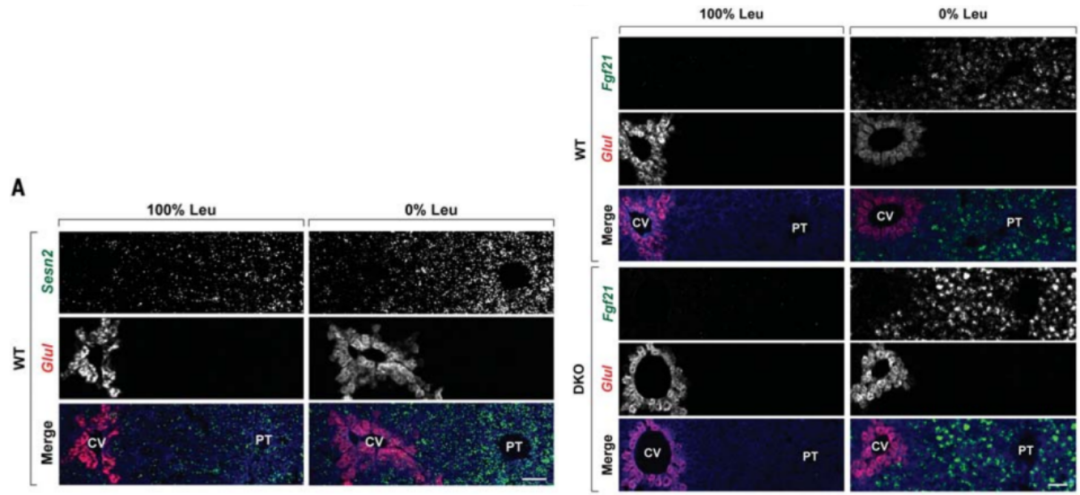
Figure 2 "spots band" in brightine induction

Figure 3 working model
In general, the work of the work in the physiological environment of mammals analyzes the specific mechanism of glitterine hunger reacting MTORC1 kinase reactions. It is found that MTORC1 perceives the glitime through the sestrin protein combined with glitine. SESTRIN1 and SESTRIN2 double knocks on mice cannot inhibit MTORC1 under the conditions of brighterine hunger, which leads to rapid losses of white adipose tissue and muscle. This is driven by the abnormal MTORC1 activity in the liver and the production of FGF21. In addition, through the analysis of the spatial distribution of SESTRIN in the expression of liver and lobular, it is found that its expression presentation characteristics are found, which is related to brilliantine to MTORC1 activity and regional specifications induced by FGF21. This work establishes a mechanism for mammalian SESTRINS under the physiological conditions of the body as a brightein sensor, and also reveals the spatial organization method of MTORC1 signaling pathway to nutritional perception. Original link:
http://doi.org/10.1126/science.abi9547
references
1. R. L. Wolfson et al., Science351, 43–48 (2016).
2. R. A. Saxton et al., Science351, 53–58 (2016)
Want to know more exciting content, come and pay attention to BIOART biological art


- END -
I heard the "flood" and moved, this town does a good job of flood prevention and drainage!

In the past few days, there have been continuous rainfall weather in our district....
Changsha City 2022 Middle and Senior Professional Title Review Work was launched

Changsha Evening News, Changsha, July 8 (All -Media Reporter Li Jing intern Chen D...