"Chinese characteristics" lung cancer general screening model announced!There are no high risk factors to screen
Author:Cancer Channel of the Medical Time:2022.09.17
*For medical professionals for reading reference

2022 ESMO Voice of China -Professor Liang Wenhua interprets a new perspective of lung cancer screening
In China, the incidence of lung cancer, the incidence of malignant tumors, and the top rate of mortality. Lung cancer screening is a key step of early diagnosis, early treatment, and reduction of mortality.
In the "China Lung Cancer Screening and Early Treatment Guidelines (2021 Edition)" (hereinafter referred to as the "Screening Guide"), it is recommended that high-risk population conducts low-dose CT screening at the age of 50-74. But clinically, the incidence of lung cancer in many non -high -risk groups cannot be underestimated. Is there any room for improvement in the current screening standard? What other screening "leakage fish"?
The 2022 European Cancer Internal Sciences (ESMO) Annual Conference was held in Paris, France from September 9th to September 13th. At this meeting, Professor Liang Wenhua from the First Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou Medical University, "Community-Based Mass Screening with Low-Dose CT FOR LUNG CANCER in Guangzhou" report was selected for LBA Essence "Medical Circular Channel" specially invited Professor Liang Wenhua to interpret issues related to lung cancer screening.
Nearly half of the high -risk groups of lung cancer have not been screened!
Smoking is a recognized carcinogenic factor. The "Screening Guide" recommends that smoking, second -hand smoke exposure, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), first -level relatives' lung cancer family history, asbestos, cigarettes and other carcinogenic people exposed to high -risk groups.
However, among Asians, women and non -smoking people suffer from lung cancer. Existing screening strategy coverage may not be comprehensive. The study aims to evaluate the test of lung cancer in the community in Guangzhou, and at the same time explores the difference between the test rate of high -risk people and non -high -risk groups, and explore the high -risk factors of lung cancer in the Chinese population.
From 2015 to 2021, the four streets in Yuexiu District of Guangzhou were studied. A total of 11,709 people participated in a low-dose CT. The results showed that 2245 (18.2%) residents discovered ≥5mm lung nodules, and 200 (1.7%) residents were diagnosed with lung cancer. Among them, 172 (86%) was 0- I pulmonary cancer.
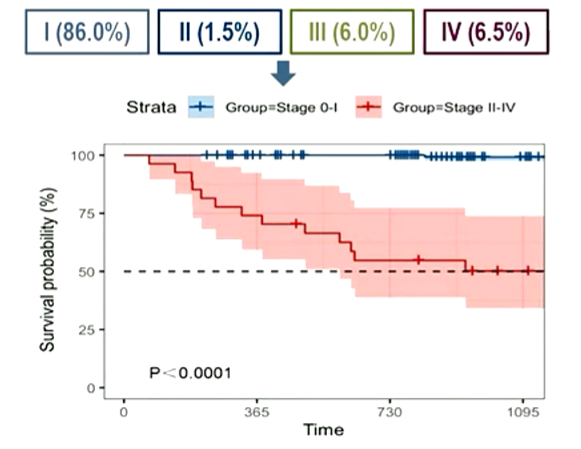
The proportion and survival rate of different stages of patients with lung cancer are confirmed.
"The total survival (OS) rate of three years of lung cancer exceeds 98%; and the three-year OS rate of lung cancer in stage II-IV is only 50%." Professor Liang Wenhua emphasized that "the main goal of screening should be as much as possible Find patients with phase 0-I pulmonary cancer and intervene in time to pursue cure. "
Further analyzing the age of patients with lung cancer, Professor Liang Wenhua said: "All lung cancer found in the age of 40-50 is in the stage 0- I, and some lung cancer over 50 years old is in the II-IV stage. The peak of lung cancer. This is consistent with previous research results. "
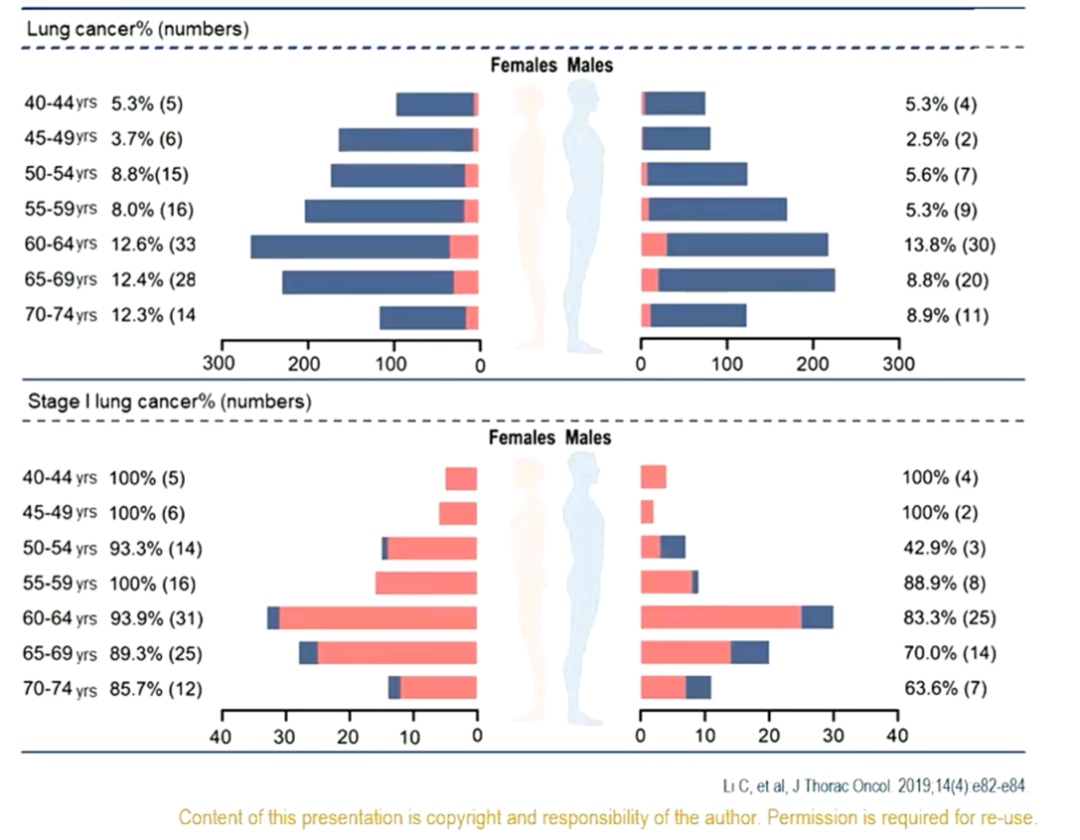
Confracted sexual and age distribution in patients with lung cancer patients
Only 37 (19.6%) and 105 (55.6%) were diagnosed with the screening standards for the comprehensive American Cancer Network (NCCN) guide and the Chinese guide.
The results of this study show that if the screening standards recommended by China Guide, nearly half of the lung cancer that can be discovered is "ignored".
Studies have also found that in high -risk groups that meet the standards of Chinese screening, the detection rate of lung cancer is 2.3%, rather than the detection rate of lung cancer in high -risk populations is 1.3%. Professor Liang Wenhua emphasized: "Although there are differences in the detection rate of lung cancer between high -risk people and non -high -risk groups, it cannot be ignored. It is worth noting that the proportion of lung cancer detected by non -high -risk population is higher than the cure stage (period I). The proportion of phase I lung cancer was detected among high -risk people. "
Screening reduces the risk of lung cancer by 63%!
Screening can find earlier lung cancer to reduce the mortality of lung cancer. The study compared the incidence and mortality of the 110,000 residents who did not accept the screening. Among the 10,000 people who received the screening, the mortality rate of lung cancer was far lower than the residents of uns screening, and the risk of death of lung cancer was reduced by 63%.

The screening team and the cumulative percentage of lung cancer in the screening group
Professor Liang Wenhua analyzed that this may be attributed to the screening of non -high -risk populations and the treatment mobilization of suspicious lung cancer patients. "In the study, a considerable number of non -high -risk groups were found to be lung cancer after screening, which gave them the opportunities for lung cancer and treatment earlier. In addition, for patients with suspicious lung cancer, we will actively mobilize their treatment."
See if you have these high -risk factors?
Existing high -risk population screening standards have not yet met the screening needs of Chinese people. What factors are related to the occurrence of lung cancer?
Professor Liang Wenhua's team may conduct questionnaires on 109 factors related to lung cancer, covering areas, smoking/second -hand smoke exposure, history of diseases, and personal health. In the end, eight factors related to the risk of lung cancer, including personal cancer history, silicon exposure, age, food allergies, asthma history, family cancer history (lung cancer and other cancers), sensitive to temperature changes, and CEA.

7 factors are correlated with lung cancer
Professor Liang Wenhua said: "We hope to incorporate more cure lung cancer in the scope of screening to further improve the effect of screening."
Among these factors, the history of age, silicon exposure, history of food allergies, and asthma history are high risk of lung cancer.
Sensitivity to air temperature changes may be the protection of lung cancer. This has a certain relationship with the sensitivity of the airway and the ability to clear the foreign body. This risk prediction model judges that the AUC of high -risk people is 0.71. "Compared to the high -risk crowd model recommended by the NCCN guide, AUC is only 0.52, and the AUC of China screening standards is only 0.62. This model has better prediction effect." Professor Liang Wenhua explained.
"And from the perspective of health economics, compared with the treatment costs of developing advanced lung cancer and the reduction of economic benefits of people's losses, screening can save about 30 million US dollars, which is equivalent to RMB 200 million socio -economic resources."
Lung cancer screening should conform to Chinese characteristics,
And improve space
"The biggest problem with lung cancer screening is the definition of high -risk groups. We need to have the characteristics of high -risk groups that meet the characteristics of the Chinese population and cost -effective. This is also what we will continue to explore in the future."
Professor Liang Wenhua introduced: "At present, we are through a series of studies, exploring the correlation between factors such as environmental and living habits and lung cancer. Through queue research or genomic association analysis, to supplement and improve the existing screening standards. In the future, we may may be in the future. It will go through a richer model, so to lock the people who may get lung cancer and screen it in time. "
"In addition, although low -dose CT is a golden standard for lung cancer screening, it also has defects, such as high sensitivity, resulting in high pseudo -positive probability (that is, what we generally call lung nodules), which may cause excessive diagnosis. Therefore, the optimization of screening tools is also necessary. "
"At present, liquid biopsy can help find specific symbols related to lung cancer in blood, and combine with low -dose CT can further improve the specificity of screening. It is expected that there will be tools that can replace CT for screening in the future. occur."
Expert Introduction
Liang Wenhua

Professor/blog director/deputy chief physician
Department of chest oncology at the First Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou Medical University
National Youqing Fund winner (oncology), young Pearl River scholar, Guangdong outstanding youth medical talent
Assistant Dean of the Guangzhou Institute of Respiratory Health, Director of the Office of the National Respiratory Medical Center
Deputy Leader of the National Key Laboratory of Respiratory Diseases National Key Laboratory
Chairman of the Commissioner of Immunotherapy for Chest Diseases in Guangdong Province
Deputy Chairman of the Guangdong Medical Association Precision Medicine and Molecular Diagnostic Branch
Youth Member of the China Clinical Oncology Society (CSCO), member of the NSCLC Special Committee, and a member of the expert group of lung cancer guidelines
Deputy editor -in -chief of Transl LUNG CANCER Res, J Thorac Dis and Ann Transl Med
Mainly engaged in comprehensive diagnosis and clinical transformation of lung cancer. So far, more than 200 SCI papers have been published, 12 points above 30 points, 33 more than 10 points, the total impact factors of 2000+, total number of quotes 27000+, H index 34, including 160 first/communication authors, including: J clin oncol (IF 50.7, two articles), nejm, bmj (IF 93.3), Lancet Oncol, Cell Res, J Thorac Oncol, J Clin Invest, Chest and other magazines.
Won ASCO Merit Awards, the Name Doctor of the People's Daily Online, CSCO, 35 most potential youth oncologists in the country, and 2020 Alidhara Hospital Green Orange Award (first medicine). , Innovation team, and national innovation contest.
The first release of this article: the medical world tumor channel
Author: oolong tea
Editor in charge: Sweet
- END -
The Meteorological Orange Evaluation of the Meteorological Orange of Lishui District [Class II/Severe]
The Meteorological Observatory of Laishui District Upgrade on July 28, 2022 Upgrade and release the high -temperature orange warning signal: It is expected that today's Yongyang Street, Development Zo...
How to ensure the production and life under the prevention and control of the normalization epidemic in the community where the trend of punching is punching?

25 building parks26 roadsIn the Internet celebrity shops and communities that gath...