What does the U.S. "chip bill" mean?
Author:Global Times Time:2022.08.11
On the 9th local time, US President Biden officially signed the "Chip and Science Act" (hereinafter referred to as the "Chip Act"), which plans to provide up to $ 52.7 billion in government subsidies for the US semiconductor industry. In the relevant manual issued by the White House in the United States, the purpose of the "Chip Act" is summarized to reduce costs, create employment, strengthen the supply chain, and fight against China.
Industry insiders interviewed by a reporter from the Global Times on the 10th stated that in the United States, it has adopted measures to request relevant companies to prohibit the sale of high -end optical machines in China, impose a "chip ban" to Huawei, and organize the "chip Quartet Alliance" to enclose China Later, the "Chip Act" opened the "rare industrial policy support for decades" in the United States. While seeking to restore the industry's dominance, restricting and preventing semiconductor international enterprises from existing manufacturing capabilities and planning in mainland China Manufacturing capabilities, and then these manufacturing capabilities to the United States to achieve the purpose of harming others and self -interest.
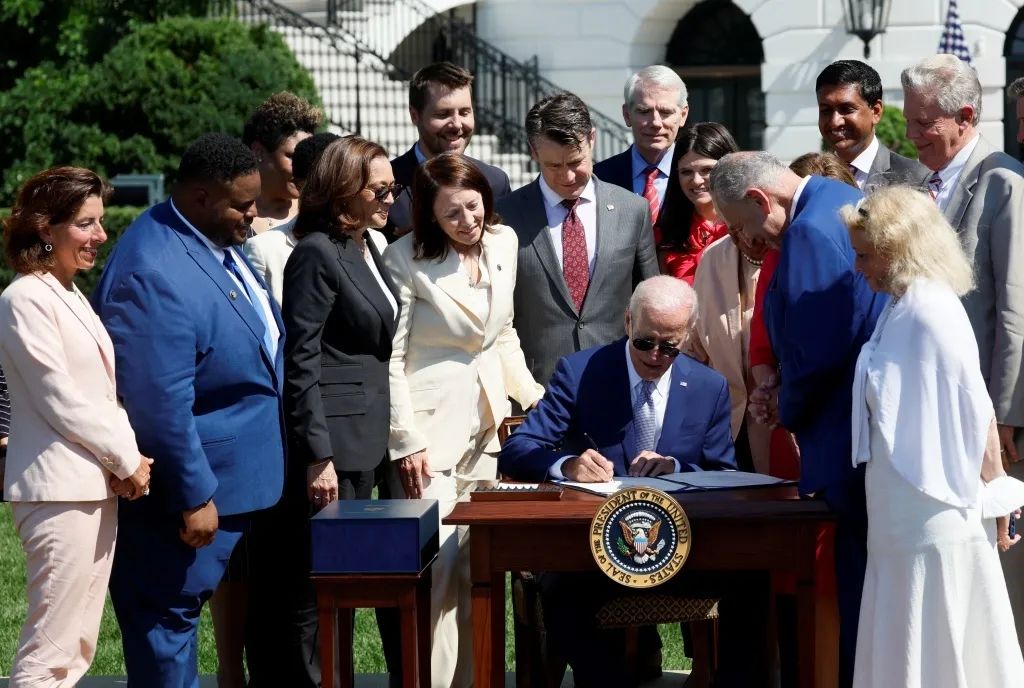

On August 9, 2022 local time, Washington, USA, US President Biden signed the "Chip and Science Act" in the White House and delivered a speech
Industry insiders also criticized that the United States has added the "Chinese guardrail" clause in the "Chip Act" to allow enterprises to choose a side team in the Chinese and American industrial policies, creating a dangerous precedent for a country's use of industrial policies to disturb the international market and the global supply chain.
What did the bill say? The U.S. government threw $ 52.7 billion to vigorously subsidize chip research and development and manufacturing
"The United States has invented semiconductors. More than thirty years ago, the United States accounted for 40%of global chip output. Later, our economic pillar -manufacturing was hollowed out and semiconductor manufacturing was overseas." Bayeng signed the "chip bill on the 9th "At the time, he made a speech," Now, this law brings semiconductors (manufacturing) back to the United States ... In the next few decades, we will lead the world again. "
As Biden mentioned, the core of the "chip bill" is to help the United States re -gain the leading position in the semiconductor manufacturing field. Industry data shows that the US share in the global semiconductor manufacturing industry has decreased from 37% in 1990 to 12% in 2020. During the same period, China's share in this field rose from almost zero to 15%.
The New York Times said that the bill integrates the content of economic and national security policies, mainly including two aspects: First, to provide about $ 52.7 billion in funding support to the semiconductor industry, and to provide enterprises with a value of US $ 24 billion in investment tax to offer For exemption, companies are encouraged to develop and manufacture chips in the United States; second, provide about US $ 200 billion in scientific research funding support in the next few years, focusing on supporting cutting -edge technology such as artificial intelligence, robotics, and quantum computing.
According to the bill documents issued by the US Congress, the "Chip Act" has a detailed planning and timetable of more than $ 200 billion in investment. According to the bill, the United States will set up four major funds to share the government's $ 52.7 billion for the semiconductor industry, of which $ 50 billion will be allocated to the "American Chip Fund", accounting for about 95%of the total amount of monopolies. The bill requires that the "American Chip Fund" funds will be used for semiconductor incentive plans to develop domestic manufacturing capabilities and R & D and labor development plans.
The semiconductor incentive plan is the top priority of the "American Chip Fund" in fiscal 2022 to 2026. The plan will cost $ 39 billion to support the development of the chip manufacturing industry. In fiscal year in 2022, the semiconductor incentive plan invested $ 19 billion, and then invested $ 5 billion in each fiscal year. In addition, the bill will provide 25%of investment tax claims for relevant enterprises. At the same time, the bill clarified the production of $ 2 billion for traditional mature process chips in fiscal 2022.
In addition to the semiconductor incentive plan, the R & D and labor development plans will also receive support of US $ 11 billion in the "American Chip Fund". In the next five years, they will be invested in the National Semiconductor Technology Center (NSTC), the National Advanced Packaging Manufacturing Plan, and other R & D and labor development projects. Essence
In the budget of $ 52.7 billion, the "US Defense Chip Fund" will receive $ 2 billion; the "American Chip International Technology Security and Innovation Fund" will receive $ 500 million to strengthen coordination and communication with foreign government partners; "the United States "Chip Labor and Education Fund" will receive $ 200 million, mainly for related talent training.
The scientific research funding support of about $ 200 billion will be assigned to the National Science Foundation (NSF), the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), the Ministry of Commerce and the Ministry of Energy. Among them, the Ministry of Commerce will obtain the power to distribute US $ 10 billion to the state and local regions to build multiple "regional technology centers" across the United States.
Why is it worthwhile in China? Use administrative forces to interfere with international semiconductor companies in China
One of the most noticeable clauses for the "Chip Act" is that companies that prohibit federal funds from obtaining federal funds have greatly increased their production chips in China in China for a period of 10 years. Companies that violate the ban or fail to amend the violation may need to be returned to federal subsidies in full.
A research report released by Huatai Securities stated that companies in China and the United States have semiconductor factories in China and the United States including TSMC (Nanjing), Samsung (Xi'an), and Hemori (Dalian). It will be restricted to build or expand advanced process wafers in China. In addition, Intel and Micron also have chip packaging and testing plants in China.
According to BBC (BBC), in the past period, all American equipment manufacturers received letters from the US Department of Commerce and informed them not to supply equipment for 14 nanometer or below chip manufacturing. Panlin Semiconductor Chairman and CEO Tim Abel, a US chip equipment manufacturer, said at the financial report on July 27 that the scope of the US technology export control of China will further expand to a foundry factory below 14 nanometers. Gu Wenjun, the chief analyst of Xinmou Research, told a reporter from the Global Times that the provision of the "Chip Act" combined with the US government's series of sanctions on Chinese semiconductor companies in recent years, and once again shows that the United States regards Chinese semiconductors as competitors. Intentionally suppressing the development of China's semiconductor industry in advanced technology.
A unnamed industry person criticized in an interview with the Global Times reporter that in recent years, the United States has adopted various means to create a semiconductor "small circle" that crowded China, and the "Chinese guardrail" clause in the "chip bill" is paired China and even the entire industry are seriously harmful. The senior semiconductor industry expert said that this clause allowed the United States to find a so -called "trustworthy" country in addition to the production semiconductor in the country, which may break the division of labor and pattern of the global semiconductor industry. In the future, the United States may also intensify, "let the country be produced and what to produce."
Regarding the relevant content in the "Chip Act", the China Trade Promotional Association and the China International Chamber of Commerce issued an objection on the 10th. The China Trade Council and China International Chamber of Commerce believe that the clauses in the bill treat some foreign companies, highlighting the use of government forcibly changing the international division of labor in the semiconductor field, harming the interests of enterprises from all over the world including Sino -US enterprises. On the one hand, this is a typical specialized industrial subsidy, which does not meet the non -discrimination principles of the WTO; on the other hand, the bill has determined some countries as focusing on and cracking downrs, which has forced enterprises to be forced to adjust the global development strategy and layout. In particular, the bill defined broadly about "any of the country", and infinitely expanded the freedom of law enforcement. It has a typical pan -political color, and the uncertainty faced by enterprises in various countries has greatly increased.
Gu Wenjun believes that under a series of combinations in the United States, the traditional market -oriented competition model of semiconductor will change. The semiconductor industry will develop from globalization, cooperation, division of labor to multi -regional, multi -ecological, and competitive development. Under a series of measures such as the "Chip Act", the expansion and development logic of international enterprises will consider more political factors, followed by market, efficiency and cost.
Before and after the signing of the "Chip Act", a number of American semiconductor companies have announced that they will expand their investment in the local area. Micron announced on the 9th that it will invest 40 billion US dollars in the United States by 2030, and this operation will be supported by the "Chip Act". Reuters reported on the 8th that Qualcomm had agreed to buy an additional $ 4.2 billion semiconductor chip worth $ 4.2 billion from the chip manufacturer's core, so that the total purchase volume by 2028 reached $ 7.4 billion.
Gu Wenjun said that the "Chip Act" intends to accelerate the construction of local semiconductor manufacturing. On the one hand, it supports the existing leading local manufacturing leaders, and on the other hand, it attracts more international companies to increase investment in the United States. This will distract the investment of international enterprises in the Chinese market, affect many aspects such as funds and talents, and then affect China's ability to obtain international resources. Earlier, international companies' layout in China is the industrial chain layout. Now it may only use China as the end market to restrict the sale of certain products. When China has shifted from R & D and manufacturing to after -sales and services in the layout of international semiconductor enterprises, the value played by China's semiconductor industry will decline, and the right to speak in the global semiconductor industry will also decrease.
Li Yan, an associate researcher at the American Institute of Modern International Relations, believes that the "chip bill" provides more international cooperation and negotiation chips for the United States. After passing the "Chip Act", the United States may also accelerate the construction of the so -called "chip Quartet Alliance", and use industrial subsidies and market access as chips as chips to draw relevant parties in South Korea, Japan, and Taiwan, to form the "backyard" of the US semiconductor industry Essence
How much influence? It is difficult for the United States to achieve the purpose of recovering the industry's dominance
Li Yan told the Global Times reporter that although the "chip bill" will play a certain role, it remains to be observed whether it can really change the global semiconductor pattern. He believes that there are several limitations of the "chip bill", such as underestimating the difficulty of the chip industry transfer and reconstruction.
Li Yan said that the US markets predict that more than $ 50 billion in funds provided by the Chip Act can basically basically meet the construction of factories in Intel, Samsung and TSMC, and cannot support the overall industrial chain from upstream to downstream. Some of these key SMEs cannot be supported by the US "Chip Act", so they will not transfer their layout. At the same time, the United States obviously estimates the necessary support factors such as talents, labor, logistics, and energy required for the transfer of the semiconductor industry chain. The United States has a significant insufficient in the above -mentioned fields and faces the contradiction between supply and demand disorders.
Some studies have pointed out that the establishment of a completely self -sufficient local semiconductor supply chain requires at least $ 1 trillion in early investment, and the "chip bill" directly invests in more than 50 billion U.S. dollars in the semiconductor manufacturing field for the entire industry. When TSMC spokesman Sun Youwen recently participated in an online discussion, he said, "The money spent for the construction capacity is really not so meaningful. 52 billion US dollars are really not a lot of money. What is the use of $ 52 billion in capital expenditure during the year? "All parties, including American scholars, also expressed doubts about the" chip bill ". Associate Professor of Indiana University in the United States Recently wrote on the Washington Post that the "chip bill" is "expensive fool" or an effective innovation catalyst, depending on project management, but it is unlikely to prevent American companies from continuing to continue to China in China in China itself in production.
The US CNBC website commented that the establishment of a chip factory is a long process that attracts the talents needed for new factories. Common regulations, labor costs and other obstacles in the US manufacturing industry may further slow down the process and timetable of American companies' production of local chips.
Li Yan also pointed out that the United States also underestimated the basic facts of international competition and interests in the semiconductor industry. The global semiconductor industry today is significantly different from the US -Japan hegemony in the 1990s. Due to the complex chip manufacturing process, semiconductor companies generally use multinational cooperation to play a comparative advantage to reduce production costs. The "chip bill" or "chip Quartet alliance" in the United States is not enough to change the realistic situation of highly dispersed and mutually dependence of the global semiconductor industry, so it cannot achieve the purpose of recovering the leadership of the semiconductor industry.
The US Think Tank Strategic International Research Center also analyzes that in the global value chain of complex and highly dependent, the US and China semiconductor companies have long been deeply integrated, and the supply chain must be fully localized and will pay huge economic and technical costs. Therefore, the global semiconductor industry is very unrealistic.
According to institutions such as Boston Consulting, if Washington adopts a "technical hard decoupling" policy, it may harm the interests of some American semiconductor companies, which may lose 18%of global market share and 37%income and reduce 15,000 to 40,000 high -skilled jobs. In other words, the subsidy provided by the "Chip Act" is likely to not be able to make up for the cost of the semiconductor company to move the factory from China to the United States.
Global Times-Global Network Zhao Jueyi
- END -
"Plastic lawns" in the UK, experts warn: "artificial fake grass" will lead to increased plastic waste

[Global Times Comprehensive Report] Fake lawn is currently popular in the garden o...
A long black birthmark of a cat eye in Indonesia resembles the masked Xia Zoro

According to the British Mirror report, recently, a cat with amazing similarities ...