Medical Interview | Professor Du Yan: Exploration of Lung-Cancer EGFR-TKI Drug Resistance-resistant and immunotherapy
Author:Physician reported tumor chann Time:2022.07.21
EGFR-TKI is the main treatment method of late EGFR mutations in non-small cell lung cancer, but almost all patients have failed to treat treatment due to sexual resistance, and subsequent treatment is in trouble. For patients with EGFR-TKI resistance, chemotherapy is considered the main treatment method, but the curative effect is not ideal. In recent years, immunotherapy for PD-1 pathways has made breakthroughs in patients with negative lung cancer in EGFR mutations, and the efficacy of immunotherapy in patients with drug resistance patients in EGFR-TKI is still controversial. It is necessary to further explore targeted therapy-based resistance PD-1 antibody therapy for drug mechanisms and immune micro-environmental types provides new treatment plans for EGFR-TKI patients with drug resistance. Professor Du Yan of the First Affiliated Hospital of Anhui Medical University invited Professor Du Yan of the First Affiliated Hospital of Anhui Medical University.

01
EGFR-TKI and EGFR-TKI resistance
Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) gene is one of the most common driving genes in non -small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). The proportion of EGFR gene mutations in NSCLC patients in China is about 50%. For patients with positive EGFR mutations, the efficacy of EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIS) is significantly better than traditional chemotherapy. It has been used as the main drug for the first -line treatment of EGFR sensitive mutations.
There are three generations of EGFR-TKI widely used in clinical practice. The first generation of EGFR-TKI mainly blocks EGFR activity through ATP competition, including Geffitinib, Elotinib, Ekntinib; second On behalf of EGFR-TKI, through the combination of co-prices with EGFR, irreversible suppression of EGFR kinases, including Afutinib and Dakinib; the characteristics of the three generations of TKI are in addition to irreversible inhibition of EGFR activation mutations, and can also overcome the acquisition of T790M mutation induction. The second -generation drug resistance mechanism, including Oshitinib, Amentinib, Verininib, etc.
However, patients with NSCLC treated with EGFR-TKI are difficult to avoid obtaining drug resistance after treatment. Most patients will produce drug resistance at 9-14 months after taking the first or second-generation EGFR-TKI. The 20-outer T790M mutation of EGFR No. 20 is the most common mechanism with a incidence of 50%. The three generations of EGFR-TKI represented by Ositinib used to overcome the acquisition of T790M mutations mediated obtaining resistance to achieve a significant effect. However, patients will be used again after 18.9 months and second-tier use in the first line of EGFR-TKI in the three generations of EGFR-TKI.
At present, research found that the drug tolerance mechanism of the three generations of medicines can be divided into other mechanisms such as EGFR dependencies, EGFR non -dependent, that is, bypass activation, and organizational type conversion. not exactly. The drug resistance mechanism is more complicated during the first -line application. 59%of the patient's resistance mechanism is unclear. The incidence of bypass activation and organizational type conversion incidence is higher. The most common of which are MET amplification (15%) and small cell lung cancer. (SCLC) Transformation. The incidence of EGFR -dependent drug resistance is relatively low. The most common of which is C797S three -time drug mutations, accounting for only 7%of all drug resistance mechanisms. There are only 25%of the mechanism in the backline application. Among the clear mechanisms, the EGFR dependency pathway is the main drug tolerance mechanism. 10%to 26%has three mutations such as C797S, such as C797S, which is higher than the first -line applications. Reserved, and 43%of patients have a T790M loss, T790M loss may be more likely to have a drug -resistant mechanism for bypass activation.
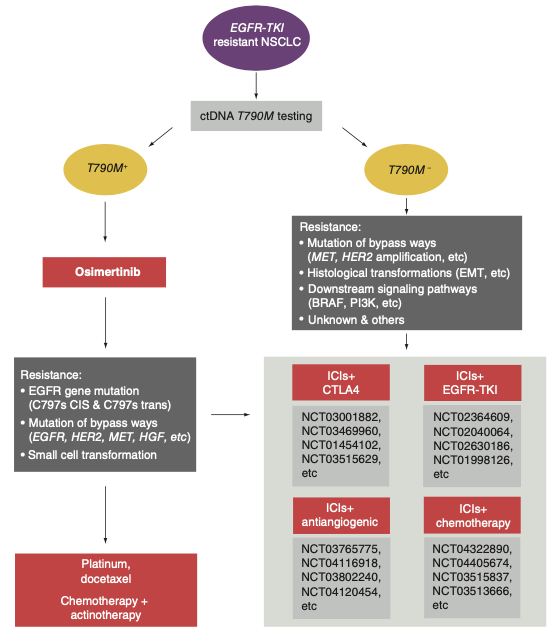
Figure 1EGFR-TKI drug resistance mechanism
02
EGFR-TKI drug resistance and immune micro environment
The blocking therapy for immune checkpoints has made breakthrough progress in driving the advanced NSCLC treatment of the driving genes of wild -type wild types. Immunotherapy is gradually becoming the most potential oncology treatment method after chemotherapy and targeted therapy. Clinical evidence shows that patients with a small part of the EGFR gene mutations can benefit from immunotherapy, and the tumor immunocus environment is an important factor affecting the efficacy of immunotherapy.
Recently, the research team of Professor Zhou Qing of the People's Hospital of Guangdong Province and Southern Medical University has recently discussed the characteristics of the micro -environment of tumor microvisal for patients with EGFR mutant lung adenocarcinoma through sequencing and multi -color immunohistochemistry. They found that EGFR negative tumor cells could promote the proliferation and functions of CD8+T cells by interferon response and PI3K-AKT-MTOR-related signaling pathways. The results also showed that the CD8+TRM cells in T cells of EGFR -positive lung adenocarcinoma, CXCL13 expression decreased, immunosuppressive factor expression increased, indicating that EGFR mutations have negative modification effects on the micro -environment of the tumor. The experimental results showed that the lack of inflammatory cells, the enrichment of the type of cell type and the low expression of the influence of the cell type and the immune examination point protein may cause EGFR mutant lung adenocarcinoma to have an immune silence environment, that is, the tumor cells of EGFR mutations can be recruited by secreting cytokine to recruit each Establishing immunosuppressive cells, while activated immune cells are seriously insufficient.
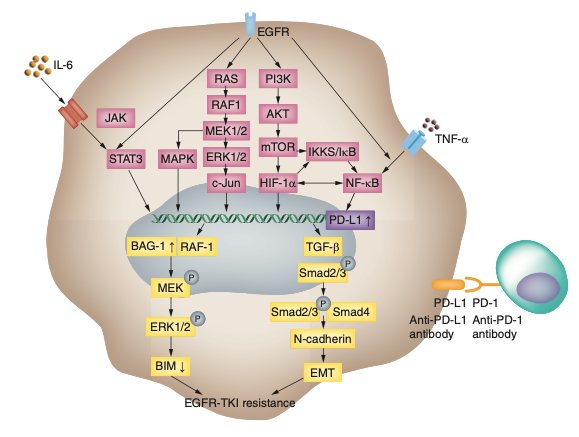
At the same time, research has gradually discovered that EGFR-TKI has the potential to affect the micro-environment of tumor. EGFR-TKI resistance is related to the "inflammatory" immune microe environment, and patients with drug resistance may benefit from immunotherapy. In 2013, Akbay and his colleagues found that the EGFR signal in the cells can be used to induce T cell apoptosis and promote the direct or indirect increase of immune escape from the expression of PD-L1 in tumor cells in the EGFR mutation NSCLC. Recent studies have confirmed that the downgrade of PI3K, AKT, and MTOR has the potential to reduce PD-L1 expression, which indicates that EGFR mutations may participate in regulating PD-L1 expression by activating the PI3K/AKT/MTOR signaling pathway. NF-κB and STAT3 are important downstream paths activated by EGFR. There are also studies that have been discovered directly or indirectly to adjust the transcription of PD-L1, and then adjust the expression of PD-L1 through the IL-6 mechanism. These research results all provide theoretical basis for the application of NSCLC in NSCLC, which is not effective in immune examination point inhibitors in NSCLC, which is not effective in targeted therapy and the expression of PD-L1. The specific molecular mechanism still needs further research.
Figure 2EGFR adjustment of PD-L1 expression
03
EGFR-TKI patients with immunity treatment status quo
Immunotherapy has continued efficacy in NSCLC patients after EGFR-TKI resistance. Several immune examination point inhibitors (ICI) for PD-1 have been authorized by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for clinical treatment of advanced NSCLC, including Nivolumab and PEMBROLIZUMAB. However, PD-1/PD-L1 single drug treatment is only effective among about 20%of the unique NSCLC patients, which is disappointing. The researchers advocate that combined therapy based on immunotherapy may be a choice. A phase II Study (CT18, NCT03513666) of Tripley Mippling and Card Platinum showed good results. IMPOWER150 studies incorporated into patients with EGFR mutations have shown that compared with chemotherapy plus anti -vascular generic drugs, ICIS combined with chemotherapy and antibody generic drugs can extend patients with PFS. Nevertheless, these two clinical research also shows a higher proportion of 3-5 adverse events.
Figure 3IMPOWER150 Comparison of EGFR mutations without progressive survival

Orient-31 is an immunotherapy (NCT03802240) as a recent random, double-blindness, and phase 3 study in patients with or without IBI305 (Berchavar Mipido) an additional EGFR mutations (NCT03802240) in patients with chemotherapy. ESMO Asia Virtual Oncology Week Annual Meeting, which was held in November 2021, announced the results of midterm data analysis. As the deadline for the first interim analysis (July 31, 2021, the median follow -up time was 9.8 months), 444 patients were randomly packed (A/B/C group 148/145/151). The median age is 57 years. The median PFS (95%CI) of IRRC is 6.9 months (6.0,9.3) in group A, 5.6 months (4.7,6.9) in Group B, and 4.3 months in Group C (4.1,5.4 To. Compared with the control group C, PFS is significantly extended (HR = 0.464, 95%CI: 0.337-0.639; P <0.0001). Compared with group B and C, the benefit trend of PFS (HR = 0.750, 95%CI: 0.555-1.013; P = 0.0584). The invalid analysis of A and B did not span the invalid boundary (HR = 0.726,95%CI: 0.528-0.998). The confirmed ORR was 43.9%, 33.1%, and 25.2%in group A, B and C. The incidence of AE occurred in level 3 was 54.7%, 39.3%, and 51.0%, respectively. Compared with separate chemotherapy, the Cyli Midelia combined with IBI305 and chemotherapy have significantly improved PFS.
In summary, the study found that for EGFR mutations, the four -medicine combined immunization scheme is a treatment plan that can be considered.
04
Professor Du Yan concluded
The EGFR-TKI for the EGFR signaling pathway has brought good survival benefits to the EGFR mutant crowd, but most people inevitably produce drug resistance in about one year after treatment. There is currently lack of available treatment options. Therefore, the research and innovation strategy is imminent. As one of the means of internal medicine treatment of tumor, immunotherapy still lacks clinical experience in immunotherapy for NSCLC patients who are resistant to EGFR-TKI drugs, and there are controversy in the results of different clinical trials. Different sub -type EGFR mutations, different administration order, time and dose may affect the efficacy of immunotherapy, and strict selection of high -standard people will help improve the result of immune therapy. In view of the potential advantages of immunotherapy in the EGFR-TKI patients, the correlation between the treatment of related biomarkers and tumor-driven factors in NSCLC in NSCLC is crucial. How to screen immunotherapy will be a topic that needs to be continuously considered in the future.
Expert Introduction
Professor Du Yan

Chief Physician, Associate Professor, and Master Graduate Master of the First Affiliated Hospital of Anhui Medical University
CSCO Youth Committee of the China Clinical Oncology Society
The Youth Committee of the China Anti -Cancer Association Cancer Clinical Chemistry Commission
Members of Chinese Lung Cancer MDT Expert Consensus Consensus Expert Group
Member of the Primary Health Cancer Professional Committee of China Junior Health Care Foundation
Director and Deputy Secretary -General of the Anhui Anti -Cancer Association
Director and Secretary -General of the Anhui Provincial Clinical Oncology Society
Hosted 3 provincial scientific and technological research projects
Published more than 20 articles in SCI papers, Chinese series of journals
The PI hosted more than 20 clinical research on multi -center drugs in China
Anhui Province Excellent Natural Science Paper Second Prize and Third Award
Capture: Li Hui
Edit: Wang Lina
- END -
Symposium for Experts of the National Industrial Design Vocational Skills Competition in 2022

Industrial design is an important aspect of implementing my country's manufacturin...
Help smart agriculture, two companies in Suzhou are on the list!

Picking fruits, spraying pesticides, feeding feed ... Today (June 27), I watched t...