Early diagnosis and early treatment, grasping the "golden growth" of children with food allergies
Author:Pediatric channels for medical Time:2022.08.31
*For medical professionals for reading reference
Summary
Food allergies have high risk of growing in retardation. Milk protein allergies are more significant than other types of allergic foods than other types of allergic foods, and they are easily dislocated to delay the disease, causing malnutrition. Early diagnosis and early treatment of food allergies are the core points of ensuring the growth and development of children with allergic children. Food avoidance+amino acid formula 2-6 weeks is the gold standard for diagnosis of milk protein allergies. The amino acid formula is 100%non -sensitivity. The use of amino acid formula for nutrition management of children with food allergies can help children pass the 6 -month high sensitivity period, and can effectively alleviate the symptoms of allergies such as the skin and gastrointestinal tract of children. Comprehensive nutrition can ensure sufficient nutritional intake and help children with food allergies catch up and grow.
1. The effect of food allergies on growth and development
Good growth is the best indicator of infant nutrition. However, the monitoring data of Chinese residents' nutrition and health status shows that the growth rate of infants and young children in my country in June to 24 is 7.17%[1]. Regular growth monitoring of children is an important means to evaluate children's nutritional status and early detection of diseases. We can evaluate the growth and development of infants based on the Z -duty evaluation method and growth curve method [2].
Food allergies are one of the high -risk factors for slow growth in infant and early childhood. Analysis of the many factors of children under the age of 7 in the nine cities in the nine cities showed that the risk of children with dairy or complementary foods in infantile or food allergies increased significantly [3].
The more types of allergic foods, the significant impact on the growth of children. For children with ≥ 3 kinds of foods, the proportion of age of age Z score and age, the height Z score <-2 (that is, the normal standard) ratio is 14.5%and 12.1%, which is much higher than the allergic allergies of ≤2 foods. Children [4]. In addition, food allergies for food allergies or allergies on gastrointestinal function can cause lack of trace nutrients, such as vitamin D, calcium, zinc, and selenium [4].
Milk protein allergies have a significant impact on physical growth than other types of allergic foods. According to the World Health Organization (WHO) children's growth and development standards (2006 edition), growth and development Z scores. As a result, the malnutrition incidence of milk protein allergic children reached 23.1%, of which low weight accounted for 45.9%, and the growth retardation accounted for 29.7%. The proportion of weight loss accounts for 24.3%[5]. Studies have shown that compared with children with no milk protein allergies, the physical growth of children's allergies is affected, and the average weight, height and BMI percentage are significantly reduced [6]. Nutrition of milk protein allergies as shown below:
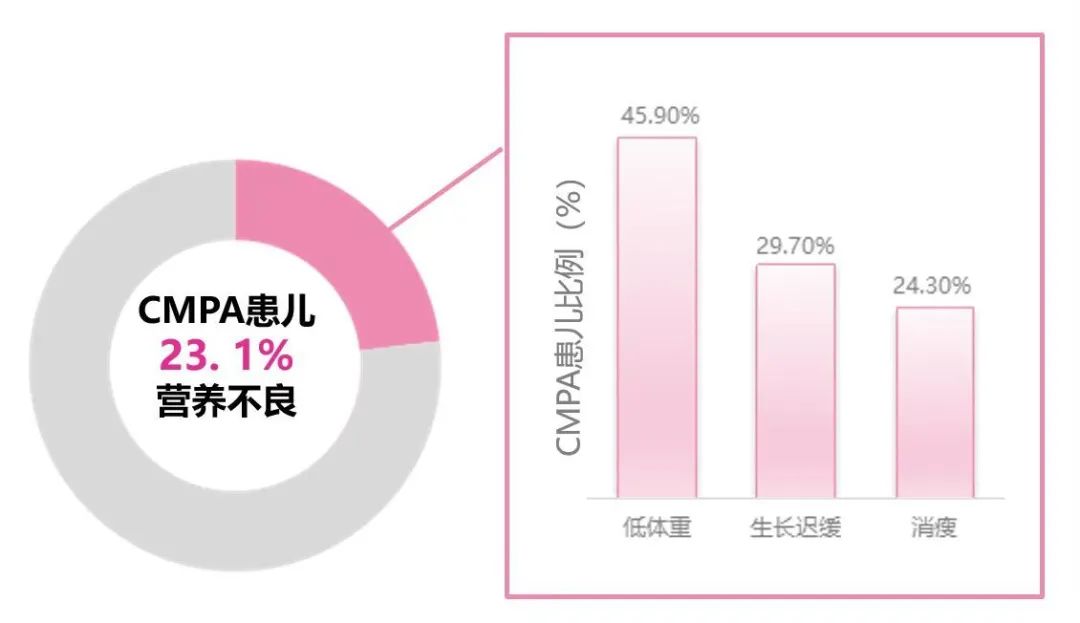
Figure 1 The proportion of milk protein allergies for various children
2. Children with food allergies
Five major reasons for growth and development
■ Reasons 1: It is easy to be misdiagnosed and delayed the condition, causing malnutrition
The diagnostic method of food allergies usually includes detailed medical history, physical examination, laboratory examination, and diagnostic food avoidance+oral food stimulation. Simple medical history and physical examination cannot be diagnosed with food allergies. Experience diagnosis of only symptoms can cause misdiagnosis and antibiotic abuse. Studies have shown that milk protein allergic gastrointestinal symptoms (including lactose intolerance, enteritis, gastritis, upper sense, functional constipation The misunderstanding rate of omissions of intestinal cases) is as high as 70%, and the antibiotic abuse rate in this study is as high as 62%[7]. The results of the laboratory test can also cause missed diagnosis. The sensitivity of the skin thorns (SPT) is only 52.8%. The clinical clinical may show false negatives. The specific IgE detection specificity of serum is only 47.7%. Clinically, it is easy to miss the diagnosis [8]. Diagnostic food avoidance 2-6 weeks+excitement test is the gold standard for food allergies, with a diagnostic rate of 90%[9, 10]. Food allergies misdiagnosis of malnutrition of children is much higher than non -misdiagnosed cases [7].
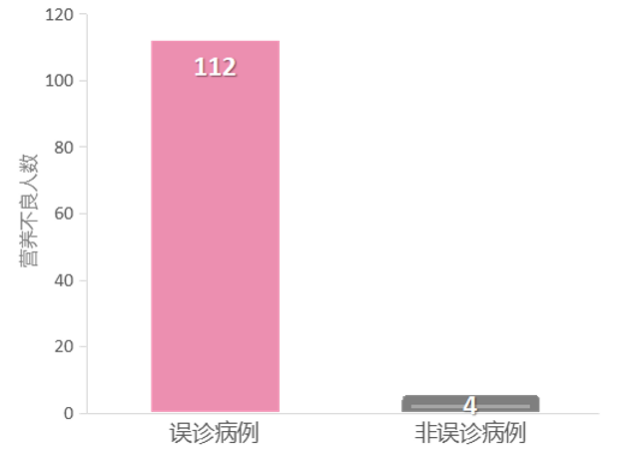
Figure 2 Number of malnutrition in misdiagnosis and non -misdiagnosis cases
■ Cause two: Intestinal inflammation and increased permeability cause too much nutrient loss
There are intestinal inflammation in children with food allergies. The inflammatory medium (cytokines, protease) in the intestine can cause further disintegration of the intestinal barrier, increase the passage of allergens, and lead to persistent inflammation reactions [11]. Intestinal permeability is a key feature of the gastrointestinal tract. It allows the effective passage of nutrients and limits the entry of large molecules (such as protein antigens) to promote the appropriate immune response to food antigen [12]. The intestinal permeability of children with food allergies is three times that of healthy children, and even after a long time after the last contact with allergens, the allergic state of the intestinal mucosa still exists, preventing the intestinal transparency from returning to the normal value [11 11 [11 , 12]. Continuous inflammation reactions and increased intestinal permeability can lead to too much nutrient loss, which eventually leads to slow growth [13].
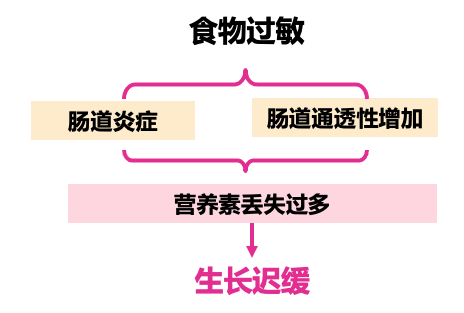
Figure 3 Food allergies lead to slow growth
■ Reason three: The incidence of feeding difficulties in infants and young children in food allergies is high, which affects growth and development
Children with food allergies are often due to the gastrointestinal functional damage and poor food experience caused by early allergies. They are manifested as feeding difficulties, refusing eating or not interested in eating [14]. About 40.2%of infant food allergies are accompanied by feeding difficulties, and 88%of infants and young children with difficulty in feeding are suffering from food allergies. Allergies with difficulty in feeding children have higher clinical manifestations. Rate [14, 15]. Figure 4 The incidence of clinical manifestations of children with difficulty in feeding children
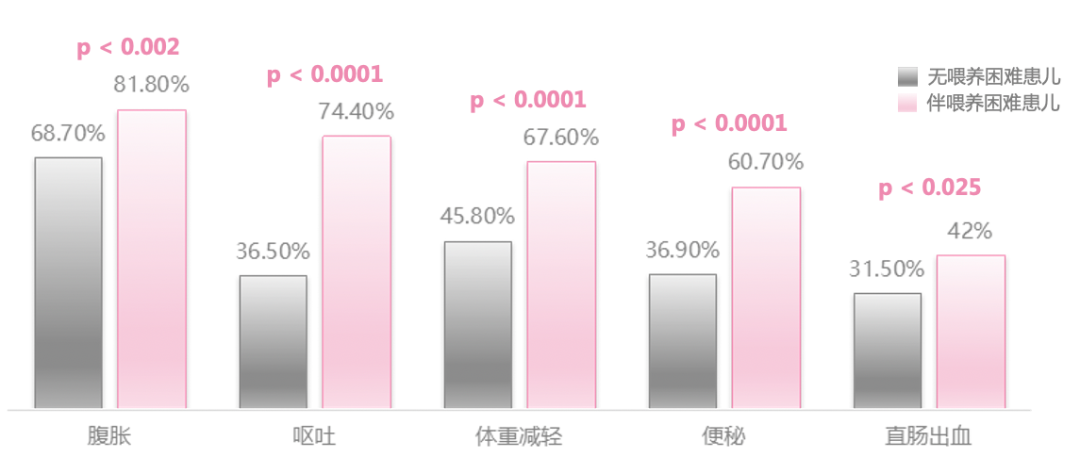
■ Reasons 4: Food allergies are related to digestive tract diseases that cause slow growth
About 60%of children's food allergies are involved in the digestive system. For example, the main symptoms of eosinophilic esophagitis (EOE) include difficulty in feeding. The main symptoms of food protein -induced bowel (FPE) include slow growth. Gastrointestinal diseases can also lead to slow growth when the condition is severe [16, 17]. These foods are allergic to gastrointestinal diseases that cause digestive tract mucosa damage, affecting nutrient absorption and growth and development [17].
■ Reasons 5: Improper supplement to eat, which directly affects growth and development
Whether the feeding behavior science directly affects the growth and development of infants and young children [18]. Adding a supplementary food will miss the sensitivity of the baby's taste, which leads to future feeding difficulties; children fail to get the need for extra food to meet the needs of growth and development, resulting in slow growth and development; children do not get enough nutrients, and they will cause nutritional deficiencies. Such as iron deficiency anemia, etc. [16]. Insufficient food supplement to infants and young children is an important cause of malnutrition in infants and young children, and the impact of malnutrition is long -term [16].
3. Management of growth and development of children with food allergies
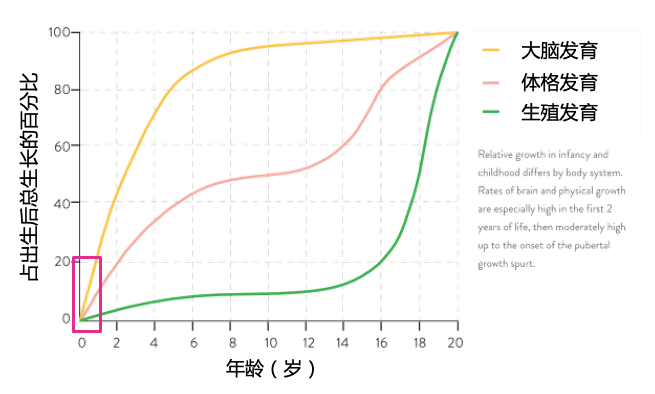
The 0-1 years old is the first golden period for the growth and development of the baby's brain and physical fitness. It requires sufficient nutrients to ensure growth and development [19, 20]. After the birth of infants and young children, the physical growth (weight and length) is mainly concentrated in 3-12 months after birth, especially in 6-12 months [21]. In order to miss the "golden growth" of children with food allergies, early diagnosis and early treatment of food allergies are the core points of ensuring the growth and development of children with allergic children.
Figure 5 Human 0-20 years old growth and development curve
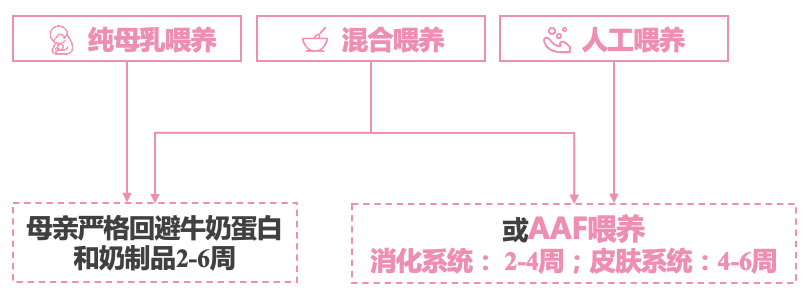
For babies suspected to be milk protein, change the amino yogurt powder for 2-6 weeks to observe the baby symptoms and signs. If there is a significant improvement, it is prompted to have milk protein allergies [14]. Multiple domestic consensus also pointed out that food avoidance+amino acid formula 2-6 weeks is a gold standard for milk protein allergies [17, 22].
When breastfeeding has the following situations, it is also necessary to consider transition to formula feeding:
(1) Mother's dietary avoidance, the symptoms of children are continuous and severe;
(2) The slow growth of children and other nutritional deficiencies;
(3) Mother's dietary exclusion leads to severe weight loss and affects the health of the mother;
(4) Mother cannot cope with the psychological burden of diet/children.
Figure 6 Food avoidance+amino acid formula 2-6 weeks is the gold standard for milk protein allergy diagnosis
For children with allergies diagnosed, nutritional assessment should be performed before diet, and nutritional consultation and intervention should be started before nutritional problems. At present, there is no standard nutritional standard for children with food allergies. Therefore, countries still recommend reference to normal children's nutrients to evaluate dietary evaluation of children to understand whether the dietary intake of allergic children is reasonable.
A completely avoiding allergenic food is the only effective method for treating food allergies [14]. Children with food allergies need to be strictly avoided during the 6 -month "high -sensitivity period" to ensure nutritional intake [23, 24]. The amino acid formula is 100%non -sensitivity, helping the children through the 6 -month high sensitivity period, and can effectively alleviate allergic symptoms such as the skin and gastrointestinal tract of children [25, 26].
Amino acid formula is comprehensive and can ensure sufficient nutritional intake. A study shows that after 6 months of feeding amino acid formula, the child has a significant growth in length, and the child with the deep hydrolyzed formula has not increased. The result shows that the amino acid formula can help children with milk protein allergic to catch up with growth [27].
0-1 years old is a rapid growth period. For food allergic babies with malnutrition or poor growth, it is recommended to conduct growth assessments every month, discover slow growth in time, and detect diet compliance at the same time. Visit once a month [14].
Summarize
The 0-1 years old is the first golden period for the growth and development of the baby's brain and physical fitness. It requires sufficient nutrients to ensure growth and development. Food allergies are one of the high -risk factors for slow growth in infant and early childhood. Among them, milk protein allergies have the most significant impact on infant growth.
In order to miss the "golden growth" of children with food allergies, early diagnosis and early treatment of food allergies are the core points of ensuring the growth and development of children with allergic children. The use of amino acid formula diagnostic foods to avoid 2-6 weeks+stimulation test is the gold standard for food allergies, which can avoid the impact of growth and development caused by misdiagnosis.
The amino acid formula is 100%non -sensitivity, helping the children through the 6 -month high sensitivity period, and can effectively alleviate allergies such as the skin and gastrointestinal tract of the child. Children with food allergies chase and grow. references
1. Ding Xinyue, et al., Chinese infants and young children are slow to grow ill and have a relationship with feeding behavior [J]. China Public Health, 2018,34 (05): 665-668.
2. Xing Yuan, et al., Empty and young children's malnutrition current and Z value evaluation methods Reference standards for reference standards [J]. Foreign Medicine (Medical Geographical Subsidies), 2009,30 (04): 208-211.
3. Zhang Yaqin, et al., China ’s nine cities under the age of seven years of age of children growing up slowly influencing factors [J]. Chinese Pediatric Magazine, 2021,59 (09): 743-751.
4.flammarion s, et al. Pediatr allergy immunol. 2011 mar; 22 (2): 161-5.
5. Xiao Yulian, et al., The clinical manifestations and nutritional status of infant milk protein allergies [J]. Chinese clinician magazine, 2019,47 (01): 92-94.
6. Robbins Ka, et al. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2014 DEC; 134 (6): 1466-1468.E6.
7. Chengzhi et al. Modern biomedical progress, 2016,116,30: 5957-5960
8.flores kim j, etal. Allergy. 2018 AUG; 73 (8): 1609-1621.
9.koletzko s, et al. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr, 2012,55 (2): 221-229.
10. Li Zailing et al..
11.könig j, et al. Human Intestinal Barrier Function in Health and Disease. Clin Transl Gastroenterol. 2016 Oct 20; 7 (10): E196.
12. Perrier C, et al. Gut Permeability and Food Allergies. CLIN Exp Allergy. 2011 Jan; 41 (1): 20-8.
13. Zhang Yequ, Hu Yan. Nutrition management of food allergies for children [J]. Chinese Pediatric Magazine, 2019,57 (03): 238-240.
14. Yu Xiaodan. Integenity of food allergies in infants and young children [J]. China Practical Pediatric Clinical Journal, 2019 (21): 1614-1617.
15.Meyer R, et al. JSTROENTEROL HEPATOL. 2014 Oct; 29 (10): 1764-9.
16. Children's Health Branch of the Chinese Prevention Medicine Association. Chinese Maternal and Child Health Research. 2019.30 (4): 392-417.
17. Li Zailing, Gong Sitang. Food allergies related to digestive tract disease diagnosis and management expert consensus [J]. Chinese pediatric magazine, 2017,55 (07): 487-492.
18. Ding Xinyue, et al., Chinese infants and young children are slow to grow sickness and relationship with feeding behavior [J]. China Public Health, 2018,34 (05): 665-668.
19. Michaelsen kf. 1.1 Child Growth. World Rev Nutr Diet. 2015; 113: 1-5.
20. Ma Jing, wait. Baby mother feeding behavior and influencing factors analysis [J]. Chinese children's health magazine, 2000,8 (3): 197-198.
21. Li Xinghong. Analysis of 220 cases of infant growth and development monitoring results [J]. China health nutrition, 2016, 26 (013): 450.
22. Children's characteristic dermatitis related food allergies diagnosis and management expert consensus [J]. Chinese dermatology magazine, 2019 (10): 711-716.
23.giovanna et al. Italian Journal of Pediatrics 2012, 38:35
24.Westra l, et al.]. Blood, 2013, 122 (13): 2205-2212.
25.host A, Halken S. Allergy, 2004,59 SUPPL 78: 45-52.
26.vanderhoof j, et al. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2016 nov; 63 (5): 531-533.27.niggemann B, et al. Pediatr allergy immunol, 2001,12 (2): 78-82.
-End-
This article is for the reference of medical and health professionals, and does not represent the platform position
The medical community strives to make any promises and guarantees for the accuracy and reliability of the content of the content when passing the audit, but not the timely and completeness of the accuracy and integrity of the cited information (if.)Any responsibilities caused by outdated content, inaccurate or incomplete information cited information.Relevant parties are requested to check or use this as a basis for decision -making.


- END -
Family Education Public Welfare Guidance: What should I do if my child cannot insist on brushing his teeth?

How to help children develop a good habit of insisting on brushing and brushing th...
Baby literacy is not necessarily clever, with these abilities is clever

As a generation of our post -90s generation, most of the education received from c...