[2022 ESMO] Broken cocoon into a butterfly, born to new | Professor Wang Zhijie: EGFR EX20INS non -small cell lung cancer treatment field adds new certificates!
Author:Cancer Channel of the Medical Time:2022.09.16
*For medical professionals for reading reference
With the development of precision medicine, the treatment of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutation of non -small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) has gained a huge leap. Among them The patient's chronic disease management model is "from ideal to reality." However, in the EGFR mutation NSCLC, EGFR 20 outer signs (EGFR EX20INS) mutations are the third largest EGFR mutation type after 19DEL and 21 L858R mutations, but it has always been a difficult problem for clinicians. [1] At the European Internal Science Society (ESMO) in 2022, a number of new progress in the field of EGFR EX20Ins made a stunning appearance, causing the academic attention. In response, Professor Wang Zhijie Wang Zhijie of the Cancer Hospital of the Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences was invited to share the current status of the EGFR EX20INS mutation NSCLC and comment on new progress in the field.
Li Bing horses, the first test is sharp: amivantamab and Mobocertinib challenge EGFR EX20INS mutations NSCLC
EGFR EX20INS mutations NSCLC, as a type of refractory disease, chemotherapy, immunotherapy, and traditional EGFR-TKI are not ideal, and new therapy is urgently needed to "break the deadlock". With the rapid development of medical technology, various new drugs/new therapies have emerged endlessly. Among them, double -specific antibody AMIVANTAMAB and small molecular TKI drugs Mobocertinib stood out.
The I/IB phase of Chrysalis studied evaluated the efficacy and safety of AMIVANTAMAB to treat the EGFR EXON20INS mutant NSCLC patients after the progress of platinum -containing chemotherapy. Data show that the overall objective relief rate (ORR) is 40%, the median without progress (MPFS) is 8.3 months, the median total survival period (MOS) is 22.8 months, and the adverse events (AE) are mostly 1- Level 2 [2]. Therefore, in May 2021, the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) accelerated the listing of Amivantamab. Mobocertinib was mainly based on EXCLAIM research by FDA. Patients with platinum chemotherapy EGFR EXON20INS mutations use Mobocertinib after using Mobocertinib, the ORR confirmed by the Independent Review Committee (IRC) is 28%, the MPFS is 7.3 months, and the MOS is 24 months. The safety characteristics are gastrointestinal tract and skin. Bad events [3].
In order to further evaluate the efficacy and safety of the two drugs, some researchers used non -anchored matching to adjust the indirect comparison (MAIC) analysis method to compare the efficacy of Mobocertinib (from EXCLAIM Studies) and AMIVANTAMAB (research from Chrysalis). The research results were disclosed at the ASCO and ISPOR conference in 2022. The results released by ASCO show that Mobocertinib and Amivantamab seem to have a general similar effect [4].
Table 1: ISPOR MAIC indirect comparative efficacy data
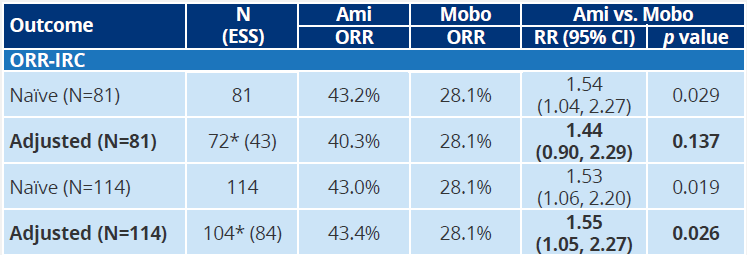
In terms of security, the data released by 2022ispor found that although the incidence of two drugs in any level of TRAE is similar, amivantamab is significantly lower than the risk of TRAE, ≥3 TeaE, ≥3 TRAE and SAE in the reduced dose than that of the decreased dose. Mobocertinib [5].
Table 2: ISPOR MAIC indirect security data
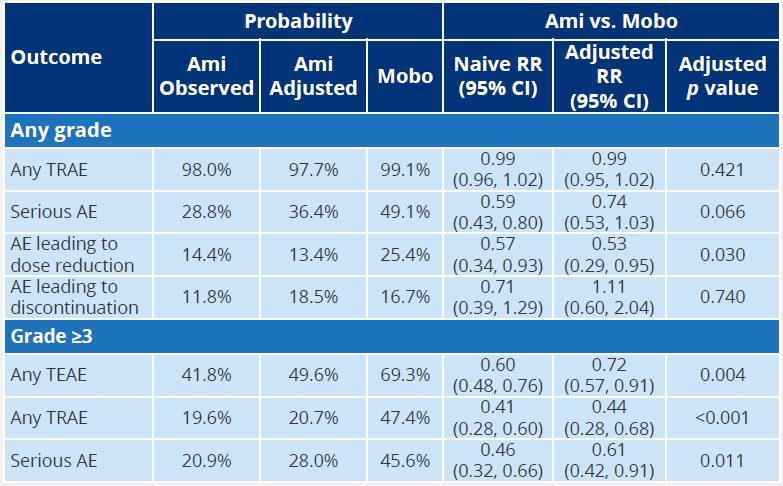
Of course, AMIVANTAMAB will also have AE in infusion reactions, but the level of these adverse reactions is mostly 1-2 [5]. In summary, how to choose a more suitable treatment plan for patients is still worth further exploration.
Surprisingly, and then reported: a number of real world research appeared in ESMO, helping EGFR EX20INS mutations NSCLC to treat "one arm force"
Phase I/II phase Chrysalis studies confirmed that amivantamab treats EGFR EX20INS mutations later NSCLC has a long -lasting relief. In order to further compare the efficacy of AMIVANTAMAB and the current systemic treatment solution in the real world, researchers have carried out a research on AMIVANTAMAB compared to the real world of Japan (RW) treatment schemes for EGFR EX20INS mutations (Poster 1115P) [6].
Research method: The study indirectly compared the efficacy of the EGFR EX20INS mutation late NSCLC patients with different system treatment solutions (including OS, PFS, and ORR). Among them, (AMI group) data for AMIVANTAMAB (AMI group) data from chrysalis studies; RW treatment scheme (external control group) data from the Asian Lung Cancer Genome Monitoring Platform (LC-SCRUM-ASIA). The EGFR EX20INS mutant of the EGFR EX20Inos mutation of the EGFR EX20Inos of the Sai (DOC)/tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI). The tendency scoring weighted method balances different groups of different groups (age, gender, smoking status, and previous treatment lines). Research results: The ORR of patients in the AMI group is significantly better than the ORR of the external control group (including DOC, TKI, IO) (as shown below).
Table 3: Accept the ORR of AMIVANTAMAB and DOC/TKI/IO for patients
In addition, compared with patients receiving TKI and IO, patients receiving AMIVANTAMAB are longer OS and PFS.
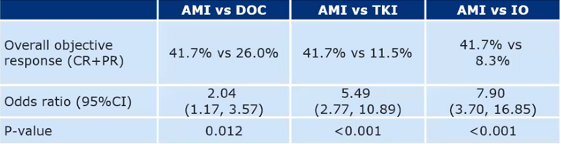
Figure 1: Accept OS (A) and PFS (B) of AMIVANTAMAB and DOC treatment patients
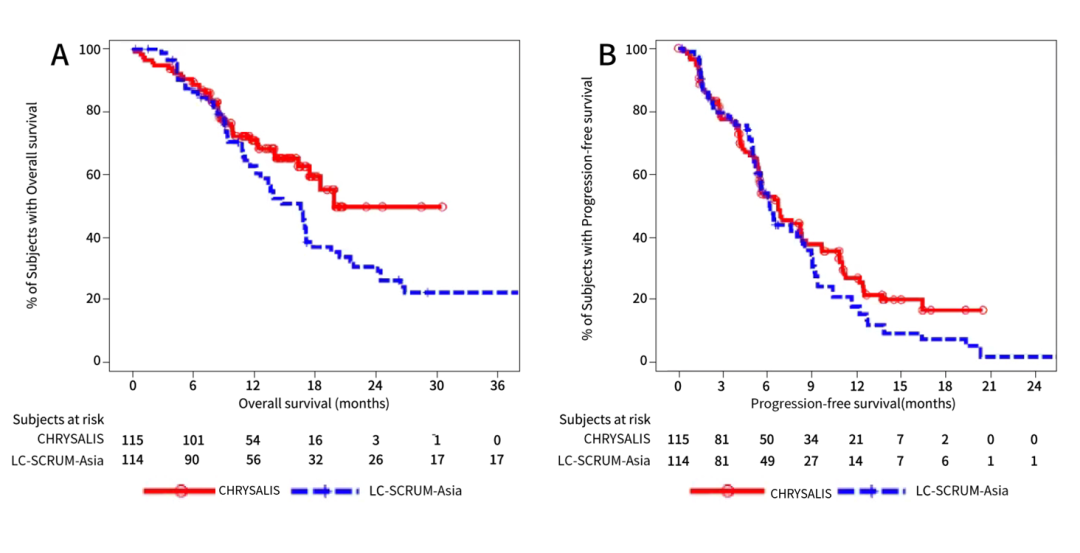
Figure 2: Accept OS (A) and PFS (B) of AMIVANTAMAB and TKI treatment patients
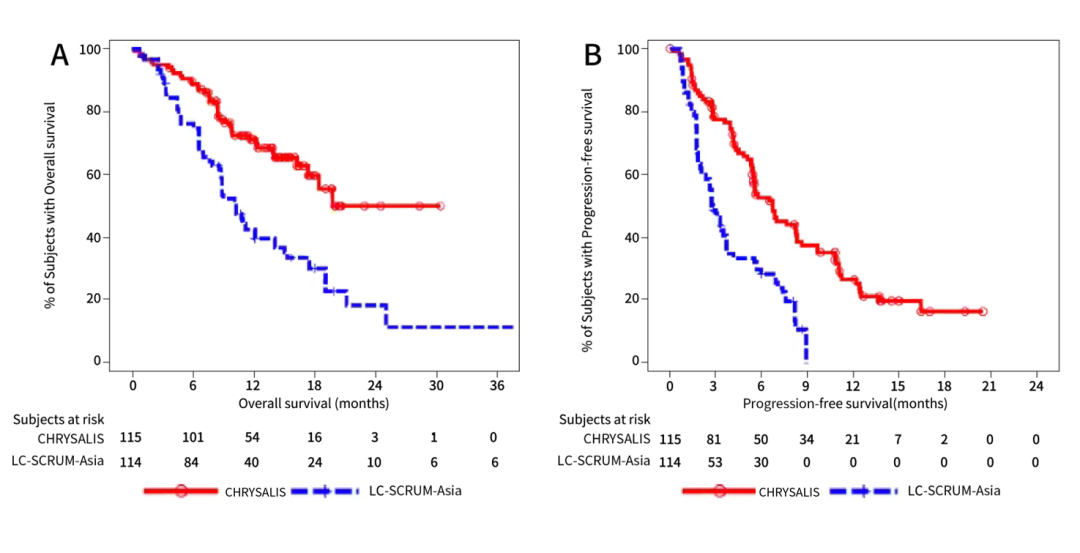
Figure 3: Accept OS (A) and PFS (B) of AMIVANTAMAB and IO treatment patients

In summary, when the lack of evidence of random test, this study provides the efficacy comparative evidence of AMIVANTAMAB and the real world treatment plan. For patients with EGFR EX20INS mutations in the failure of platinum chemotherapy, amivantamab is an effective treatment option. Essence
Coincidentally, this year's ESMO conference also reported another AMIVANTAMAB compared to the research of EGFR EX20INS mutations (Poster 1109P) for EGFR EX20Ins. [7]. Amivantamab's related data also comes from Chrysalis Studies (the deadline for March 2021). The external control (EC group) data comes from the LC-Scrum-Asia screened by Platinum chemotherapy. Looking back on sexual analysis. The difference is that the research aims to evaluate all of the use of AMIVANTAMAB as well as OS, PFS, and converted to the next treatment time (TTNT) and ORR of Asian patients and Japanese EC data. Data show that compared with the external control group, the AMI group (all and Asian patients) have longer OS, PFS, TTNT, and ORR advantages are obvious. Among all patients, the ORR of the AMI group and the external control group was 41.7% VS 14.1% (P <0.001); the median PFS was 6.7 months VS 4.7 months (HR = 0.59, 95% CI 0.45-0.78) ; The median OS is 19.9 months VS 14.1 months (HR = 0.59, 95% CI 0.40-0.88); the median TTNT is 12.2 months vs 5.1 months (HR = 0.39, 95% CI 0.29-0.53) Essence Analysis of data from Asian patients found that the AMI group also has clinical advantages.
In addition to Japanese research, this time ESMO also announced the results of many other European real world research. Among them, an AMIVANTAMAB compared to the European Real World Standard Treatment Plan (SOC) for EGFR EX20INS mutations for platinum drug chemotherapy failure. During the day, the medical record data from 19 hospitals from France, Germany, Italy, the Netherlands, Portugal, Spain, and Britain will conduct the clinical ending of the AMI group (from the study of Chrysalis) and the RW SOC group (from Caterpillar-Rwe research). Comparison [8]. The results showed that the OS, PFS, and TTNTs of the AMI group were significantly and better than RW SOC.
Table 4: The results of the AMI group and the RW SoC group
Another "Poster 112P) and the" Poster 112P) of the "French real -world treatment plan for the EGFR EX20INS mutations and the II Phase II data of AMIVANTAMAB" (Poster 1122p) and the patients from the II data of AMIVANTAMAB (Poster 1122p) and the patients from the ch queen D quer of the Chrysalis test) The RWCP group (patients from the AMLC ESME database) aims to compare OS, PFS, and TTNT [9] of the two groups of patients. After the correction, the baseline characteristics of the two groups are balanced. The results showed that the OS, PFS and TTNTs of AMI groups were significantly better than the RWCP group. The median OS of the two groups is 22.8 months VS 13.0 months (HR = 0.49, 95% CI 0.29-0.82; P = 0.007); the median PFS is 6.9 months vs 5.7 months (HR = 0.56, 95, 95, 95, 95 % CI 0.37-0.85; P <0.001); the median TTNT is 12.4 months vs 7.8 months (HR = 0.48, 95% CI 0.32-0.72; P <0.001). The results of the above research show that amivantamab is an effective treatment option compared with the treatment plan used in the real world, which can significantly improve the OS, PFS and TTNT of the EGFR EX20INS mutations late NSCLC.
In addition to amivantamab data, this ESMO also announced the results of Mobocertinib related research (Poster 1111P). Among them, a real world study of a MOBOCERTINIB treatment of EGFR EX20INS mutations NSCLC was included in 556 patients from June 2020 to December 2021, which aims to evaluate MOBOCERTINIB to stop medication (TTD) for 6 months. The possibility of continuing treatment in 12 months [10]. Data show that after the patient is used, the mid -position TTD is 5.3 months. The probability of continuing treatment in 6 months and 12 months was 48%and 32%, respectively. Patients with previous treatment lines (LOT) are 1 (n = 233), and the median TTD is 5.6 months; patients with previous LOT ≥ 2 (n = 287) have a median TTD of 4.8 months. Among 287 patients, Mobocertinib was treated ≥2 courses. The TTD was 11.6 months, and the probability of continuing treatment at 69%and 46%in 6 months and 12 months. This reminder, in the real world, Mobocertinib is expected to make EGFR EX20INS mutations NSCLC patients benefit.
Expert Reviews
NSCLC is the most common subtype of lung cancer, often accompanied by EGFR mutations. EGFR EX20INS mutation is a relatively rare EGFR gene mutation. Its structure is different from the classic EGFR gene mutation. It can produce resistance to EGFR-TKI and is relatively difficult to treat. For NSCLC patients carrying EGFR EX20Ins mutations, chemotherapy, traditional EGFR-TKI, and immunotherapy are relatively limited. There are currently no uniform standardized treatment recommendations. Therefore, new treatment strategies are urgently needed to improve the ending of patient treatment.
In 2021, the US FDA was approved by AMIVANTAMAB and Mobocertinib to treat the crowd. Amivantamab is a humanized EGFR/C-MET dual-target dual-target special antibody, which can promote the degradation of receptor-antibody complexes by binding the outer section area to give play to the treatment. Like other new drugs, AMIVANTAMAB related studies are also tried to first try back -line treatment after the failure of the first -line standard chemotherapy. Nowadays, a number of studies are configured with "external controls" derived from real -world data for the Chrysalis research. In this way, the EGFR EX20INS mutant NSCLC crowd after receiving the progress of platinum chemotherapy can be compared with amivantamab and existing treatment strategies. Judging from the European and Japanese data disclosed in this time, amphantamab has obvious benefits compared to real -world treatment plans, and many research results are more consistent. Among them, ORR exceeds 40%, showing good anti -tumor activity with good drugs; in terms of survival benefits, compared with external control treatment patients, OS and PFS who received AMIVANTAMAB treatment are longer. This is also consistent with the separate analysis of the real world database of the United States before. In terms of security, amivantamab is mostly 1-2 levels of AE, and good tolerance is good. The real -world data of Mobocertinib released this time shows that after the patient's medication is ≥2 courses, TTD can be extended for about 11 months, and the benefits are more obvious. Therefore, these real world research data boosted the EGFR EX20INS mutation NSCLC research to enter the "fast track", bringing new hope to patient treatment, and also looking forward to more disclosure of the results of the research.
The medical road is long, and constant search: More new drugs are explored in the challenge, moving forward in the light "
At this ESMO meeting, reports about Mobocertinib, in addition to the real world research data, also disclosed a "Mobocertinib the treatment of EGFR EX20INS mutations NSCLC stage I/II studies: update results for patients (PPP) for platinum" "" " (Poster 988P) [11]. This study consists of 3 parts: open labels, multi -center clinical studies include dose increase/expansion queue and Exclaim extension queue. The main research final is the ORR evaluated by IRC. The results showed that the orr evaluated by IRC was 28.1%, the median Dor was 15.8 months, and the mid -bit PFS was 7.3 months; the common Trams was diarrhea (92%), rash (46%), metalitis (38%),, 38%),, 38%),, 38%),, 38%),, 38%),, 38%) Subsidity (37%), nausea (34%), vomiting (32%) and dry skin (31%). ≥ 3 TRE (≥10%): diarrhea (23%); 1 patient (& 2%) was stopped due to AES: diarrhea (4%). In addition to Mobocertinib, the research data of another small molecule TKI drug Sunvozrtinib also landed on this ESMO. The results showed that no matter what kind of treatment was accepted, Sunvozertinib was used for EGFR EX20INS mutations NSCLC patients (Poster 987P) [12]. As of July 30, 2021, a total of 110 patients with NSCLC with EGFR or HER2 mutations were included in the study (from WU-Kong1 and Wu-Kong2 studies), of which 56 were mutations with EGFR EXON20INS.在疗效分析集中,患者既往接受了1-10线治疗,包括铂类化疗(52例,92.9%),EGFR-TKIs(25例,44.6%),PD(L)-1抑制剂(17例, 30.4%), and other therapies. PR is observed at the dose level of 100 mg-400 mg (maximum tolerance, MTD). Researchers are consistent with ORR evaluated by IRC. No matter what kind of treatment was received, patients have anti -tumor activity. In the past, the security of platinum chemotherapy, EGFR-TKI or PD (L) -1 inhibitors did not affect the security of Sunvozertinib.
Expert Reviews
A targeted new drug research and development of EGFR EX20INS mutations NSCLC has become a hot spot in recent years. From traditional EGFR-TKI to Sunvozertinib reported at this year's ESMO conference [9-12] However, the current information shows that the traditional EGFR-TKI has limited efficacy of the EGFR EX20INS mutation NSCLC. The new targeting drugs brought the dawn of the treatment for patients. However, whether these drugs can bring better prognosis to such patients still need More studies are demonstrated. The efficacy data of Sunvozertinib is currently effective in the targeted drugs of the EGFR EX20INS mutation NSCLC. Its adverse reactions are also easy to tolerate after dose adjustment, but more large sample clinical trials still need to be verified. In addition to Mobocertinib and Sunvozertinib, other new drugs (such as CLN-081, etc.) are also underway. Who can go further and need to compete from more dimensions, if the size of the adverse reaction; how to control the control of the brain metastases; Good medication convenience and compliance. Looking forward to not far, EGFR EX20INS mutations NSCLC treatment can also usher in "spring".
references:
[1].Heather Burnett, Helena Emich, Chris Carroll, et al. Epidemiological and clinical burden of EGFR Exon 20 insertion in advanced non-small cell lung cancer: A systematic literature review[J]. PLoS One. 2021;16(3 ): E0247620.
[2] .amivantamab in Combination with Chemotherapy in Patients with Advanced Non-Small Cell LUNG CANCER (NSCLC). WCLC2021.ABS P50.04.

[3].Mobocertinib in NSCLC with EGFR Exon 20 Insertions: Results from Exclaim and Platinum-Pretreated Patient Populations. WCLC2020. OA04.03.[4].Matching-adjusted indirect comparison (MAIC) of mobocertinib versus amivantamab in patients with non– Small Cell LUNG CANCER (NSCLC) with EGFR EXON 20 Insertions (ex20ins). ASCO2022.ABS 9115.
[5]. Matching-Adjusted Indirect Comparison of Amivantamab vs. Mobocertinib in EGFR EXON 20 Insertion-Mutated Non-Small Cell LUNG CANGER. Ispor2022. ABS 115347. ABS 115347.
[6].Amivantamab vs Real World (RW) Therapies for Advances Non-Small cell Lung Cancer(aNSCLC)with Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR) Exon 20 insertion Mutation (E20i) in Japan. ESMO2022.Abs 1115P.
[7] .Amivantamab vs Real World (RW) Therapies in Japan Patients with Advanced Non-Small Cell Luna Cancer (ANSCLC) Epidermal Growth Factor (EGFR) EXO9.3Smral23Smewsm.
[8].Amivantamab compared with European,real-world (RW) standard of care (SoC) in adults with advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) with activating epidermal growth factor (EGFR) Exon 20 insertion mutations (Exon20ins) after Failure of Platinum-Based Therapy. ESMO2022.ABS 1117p.
[9] .An Adiusted Comparison of Amivantamab Phase II Data Versus Real-World Clinical Manaements
[10].Real-world treatment duration in patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) with EGFR exon 20 insertion (EGFRex20ins) mutations receiving mobocertinib through the global Expanded Access Program (EAP). ESMO2022.Abs 1111P.
With EGFR EXON 20 Insertion Mutations. ESMO2022.ABS 987p.
Document number: EM-110395 Approved Date: 2022-09-15
*This article is only used to provide scientific information to medical people, and does not represent the viewpoint of this platform


- END -
From 18:00 on September 6th to 18:00 on September 7th, there are no new local new crown virus -positive infections in our city | This round of epidemic is Omikon BA.5.2 mutant strains.
On September 7, the Harbin Municipal Government News Office held a press conferenc...
Beijing: From 0:00 to 15:00 today, there are 3 cases of new local new crown pneumonia virus infections, 2 cases of Daxing, and 1 case of Chaoyang
On August 27th, at the 390th press conference of the prevention and control of the new coronary virus pneumonia in Beijing, Liu Xiaofeng, deputy director of the Municipal Centers for Disease Control a