MET TKD: How much do you know about this rare type of lung cancer mutation?
Author:Cancer Channel of the Medical Time:2022.06.21
*For medical professionals for reading reference
Latest research progress courier ~
On June 3-7, 2022, the annual American Clinical Oncology Society (ASCO) Annual Meeting was held to bring cutting-edge and authoritative academic feasts to doctors and practitioners in the field of cancer diagnosis and treatment. As one of the most incidence and mortality in the world, lung cancer has attracted much attention from clinicians. At this ASCO annual meeting, many research progress has been announced. Among them, in the field of lung cancer targeted therapy, in addition to the more familiar EGFR, ALK, NTRK, ROS1 and other drive gene mutations, some emerging targets have also ushered in a breakthrough. Let's understand the latest progress about the mutation of Met Twitherase Field Domain (MET TKD).
Met TKD mutation: potential new molecular subtype of NSCLC targeted therapy
The abnormal activation of the MET pathway can cause the development of tumors. The main forms of MET pathways include MET14 outer outer sub -jump mutations, MET amplification, MET protein excessive expression, and MET fusion. A study published by the ASCO Annual Conference in 2022 explored a rare molecular subtype -the occurrence of Met TKD mutations, clinical pathological characteristics, and treatment schemes (ABSTRACT #9124) [1].
This study uses clinical pathology and genome data extracted from a multi -institutional tumor queue. These tumors are performed in Genie V10, China Cancer, and International Cancer Genome Alliance/Cancer Genome (ICGC/TCGA) data concentration for genome analysis. Essence At the same time, the researchers used an independent queue (including the NSCLC tissue and liquid sample) from the independent queue (including the NSCLC tissue and liquid sample) from the Foundation Medicine genome database.
The results of the study showed that in the entire queue (n = 106,379), a total of 662 samples (0.6%) detected 668 MET TKD mutations (not accompanied by MET14 outer slogan jump mutations) (Table 1 and Figure 1).
Table 1: The incidence of MET TKD mutations and MET14 outer show jump mutations in the entire queue
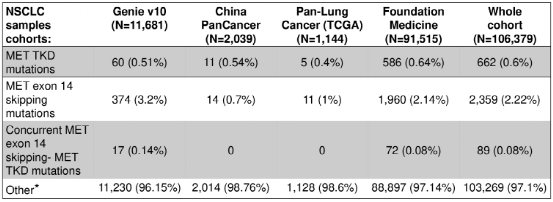
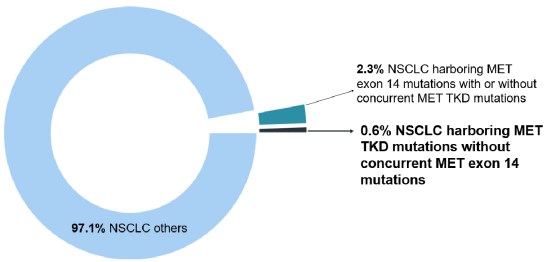
Figure 1: In the entire queue, compared with MET14 outer Xianzi jumping variants, the incidence of MET TKD mutations (not accompanied by MET14 outer outer jump mutation)
Among these 668 MET TKD mutations, the pathogenic significance of 525 mutations is unclear, and 143 (21.4%) have known carcinogenic potential, including MET H1094y/L/D/N/R, D1228N/H/V. L1995V/F, M1250T/i, Y1230H/C/G (Figure 2A, B).
Among the 662 NSCLC samples of Met TKD mutations (not accompanied by MET14) with complete genome data, 269 cases (41%) were also accompanied by KRAS, EGFR, ROS1, BRAF, ERBB2, ALK or RET driver Genetic mutations, 393 cases (59%) have no other driving gene mutations (Figure 2 C), and 28 cases (4.2%) samples were detected in MET amplification common mutations.
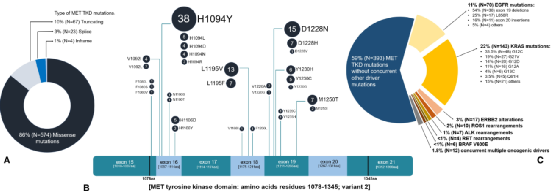
Figure 2: The features of MET TKD mutations in NSCLC (not accompanied by MET14 outer appendal jump mutation)
Among the patients available for population statistics, compared with MET14 outer Xianzi jump mutations NSCLC patients (N = 390), MET TKD mutant NSCLC patients (N = 75) are obviously younger (medium age 63 VS 73 years old, 73 years old, 73 years old, 73 years old, 73 years old, 73 years old, 73 years old, 73 years old, 73 years old, 73 years old, 73 years old, 73 years old. P <0.0001), but there is no significant difference in gender and self -reporting race.
Expert Introduction
Case sharing: Researchers also shared the curative effect of 2 cases of MET TKD mutations (not detected by other drive gene mutations) NSCLC patients with MET-TKI [Elzovantinib (TPX-0022)] treatment. One of them is a 64-year-old male lung adenocarcinoma patient carrying MET H1094Y mutations, and after being treated with Elzovantinib, the tumor shrinks -56.8%to achieve partial relief (Figure 3A); the other is a 80-year-old male NSCLC patient with Met F1200I mutations. Tumor shrinks -51.4%after treatment, and also reaches partial relief (Figure 3B).
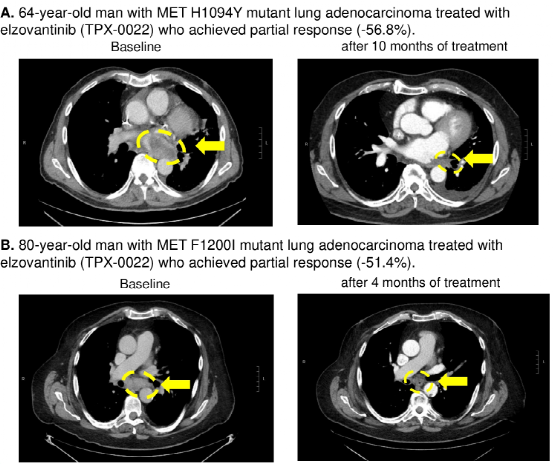
Figure 3: Met TKD mutant NSCLC patients with the curative effect of Elzovantinib therapy
The results show that the detection rate of MET TKD mutations (not accompanied by MET14 outer appearance jump mutation) in NSCLC is 0.6%, and there are usually no other known driving gene mutations. Met TKD mutations may be a new targeted molecular subtype in NSCLC, and MET-TKI may be effective for such patients.
Met pathway is abnormal, you must know these diagnosis and treatment progress!
In recent years, with the continuous deepening of people's understanding of MET pathways, MET targeted therapy has developed rapidly. Among them, MET14 outer appende jumping, as the primary drive gene of NSCLC, is about 2%-3%in the overall patients [2]. Among them 20%-31.8%[3,4]. At present, MET-TKI Savinib, Capmatinib and TEPOTINIB have been approved at home and abroad. In addition, various MET-TKIs such as Gomiminib are under research and development. Research data [5,6] shows that the median general survival (OS) of the patients who are treated with MET14 in the treatment of MET14 can reach 12.5 months, and the mid -level no progressive survival period (PFS) is 6.9 months. And the objective relief rate (ORR, 49.2%) and the disease control rate (DCR, 93.4%) are excellent. In addition, Savacinib took effect quickly, with a median effect of 1.4 months. These results remind the significant clinical benefits of Savacini treatment.
In addition, in Phase II VISION study [7], TEPOTINIB has lasting clinical activity to patients with NSCLC in Met14, and the general population ORR is 44.7%, and the safety is good. Glory Study [8] shows that the ORR of Gumatinib is 60.9%, and the ORR of patients with initial treatment is slightly better than patients with 66.7%and 51.9%, showing good clinical benefits. At the 2022 ASCO conference, the results of the Chrysalis study MET-2 queue [9] showed that the bispecific antibody drug AMIVANTAMAB was used in MET14 out-of-revealing child jump mutations NSCLC. ORR in patients in patients with MET inhibitors and previous MET inhibitors was 57%, 47%, and 17%, respectively.
In the 2022 edition of the "Chinese Clinical Oncology Society (CSCO) Non -small Cell Cancer Diagnosis and Treatment Guidelines" [10], in the recommendation of the late -stage NSCLC medication of the MET No. 14 jumping mutation, the Saverni obtained the first line Class II recommendations (3 evidence), CAPMATINIB and TEPOTINIB obtained Class III recommendation (Category 3 evidence). At the same time, the molecular typing part of the 2022 version of the CSCO guide also increased MET14 external sub -jump mutation detection from level II recommendations to level I (Category 3 evidence), which fully reflects the importance of the diagnosis and treatment of MET14 out -of -appearance sub -jump mutations.
In addition to MET14, Met14 jumping jumps, MET amplification has also attracted much attention in NSCLC. Studies have shown that the incidence of MET amplification as a primary driver gene is 1%-5%in the initial governance patients [2]; as a secondary driver gene, the incidence of the first/second-generation EGFR-TKI drug resistance rate is It is 5%-22%[11,12], the incidence rate after three generations of EGFR-TKI is 15%-30%[13,14]; as a common drive gene, the incidence of the incidence of EGFR positive patients It is 2%-10%[15,16].
At present, the treatment of MET amplification NSCLC has made many progress. For example, TATTON Research [17] has initially confirmed the efficacy and safety of the EGFR-TKI resistant NSCLC patients with Oshitinib dual target therapy for MET; the research and safety of patients with NSCLC; Oshitininin resistant NSCLC, which combined with Lazertinib to treat MET amplification, also shows the initial effect.
However, MET pathways such as MET fusion, MET expressions, MET TKD mutations, etc., current evidence -based medical evidence is still limited. In the future, it is hoped that with the development of more research Essence
references:
[1]Activating MET kinase domain mutations define a novel molecular subtype of non–small cell lung cancer that is clinically targetable with the MET inhibitor elzovantinib (TPX-0022). 2022 ASCO, Abstract #9124.
[2] GUO R, ET Al. Met-Dependent Solid Tumours-Molecular Diagnosis and Targeted therapy.nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2020; 17 (9): 569-587.
[3]Tong JH, et al. MET Amplification and Exon 14 Splice Site Mutation Define Unique Molecular Subgroups of Non-SmallCell Lung Carcinoma with Poor Prognosis.Clin Cancer Res. 2016;22(12):3048-3056.[4]Mo Hn, et al. Targeting met in a cranedronic disliced. 2017; 3 (3): 148-153.
[5]Lu S, Fang J, Li X,et al. Once-daily savolitinib in Chinese patients with pulmonary sarcomatoid carcinomas and other non-small-cell lung cancers harbouring MET exon 14 skipping alterations: a multicentre, single-arm, open -label, Phase 2 Study [J]. Lancet respir med. 2021; 9 (10): 1154-1164.
[6] S. Lu, J. Fang, x. Li, et al. Final Os Results and Subgroup Analysis of Savolitinib in Patients with Met Exon 14 Skipping Mutations (Metex14+) nsClc. 2022 ELCC. ABS 2MO.
[7]Xiuning Le,etal.Tepotinib Efficacy and Safety in Patients with MET Exon 14 Skipping NSCLC: Outcomes in Patient Subgroups from the VISION Study with Relevance for Clinical Practice[J].Clin Cancer Res.2022;28 (6): 1117 --1126.
[8] Shun Lu, yongfeng yu, jianya zhou, et al. Phase II Study of scc244 in NSCLC Patients Harboring Met EXON 14 Skipping (METEX14) Mutations (GLORY Study). 2022 ACR. ABS CT034.
[9] Amivantamab in Patients with NSCLC with Met Exon 14 Skipping Mutation: Updated Results from the Chrysalis Study.asco 2022, ABS 9008.
[10] Guide Working Committee of the China Clinical Oncology Society. China Clinical Oncology Society (CSCO) non -small cell lung cancer diagnosis and treatment guide 2021 [M]. Beijing: People's Health Publishing House.
[11] Recondo G, et al.TargetingMetDysregulation in Cancer.cancer Discov.2020; 10 (7): 922-934.
[12]Bean J, et al.MET amplification occurs with or without T790M mutations in EGFR mutant lung tumors with acquired resistance to gefitinib or erlotinib.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007;104(52):20932-20937.
[13] Ramalingam SS, et al. 2018 ESMO. Abstract LBA50.
MET AMPLIFICAON As a Determinant of Tyrosine Kinase Inchibitor Resistance in Epidermal Growth Factor-Mutant Non-Cell LUNG CANCER.J Clin Oncol.
[16] li xm, et al. Clin Lung Cancer. 2020; S1525-7304 (20) 30334-x.
, Open-Label, Phase 1B Study [J]. Lancet Oncol.2020; 21 (3): 373-386.
[18] Amivantamab Monotherapy and in Combination with Lazertinib in Post-Wigfr-Mutant NSCLC: Analysis from the Chrysalis Study. ESMO 2021,1192mo.
*This article is only used to provide scientific information to medical people, and does not represent the viewpoint of this platform


- END -
Wenling Meteorological Observatory issued heavy rain blue warning [Class IV/general]
Wenling Meteorological Observatory issued a heavy rain blue warning signal at 9:15 on June 10, 2022: Affected by low vortex cuts, yesterday at 20:00 to 08:00 today, the rainfall in our market was 23.1
Woman!Huizhou a girl hand card grinding machine doctors doctors fight together to rescue

Near the summer vacation, children are going to leave the campus and enjoy holiday...