Data | 55 million people around the world are losing their memory. Can the drug be saved?
Author:Nju trendy Time:2022.09.21
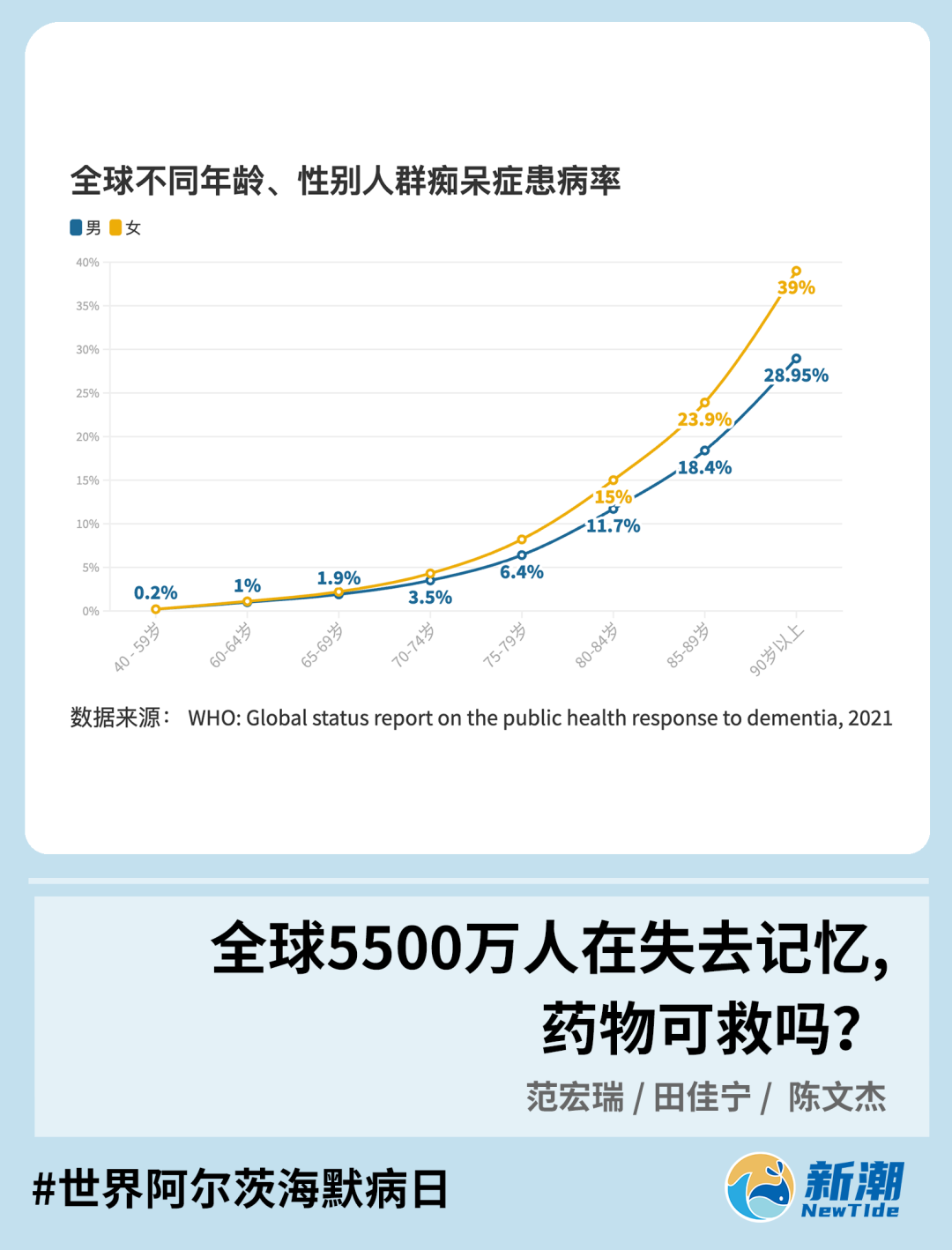
Photo | Future Editorial Department · New Wide Student
Fan Hongrui Tian Jianing Chen Wenjie
Edit | Ke Xinyu
Instructor | Bai Jingjing
If people's memory is a cup of water, Alzheimer's disease is like constantly shaking the hand of this glass of water. At first, it was only the upper -level memory that was poured, and then the water in the cup was gradually exhausted.
Today, Alzheimer's disease is the most common dementia among people over the age of 65, accounting for about 60%-70%of the patients.
More and more people are losing memory
In 1910, Alzheimer's disease was formally affirmed by the medical community and named it for his doctor Eros Alzheimer. Alzheimer's disease is a type of dementia, and the latter is also known as "major neuropia cognitive disorder". It is not a specific disease, but it can seriously affect memory, behavior, thinking, and social abilities. A person's daily life and social autonomy.
After spontaneous Alzheimer's disease, more and more "unknown dementia" patients were diagnosed with Alzheimer's disease. They will slowly lose their memory and energy, and farther away from their familiar life.
According to the "2021 World Alzheimer's Disease Report" published by the International Alzheimer's Disease International (ADI), Alzheimer's disease is currently the seventh cause of death in the world. In 2020, more than 55 million people around the world were diagnosed with this disease. It is expected that by 2050, global dementia patients will exceed 150 million, most of which are Alzheimer's patients.
According to the statistics of WHO, the number of patients with Alzheimer's disease is incomplete. The older the age, the more patients are.
Due to the differences in medical level and the degree of cognition of the disease, the number of patients will actually be more. According to ADI CEO Paola Barbarino, Paola Barbarino estimates that there may be less than 25%of those who have been diagnosed with Alzheimer in the world. In low -income countries, this ratio may be as low as 10%as low as 10% Essence If this ratio is estimated, there may now be more than 200 million patients with Alzheimer's disease, which means that more than one of each of them is more sick.
The number of Alzheimer's patients in my country accounted for one -fifth of the world's confirmed diagnosis, ranking first in the world. The "China Alzheimer Disease Report 2021" jointly released by Shanghai Ruijin Hospital and Fudan University School of Public Health shows that there are 264 million people over 60 years of age, including 9.83 million patients with Alzheimer's disease. More than three elderly people suffer from Alzheimer's disease. In addition, the papers released in 2019 in "Liu Ye Dao" showed that Alzheimer's disease and other dementia have jumped into the fifth cause of the Chinese population. At present, the domestic diagnosis rate is still rising. The paper shows that by 2050, the number of patients in China will exceed 40 million, and the annual treatment cost will reach US $ 188,818 billion.
Pharmaceutical research and development: a long battle
In order to fight Alzheimer's disease, drug research and development has become the common goal of government, scientists and pharmaceutical companies. In fact, this is a long battle.
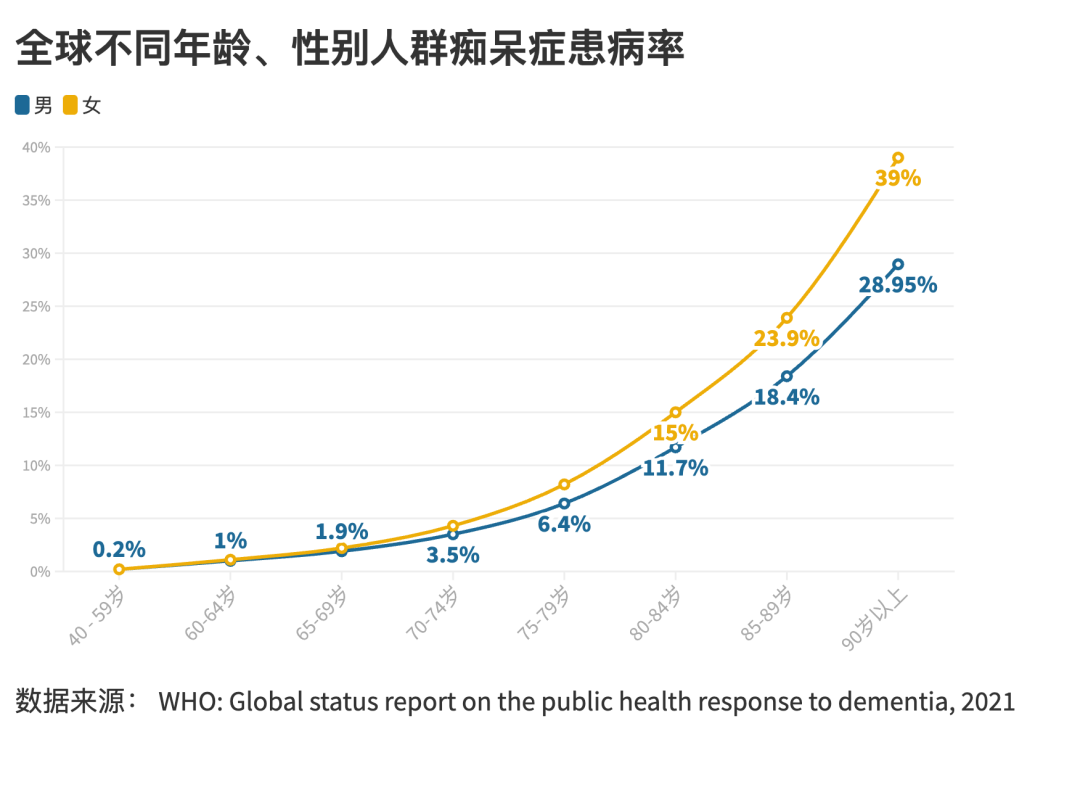
After continuous exploration, the medical community has proposed a variety of hypothesis, with different targets as the goal, trying to develop a drug that can treat Alzheimer's disease. Target is the binding site of the drug in the body, including genetic sites, receptors, enzymes, ionic channels, nucleic acid and other biomargers.
According to different hypotheses of Alzheimer's disease, the targets of drug development are also different. A variety of drugs developed according to different target types are conducting clinical trials at the same time, in which neurotransmitter receptors, β amyloid proteins, TAU proteins, etc. are mainly.
The so -called neurotransmitters are a type of chemical that transmits information between neurons. When specific neurotransmitted production is reduced, it may cause memory disorders and cognitive decline.
Acetylcholine (ACH) is a neurotransmitter. Turkhus from John Hopkins University found in a corpse test against Alzheimer's patients that the patient's brain lost a large number of neurons to produce acetylcholine, which led to "choline hypothesis" -s use Add acetylcholine to try to treat Alzheimer's disease.
At the beginning, researchers tried to add acetylcholine to their diet, or directly applied acetylcholine to the human body, but did not improve the cognitive ability of experimental objects. This is because the "acetylcholine enzyme (ACHE)" produced in the human brain breaks down the acetylcholine. Therefore, the researchers believe that as long as they directly inhibit the generation of ACHE, they can make acetylcholine in the human body more long, and this may improve the cognitive manifestations of mental patients such as Alzheimer's disease. Based on this hypothesis, people have developed many ACHE inhibitors to treat Alzheimer's disease.
In 1986, HUPERZINE A, which was extracted from snake -footed stone fir from the snake -footed stone fir in 1986, was an ACHE inhibitor. The approved drugs in China include galantamine hydrobromide, Rivastigmine Tartrate, Rivastigmine, and Donepezil Hydrochiloride. It is a pity that this method "treats the standards and not the root cause" can only be used to improve the patient's cognitive performance. If you want to treat Alzheimer's disease, you may need to start with the plaques in the brain.
The abnormal plaques observed by Dr. Eroos Alzheimer in the patient's brain slices provided clues to find the cause and treatment of Alzheimer's disease. In 1927, the academic community determined that these plaques were "starch protein". Just like its name, this protein is like starch. It accumulates in the patient's brain, forming plaques, which will affect neural activity.
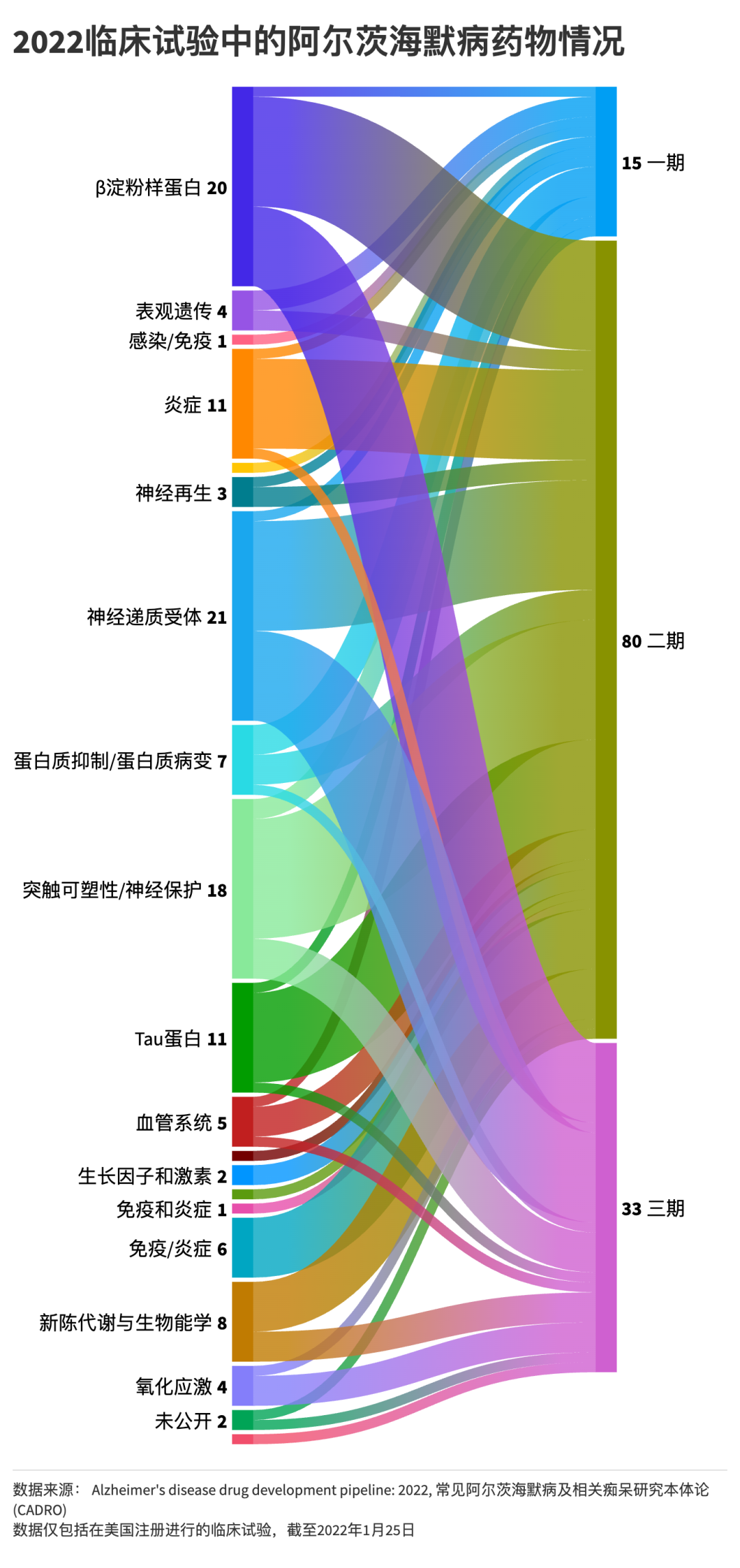
Scientists have proposed a variety of assumptions on the cause of amyloid protein. The most persuasive is "β-starch-like protein-grade hypothesis". This hypothesis believes that genes or other factors have led to the formation of β-starch-like proteins in the brain, and gradually accumulation to form primary fibers, causing neurons to die.
Once this hypothesis was proposed, it became the mainstream of Alzheimer's study. Although it is still unable to solve many difficult problems, the cause of Alzheimer's disease is the most convincing. Today, among Alzheimer's related papers, the number of papers on β-starch-like protein is the largest.
However, the development of β-starch protein drugs failed in succession, and people gradually switched to another brain characteristic "TAU protein" of Alzheimer's patients.
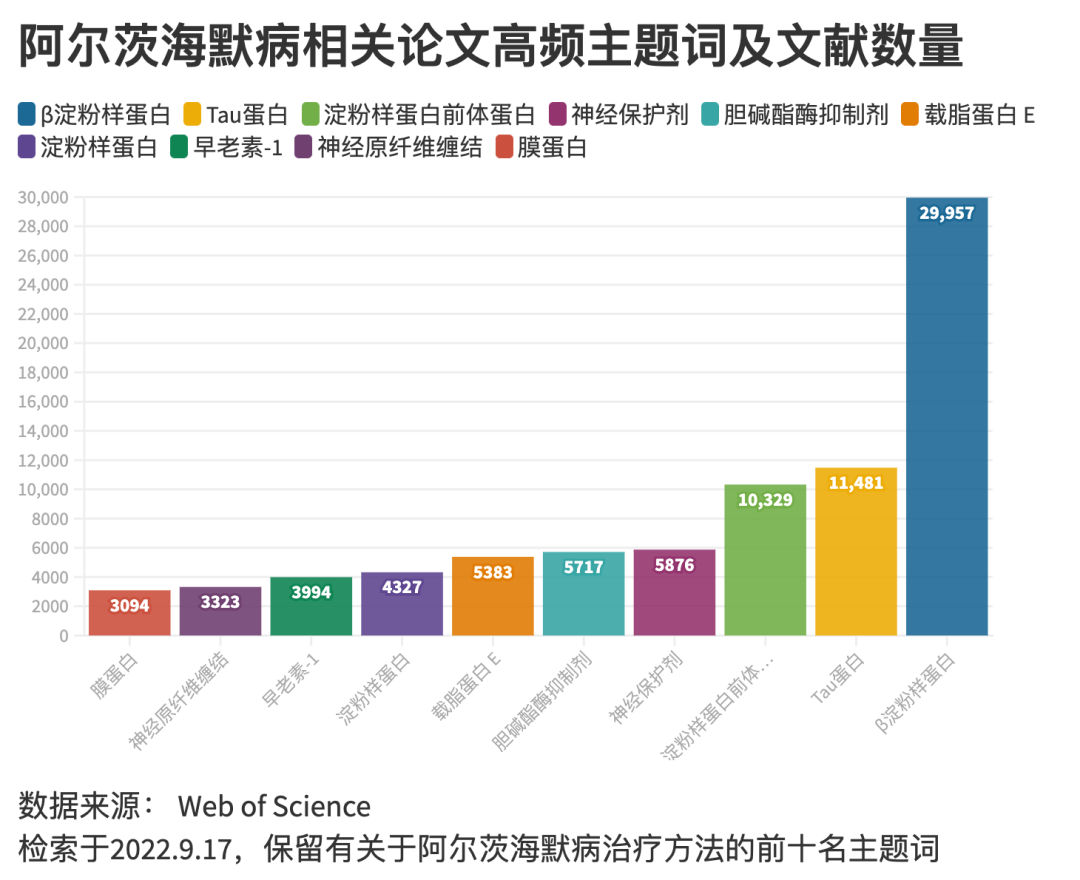
Scientists have found that, in addition to the accumulated β-amyloid-like protein, there are generally blurred clusters in the brain of Alzheimer's patients. Packing, eventually named it "TAU protein".
Different from the β-starch-like protein that has not been determined, the "TAU protein hypothesis" has clearly discovered the function of TAU protein: it will combine with the microtubquine in the brain and stabilize them. Once the TAU protein fails, the microtubules will weaken, and then the axis collapse, the brain signal is stopped, causing cognitive recession. The hypothesis believes that this is the real cause of Alzheimer's disease.
At present, TAU protein and β-starch protein have become the two major pathological symbols of Alzheimer's disease. Under the leadership of these two mainstream hypotheses, the medical community successfully developed an imaging diagnostic agent of Alzheimer's disease through many clinical trials for more comprehensive assessment of patients.
But unfortunately, the above two theories are just "hypothesis". At present, the medical community has not fully grasped the cause of Alzheimer's disease, and has not found the appropriate drug or treatment method to cure Alzheimer's disease. It can only take treatment measures to relieve symptoms and delay the development of the disease.
At the same time, the development of drugs has also been repeatedly frustrated in clinical trials. According to reports, from 1998 to 2017, 146 Alzheimer's drugs in the world announced failure during the clinical trial stage. In the 1355 clinical trial records included in clinical trial database developed by the National Medical Library (NML) and the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA), 155 records were shown in the 1355 clinical trial records included in the 1355 clinical trial records, which shows that it should be "terminated". Drugs may have high risk of death or invalid for Alzheimer's disease.
In the long and twisted research and development history of Alzheimer's disease, the research and development of the vaccine "Solanezumab" was highly hoped, but eventually ended in failure.
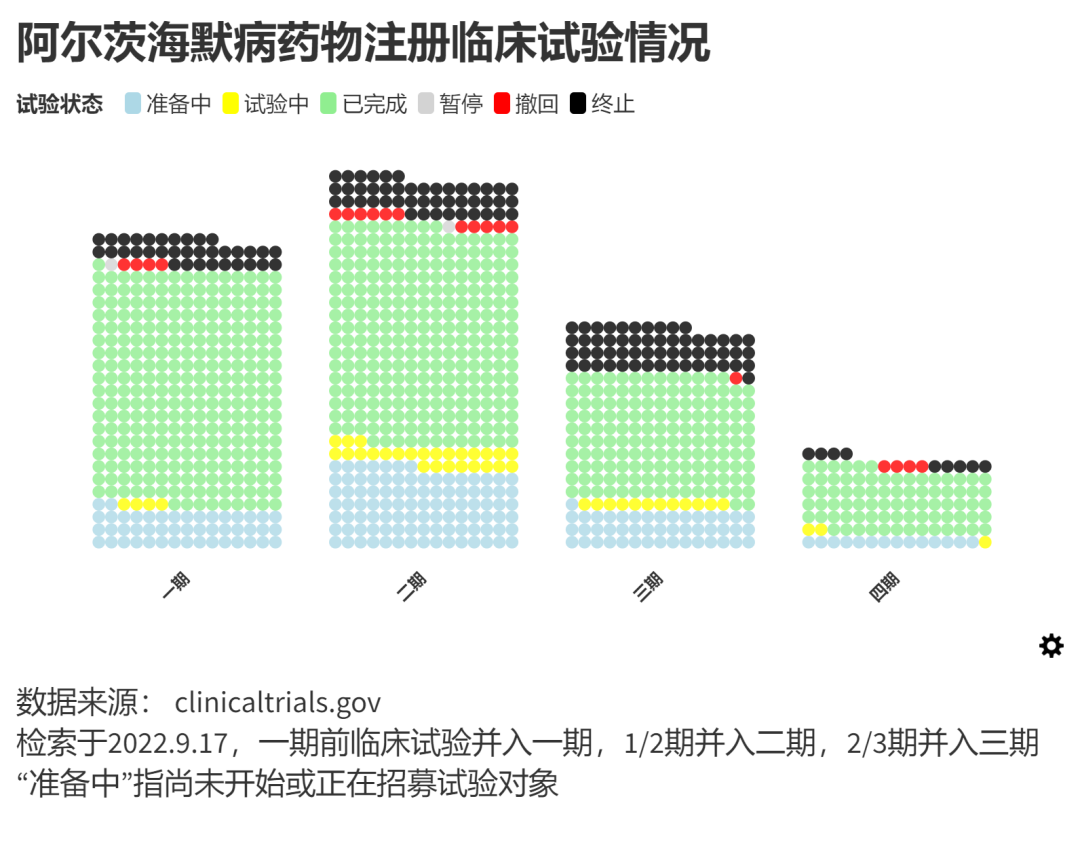
As a β-starch-like protein antibody, the performance of "Sora bead monoclonal" in cells and animal research is very exciting: it is like a drainage port that brings together β-amyloidin, and from the brain of the experimental rat's brain The ministry cleared and improved their memory. However, the test results of "Sora Zhuzab" for the human body are disappointing. In human experiments, the performance of the "Sorazab" recipient is the same as the placebo receptionist. Its R & D company subsequently abandoned the development of the "Sorazab" vaccine.
People still failed to wait for this long -awaited "medical miracle". From 2003 to 2019, there was no new medicine in the field of Alzheimer's disease. Until November 2, 2019, the National Drug Administration of China announced that it would be conditional to approve the listing application of the man-dewed sodium capsule (GV-971, also known as the "Nine Phase 1"). Original innovative medicine was included in medical insurance in December 2021. However, the medical community has always had objections to the therapeutic effect of "Ganlu Sodium".
In 2021, the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved the ADucanumab (ADUCANUMAB) through the rapid approval channel. This is the first time that FDA approves new drugs for Alzheimer's disease after 18 years. However, the listing of Adukani monoclonal resistance is also controversial. It has side effects and has not passed the entire approval of FDA review experts. On April 22, 2022, Bo Jian, a drug developer, announced that it decided to withdraw an application for listing in Europe. Until now, there are less than ten Alzheimer's drugs who have passed layers of experiments and successfully applied for listing, most of them are targeted at symptoms rather than disease.
Alzheimer's disease and future
In recent years, more than one hundred drugs against Alzheimer's disease each year are undergoing clinical trials, and various fields are continuously exploring. This is a long battle. Some of the drugs have experienced many clinical trials, but they are still improving therapy and adjusting dosage, trying to improve the test results, and promote drug development. These drugs will become the hope of patients with Alzheimer's disease and their families around the world.
"World Alzheimer's Report 2021" called for the global health care system to conduct annual brain health examination for people over 50 years old. Governments of various countries must screen Alzheimer's patients as soon as possible to deal with early interventional treatment of nerve retreats, delay the loss of cognitive functions, to respond to the increase in global population aging and medical services.
But in this battle, in addition to the government, pharmaceutical companies, scientists, and Alzheimer, there are also all of us. Before a drug that can truly treat Alzheimer's disease, we are the best potion to help patients fight against this dual battle of physiology and psychology.
Shanghai's "post -70s" female writer Xue Shu recorded the time of his father within two years after his father's illness. Father, who has decreased sharply in intelligence, memory, and self -care, can no longer identify everyone around him. But they still accompany him every day, talk to him, take him out for a walk, and help him repair his hair and hair ... Xue Shu said: "Except for this family, this was from a wife, and a pair of children. He has nothing to make up the home. "
In fact, with the acceleration of the aging of society and the youth, more and more people around them suffer from Alzheimer's disease, but the disease propaganda and popularization are far behind. In the face of Alzheimer's patients, what kind of values should we have and what measures we should take are particularly important.
September 21st every year is the day of Alzheimer's disease. The theme of this year is "Knowing and Preventing Early Wisdom -Working to the Future." Although the course of the development of drugs is still long, as long as we join hands, knowing the confidant, early preventing and early wisdom, we can better protect the valuable memories of tens of thousands of patients' families.
8. Xue Shu. People who go far 2015 [M]. Shanghai Culture Press Helping Family and FRIENDS UNDERSTAND ALZHEIMER's Disease (National Institute on Aging of Nih)
Recommendation
Documentary | Consultation: "Professional Patient Family"
Photography | The first day of welcoming the new day of the Nanda Drum Tower Campus

Video | Freshman Finding: What do NJUER want to do on the lawn in front of the North Building?


- END -
Chengdu Primary and Middle School Online Teaching First Day: The principal incarnates the "anchor" of the Internet
On the first day of online teaching in Chengdu Elementary and Middle Schools, the principal incarnate into the Internet anchor and the students gathered in the cloudsThe Chengdu Education Bureau iss
Qiqihar City held the 15th press conference of the epidemic prevention and control work

On the morning of August 21st, Qiqihar City News Office held the fifteenth press c...