2022 ILC Hot Delivery -the impact of long -term albumin application on medical resources
Author:Digestive liver disease channe Time:2022.07.21
For medical professionals for reading reference

The medical community cooperated with the Ministry of Medicine of Takeda, and was fortunate to invite Professor Huang Jianrong, the First Affiliated Hospital of Zhejiang University Medical College to further interpret the impact of long -term application of albumin at the EASL ILC 2022 conference.
In recent years, long -term application of albumin treatment can improve the prognosis of patients with cirrhosis and ascites, and has updated the previous understanding of gifted protein treatment. However, the economic benefits of the long -term application of albumin are controversial. In June 2022, the annual European Liver Research Association (EASL) International Liver Disease Conference has been held online and offline, and many experts have shared the latest progress of long -term use of human blood albumin in the treatment of liver cirrhosis.
At this conference, Professor Elisabet Viayna in the UK introduced a research on a discrete event simulation model (DES), which aims to evaluate the economic and clinical effects of patients with ascites who have long ascites and ascites without complications. The results showed that patients with cirrhosis without other complications were related to the reduction of albumin for a long time and reduced use of medical resources. This article focuses on the clinical research of patients with albumin in recent years to treat patients with liver cirrhosis and ascites, and combines the latest progress of the EASL ILC2022 conference to explore the impact of long -term application of albumin on medical resources.
Long -term human blood albumin infusion can be reduced
The mortality and hospitalization rate of patients with cirrhosis and stubborn ascites
The short -term application of albumin can improve the short -term prognosis of patients with cirrhosis. On the basis of this, the long -term application of albumin has widespread attention on the survival rate and complications prevention and control of patients with cirrhosis. In 2019, Di Pascoli et al. [1] carried out a forward -looking research for long -term treatment of albumin treatment for patients with cirrhosis and stubborn aspiration.
The study incorporated 70 patients with hepatic stubborn and stubborn ascites, of which 20 patients received standard therapy (SOC), and 45 patients received long -term treatment of human hemoglobin twice a week, 20 g each time. For patients who receive long -term albumin treatment, the average dosage of albumin is 60.7 ± 15.2 g per week (the average dosage of the average usage of albumin during puncture is 20.7 ± 15.2 g). For patients receiving standard treatment, the average dose of albumin is 22 ± 14.1 g per week. The main ending is the 24 -month mortality rate, and the median follow -up time is 408 ± 394 days.
The results of the study showed that during the 24 -month follow -up, 15 patients in the albumin group and the standard therapy group died; 5 patients had liver transplantation of 5 patients, and 2 patients had liver transplantation for 2 patients. The 24 -month cumulative mortality of patients with albumin treatment is significantly lower than those of patients with standard treatment (41.6% vs 65.5%; P = 0.032) (Figure 1).
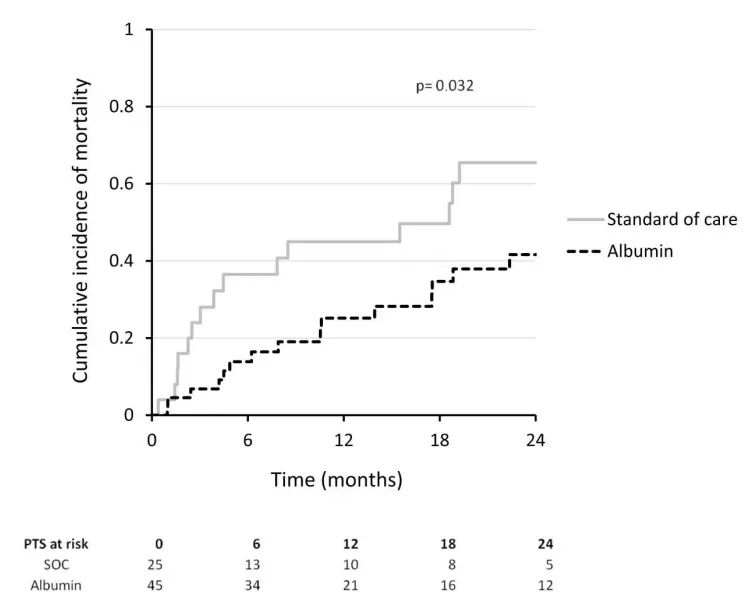
Figure 1: Compared with standard treatment, the mortality rate of albumin long -term treatment is reduced
The study also further explored the impact of long -term human blood albumin therapy on patient hospitalization rate. The results showed that the time for the albumin group without urgent hospitalization was significantly longer than the standard treatment group (P = -0.008) (Figure 2). The main causes of the two emergency hospitalization are infection and ascites. Compared with standard therapy patients, patients with long -term treatment of albumin due to hepatic encephalopathy (64.5% vs 26.9%; P = 0.016), ascites (71.0% vs 37.1%; P = 0.002), spontaneous bacterial peritonitis (SBP (SBP , 50.6% vs 7.9%; P = 0.004) and non -spontaneous bacterial peritonitis infection (88.6% vs 27.2%; P = 0.001) 's 24 -month hospitalization rate decreased significantly (Figure 3). The results of the above research support albumin is expected to be a new way of treatment, increasing the survival rate of patients with cirrhosis and ascites, and reducing the incidence of complications of patients with hepatoplastic ascites.
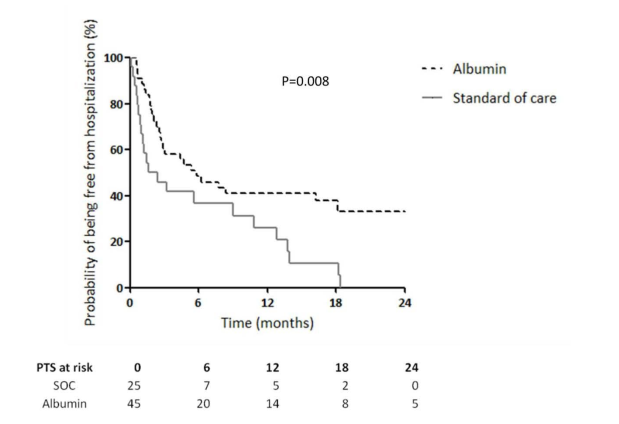
Figure 2: Compared with standard treatment, the long -term treatment group of albumin does not require an emergency hospitalization treatment time to be extended
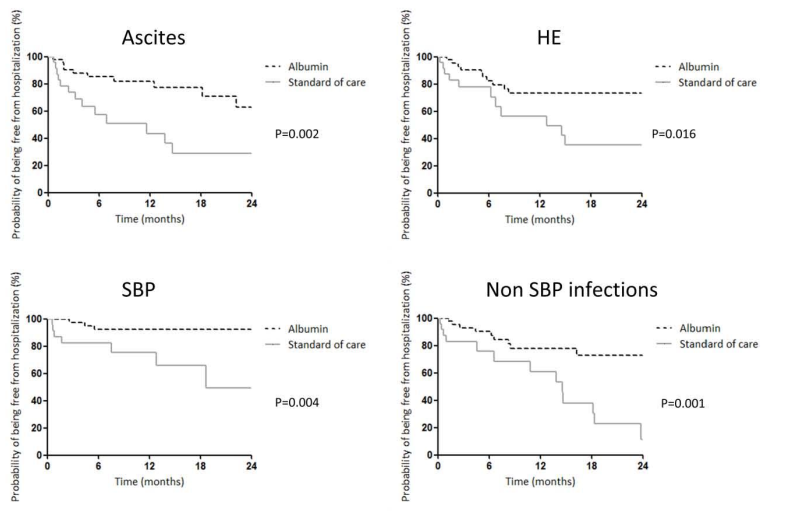
Figure 3: Compared with standard treatment, the long -term treatment of albumin has significantly reduced the incidence of hepatic brain disease, ascites, SBP and non -SBP infections
Fully -closed human hemurin infusion
It can reduce medical expenses caused by blood flow infections
The way of albumin long -term infusion can be divided into three types: fully open, semi -open, and fully confined. During the infusion, patients may have blood flow infection, which affects the hospitalization rate, mortality and medical expenses. Blood flow infection (BSI) is a serious systemic infection, where the central catheter -related blood flow infection (CLABSI) is the most common. There are research tables [2] Mingming that the incidence of CLABSI in 7 severe care rooms (ICUs) in 4 hospitals in China is 7.66/1000 CVC (central vein catheter), which is more than three times the incidence of ICU CLABSI in the United States. In addition, a research queue study in Italy [3] showed that the hospitalization costs increased due to CLABSI extended the hospitalization time. Each patient increased an additional 19.1 days of hospitalization and needed additional payment € 15,413.
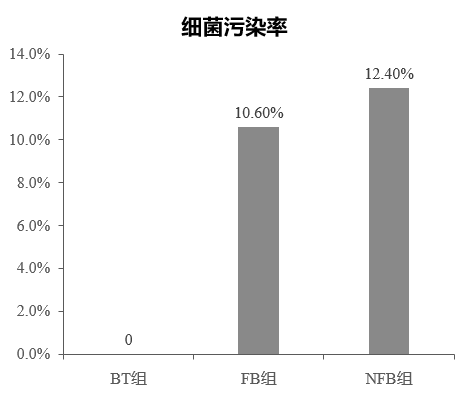
A multi -central control study carried out by Hu Bijie and others [4] in Shanghai, Shanghai, Zhejiang, and Shandong, China, compared the infusion of full -closed soft bag infusion and ordinary bottled and default system in the process of intravenous infusion. Effect of microbial pollution. The results showed that the bacterial pollution of the full -closed soft bag infusion (BT) group was zero, which was significantly lower than that of the ordinary bottle liquid (FB) group (P = 0.000) and the intake needle without filtering the membrane Ordinary bottle container (NFB) group (P = 0.000) (Figure 4). Therefore, the use of a full -closed soft bag infusion system can reduce bacterial pollution, reduce the incidence of CLABSI, and thereby reducing medical expenses. Figure 4: Bacterial pollution rates of different albumin infusion methods
Long -term human blood albumin infusion can reduce total medical expenses
Although many tests have proved the benefits of long -term application of albumin, the economic benefits of the long -term application of albumin and the value of changing clinical practice are still controversial.
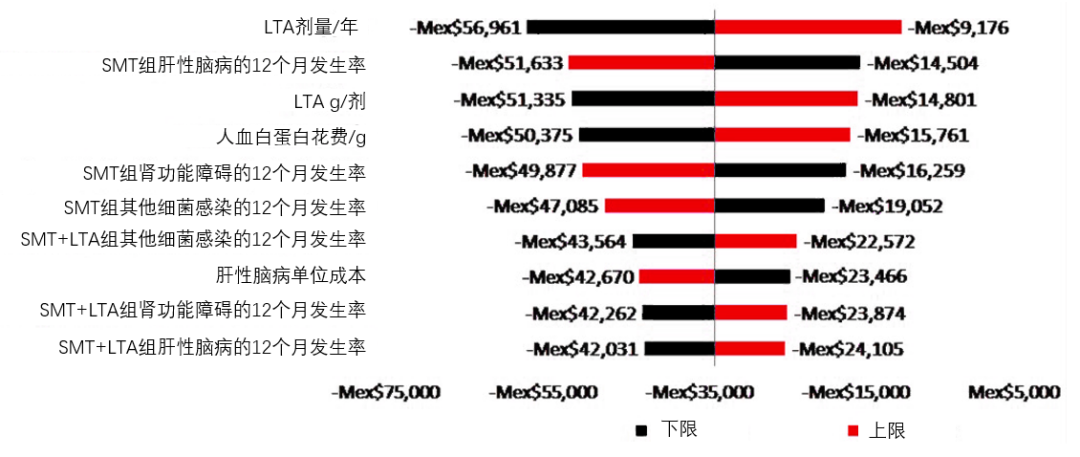
Recently, a Mexican study evaluated the incremental cost of long -term albumin infusion (LTA) therapy for patients with liver sclerosis compared to standard drug treatment (SMT) [5]. The medical expenses of patients need to consider the treatment costs (SMT or SMT+LTA), the incidence of complications, and medical resource utilization (HCRU). It is estimated that LTA requires additional medical costs, mainly from the Pharmaceutical costs of human hemoglobin (MEX $ 91,334) and follow -up follow -up of LTA (MEX $ 28,128). The cost savings related to LT are mainly due to the reduction in treatment costs of hepatic brain disease (-MEX $ 48,008), renal insufficiency (-Mex $ 38,073), and refractory ascites (-Mex $ 18,160). Overall, compared to SMT treatment patients, SMT+LTA treats patients with total medical expenses for patients with a reduction in MEX $ 33,417 (Figure 5).
Figure 5: When the incremental cost of incremental incremental costs of each hepatic cirrhosis increases or decreases by 20%, 10%of them have a maximum variable.
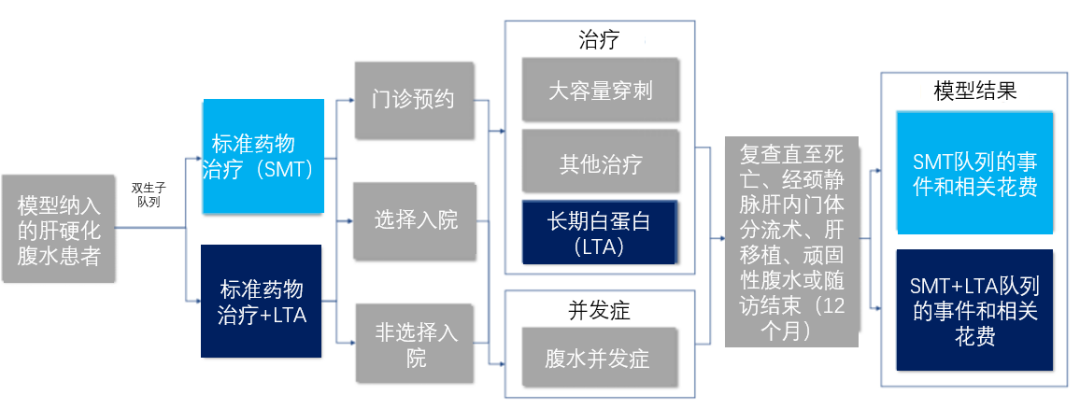
At this conference, a study of an analog model published by Professor Elisabet Viayna from the United Kingdom [6] also showed that the medical cost of LTA treatment of non -complicated liver cirrhosis patients decreased. Discrete event simulation model (DES) is a health economy modeling technology. Among them, the course of simulation of individual patients with time is pushed. (Image 6). The study was included in 100 patients, 30%received SMT+LTA (40G twice a week in the first two weeks, and then 40g once a week), the remaining SMT was followed, and the follow -up was 12 months.
Figure 6: Simplified structure of discrete event simulation models
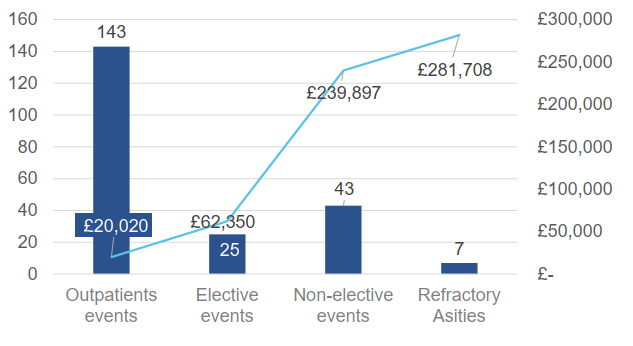
The results of the study showed that the use of LTA reduced the hospitalization rate of 12.6%and reduced the incidence of complications related to liver cirrhosis; the incidence of refractory ascites in the LTA group decreased from 37%to 30%. SMT+LTA can save up to 264,589 pounds of total medical expenses each year (Figure 7).
Figure 7: The number of events avoided by LTA treatment and related cost savings
Summarize:
At present, studies have found that long -term albumin therapy can increase the survival rate of patients with cirrhosis and ascites, reduce the incidence and hospitalization rate of complications, and provide a new overall treatment idea for liver cirrhosis and ascites. In addition, researchers are paying attention to medical expenses for long -term albumin treatment. Many studies have shown that long -term albumin treatment can reduce total medical expenses. Therefore, based on the clinical benefits and economic benefits of long -term albumin treatment, long -term albumin treatment is expected to become a safe and effective treatment plan.
Expert Introduction
Huang Jianrong

Administrative duties:
Deputy Director of the National Key Laboratory of Infectious Diseases
Deputy director
Deputy Chief Editor of China Journal of Clinical Infection
Academic
Group Leader of Parasitic Society of Chinese Medical Association
Deputy Director of National Liver Failure and Artificial Liver Expert Committee
Standing Committee Member of the Chinese Society of Prevention Medicine
Member of the Tropical Diseases and Parasitic Branch of the Chinese Medical Association
Member of the Infectious Physician Branch of the Chinese Medical Doctors Association
Standing Committee Member of the Chinese Medical Association Integrated Medical Infectious Physician Branch
Chairman of Zhejiang Medical Association Tropical Diseases and Parasitic Branch
Deputy Chairman of the Zhejiang Medical Association Liver Disease Branch
Get honorary title
In 2022, the National Health and Health Commission "eliminates malaria work" advanced individual
In 2019, the National Health and Health Commission "Health Guard" pays tribute to the character award
In 2016, the national anti -Ebola bleeding fever advanced individual
"Most Beautiful Zhejiang" year in 2015
2012 "Science Chinese" year figure
Zhejiang Province has outstanding contributions to young and middle -aged experts
7 winners of the national, provincial and ministerial scientific and technological achievements awards
Major special heavy liver scientists in the national infectious disease
The medical, teaching, and research work that has long been engaged in infectious and parasitic diseases is good at the treatment of hepatitis B and the treatment of hepatitis B and the treatment of fatty liver and the treatment of fatty liver, and cured many patients. He has won ten national and provincial and ministerial awards, and has been awarded by the Central Committee of the Communist Party of China, the State Council, and the Central Military Commission. Participate in the writing of multiple infectious diseases and science books.
references:
[1] Di Pascoli M, et al.long-term adminivity of human albumin improves survival in patients with cirrhosis and refractory ascites.2019 jan; 39 (1): 98-105. .A hospital-wide reduction in central line-associated bloodstream infections through systematic quality improvement initiative and multidisciplinary teamwork.Am J Infect Control.2019 Nov;47(11):1358-1364.
[3]Orsi GB,Di Stefano L,Noah N.Hospital-acquired,laboratory-confirmed bloodstream infection:increased hospital stay and direct costs.Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol.2002 Apr;23(4):190-7.
[4] Hu Bijie, Gao Xiaodong, Zhou Chunmei, Lu Qun, Sun Yumei, Zhang Yan, Yu Xiujuan, Wang Wenjuan, Ren Jin Lan, Huang Shenglei, He Lixian .baxter full -closed soft bag and ordinary bottle discharge fluid in the simulation of bacterial pollution in the infusion [ J]. Chinese Hospital Infectious Magazine, 2005 (05): 499-502.
[5] MOCTEZUMA-VELAZQUEZ C, ET Al.Economic Evaluation of Long-Term Albumin Use in Cirrhosis Patients from the MEXICARTHCAREM PERSTIVE.AN Hepatol.02222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222 222 MAR -APROL.20 MAPATM. 2202 MAPARR-M (Mompe that Mekt. Mompe. Momor-Mompe.an-T that of -ces that of -ces that way thatt thatt thatt thatt thatable that can that Oks
[6]Elisabet Viayna,et al.Long term albumin administration is associated with reduced healthcare resource use in patients with uncomplicated cirrhotic ascites:results from a simulation model.2022 ILC.FRI499.
Approval coding: VV-MEDMAT-71350
Approval time: July 2022
Disclaimer: This content is only for Chinese medical and health professionals. It aims to provide scientific information to medical professionals for personal learning and reference. If you are not medical professionals, do not participate or spread.
-End-
This article is only used to provide scientific information to medical professionals and does not represent the platform position

- END -
Dang Xiaolong attended the first batch of cultural master studios in our city and unveiled

Cultural sharing, civilization infiltration. On July 10, the city's first batch of...
Kangding Yi Hotel Fire Official: Improper fuel operation caused the fire injury in the store

On the evening of July 18, a video shot by netizens showed that a hotel in Kangdin...