Small width, a large function -a mechanism for the generic difference between individual metabolic differences with the model as a model
Author:Bioart biological art Time:2022.08.02

Written article | A Tongmu
Responsible editor | Xi
Megers of metabolic enzyme encoding genes can cause excessive accumulation/consumption of metabolites, and induce the occurrence of congenital metabolic diseases, such as propyl acrocyrous enzyme A -carboxylase sub -macro -mutations in patients with ingrains. Children can diagnose whether the 3-hydroxypenate (3HP) in the newborn screening is diagnosed with an abnormal accumulation [1,2]. On the other hand, the metabolic difference between individuals is the result of the interaction of genetic background, nutritional intake, intestinal flora and other environmental factors. Due to differences in diet and lifestyle, the genome and gene expression between different individuals It is still difficult to achieve when the differences between mutations are linked to metabolism.

Recently, Albertha J. M. WALHOUT Laboratory, Frank C. Schroeder Lab and Erik C. Andersen Laboratory of Frank C. Schroeder University of Cornell University in the United States collaborated in Nature magazine entitled C. Elegans As A Model for Inter-Inter-IndiDual Variation In Research articles of Metabolism, by comparing the metabolic differences of three wild nematodes and laboratory nematodes, the author found that the abundance of known metabolites and unknown metabolites (Metabolites that have not ben previously demer) in different nematodes has obvious differences, of which metabolism The genetic variation of enzyme HPHD-1 causes the intermediate 3HP of the padonic acid diversion pathway in the wild nematode and the abundance of unknown metabolic composite (3HP-AAS) composed of 3HP and amino acids. This study is based on the metabolism of the nematode as the breakthrough, revealing the regulation mode of the metabolic difference between the genetic variation that causes the metabolic difference between the individual.

The author selected the laboratory nematode strain (N2) and three wild nematodes (BRC20067, CB4856, and DL238) with different sources of the laboratory (N2) and three sources. Endo-Metabolomes and metabolic secretions (Figure 1A). In order to characterize the difference between the metabolic spectrum between the 4 kinds of width strains, the author used the XCMS and the Metaboseek platform to perform a comparative metabolic group analysis. It was found that hundreds of metabolites were significantly different from the N2 reference nematode strain. Enrichment, such as several kinds of wild nematode, are more abundant than N2. It is worth mentioning that the author has identified more than 200 metabolites with high -level groups, and most of the metabolites were not characterized before (Figure 1B). Among these metabolites, the most significant specific -specific compounds are 3HP generated by the metabolites caused by propionic acid diversion. Compared with the average value of other three types of nematode, it has more than 7 times that of the secretion of metabolites of DL238 nematodes.
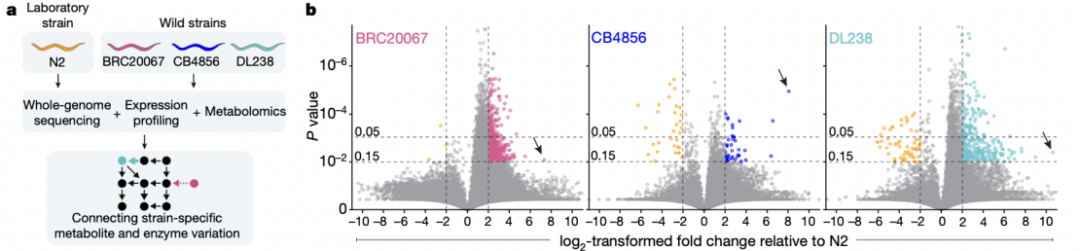
Fig
It is known that under sufficient vitamin B12, the transcription of propionic acid shunt genes is suppressed, and propyl -coenzyme A metabolizes is alienlyla enzyme A; and under the lack of conditions of B12, propionic acid diversion will be activated, and the propyrase enzyme A will be C. Acid diversion path degradation. The increase in the content of 3HP (intermediate of propionic acid diversion pathway) in DL238 nematodes implies that the flux of padonate is blocked in DL238 nematode. Further analysis of the composition and pathway enrichment of differentiated metabolites found that these differences metabolites usually have a complex structure (3HP-AAS) composed of 2-hydroxypenate/3HP and amino acids. In view of the huge differences between 3HP and 3HP-AAS abundance, and the propionate metabolic nesting to human evolution is quite conservative, the author continues to analyze the metabolism and differences of 3HP and its derivatives.
First of all, the author speculates that when propionic acid degrades through typical vitamin B12 dependent channels, the synthesis of 3HP-AA complex will be suppressed. Unexpectedly, the author found that supplementing vitamin B12 will significantly inhibit the synthesis of DL238 nematode 3HP-AA. 3HP can be oxidized to oblopyate semi-oxygenase-1 (HPHD-1) by hydroxide-1 (HPHD-1), and the expression of inhibiting the HPHD-1 encoding gene in the N2 nematode will lead Essence Cyidine decomposition metabolism will generate propyl COA and enter the padonic acid diversion pathway. The author conducts N2 nematodes and HPHD-1 mutant N2 nematodes by feeding 13C5 labels (13C5-Val) The results show that the 3HP-VAL content of isotopes in HPHD-1 mutant is higher. Therefore, DL238 nematodes will adjust the padonic acid diversion pathway to enrich 3HP and 3HP-AAS, and to achieve reconstruction of propionic acid metabolism by promoting the combination of 3HP/propionic acid and amino acid.
Inhibiting N2 nematode HPHD-1 gene expression can cause 3HP and 3HP-AAS abnormalities to increase, is the high content of 3HP and 3HP-AAS in DL238 nematodes caused by HPHD-1 gene mutations? The author found that there are two mutations in HPHD-1 of DL238 nematodes, namely K172M and L268P. K172M is located in the non-conservative area of enzymes, while L268P is located in a conservative area. After the author builds a mutant body width, the effect of DL238 nematodes HPHD-1 mutation on 3HP and 3HP-AAS abundances, and found that DL238P268L mutant nematodes of 3HP and 3HP-AAAS synthesis drop sharply, while 3HP and 3HP of N2L2L268P mutant nematodes -AAS synthesis is significantly enhanced. M172K mutations have little effect on the 3HP synthesis of N2 nematodes, but K172M will lead to a decrease in 3HP synthesis of DL238 nematode. It can be seen that the L268P mutation of DL238 horseshd-1 is the main reason for the increase in the increase in 3HP and 3HP-AAS synthesis. In addition, the abundance of the N-propyl-AAS in the DL238 and its HPHD-1 mutant is still higher than that of N2 and its mutant nematodes, which has nothing to do with HPHD-1 mutation. It can be seen that DL238 nematodes have a propion acid metabolic mechanism different from N2 nematodes. In addition, the author found that it can strongly delay the development of DL238 nematodes under the exogenous 3HP, but it has a small impact on N2 nematode. HPHD-1 L268P mutations will cause N2 nematodes to produce similar development delays to DL238, and the P268L mutation of DL238 nematode will alleviate the development delay caused by 3HP exposure. Therefore, a single amino acid mutation is the basis for metabolic regulation of nematodes to an excess 3HP toxicity to generate physiological reactions.
Not only that, the author also found that the other 8 kinds of wild nematodes carrying HPHD-1 mutations 3HP and 3HP-AAS have also increased significantly. Bio synthesis and adapt to low -throughput status. In addition, the degree of enrichment of N-propyl-AAS of 6 of the eight wild nematodes is significantly higher than that of N2 nematodes, which further confirms the significant difference between wild nematodes and N2 nematodes.
Finally, the author analyzed the expression mode of propionic acid diversion genes and found that the three types of gene expression of the three types of propionic acid diversion of the DL238 nematode were significantly increased, which showed that the DL238 nematode was made in two ways to reduce the reduction of HPHD-1 catalytic flux in two ways. The reaction, that is, the 3HP is first converted to 3HP-AAS, and then induces the expression level of encoding genes such as Pedic acid shunting enzyme coding genes such as HPHD-1.
In summary, this study studied the relationship between individual metabolic differences and genomic mutation with the model as a model, and found that there was a significant difference in the metabolic mechanism between the wild thread and the reference of the laboratory. In order to investigate its reasons, the author combines the comparative metabolic group and genomics, revealing that a single amino acid mutation in metabolic enzymes can induce the synthesis of a new type of metabolites and lead to differences in the metabolic mechanism between different widths. This study analyzes us for us The occurrence mechanism and propionic acid metabolic mechanism between individual metabolism provides new insights.
Original link:
https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-022-04951-3
references
1. Wilcken, B., Wiley, V., Hammond, J. & Carpenter, K. Screening Newborns for Inborn Errorism by Tandem Mass Spectrometry. N. ENGL. 348, 2304–231 (2003).
2. DEODATO, F., Boenzi, S., Santorelli, F. M. & Dionisi-Vici, C. Methylmalonic and Propionic Aciduria. Am. J. Med. CNet. CNet.
Want to know more exciting content, come and pay attention to BIOART biological art


- END -
For details!This is like this without the epidemic community ...

The community is my homeGovernance depends on everyoneCommunity is the basic unit ...
The first China -Europe Train "Ten West Europe" assembly trains

On the morning of July 20th, the first China -Europe trains Ten Western Europe ass...