New mechanism for stereotypes to regulate emotions
Author:Bioart biological art Time:2022.09.11

Responsible editor | Xi
#Neuroscience and brain science#
The body-oriented stereotypes (BODY-FOCUSED Repetitive BehaviViors (BFRBS) is a common nerve and mental disease. Patients will repeatedly appear non-functional behavior for their own parts, such as repeated hair extraction, peeling and bite Fingers and other behaviors. This may be a kind of behavior -induced behavior shared by humans and animals, which aims to resist anxiety caused by pressure to reduce stress by reducing alertness or mobilizing the emotional regulation system in the brain. BFRBS patients show that anxiety relieving or having pleasure after performing stereotypes, similar to a reliable satisfaction. Although psychology believes that BFRBS behavior helps to control negative emotions, it is unclear that this kind of rings mechanism interacts between this stereotype and emotional regulation. Similar to humans, animals will significantly increase a stereotypes when facing stress, that is, self -rational behavior. At present, it is unclear how the neurons cluster that controls this kind of duplicate behavior is connected and affects the neurons cluster related to emotional regulation, and whether this stereotype repeated behavior will have a reward effect.

On September 6, 2022, a team of researcher Huang Ju in Shanghai Jiaotong University School of Medicine published an article on Neuron Magazine EXCITATORY SST Neurons in the Medial ParalemnisCal Nucleus Control Repetive Self-Grooming and Encode reward. Ring mechanism.

In this study, the research team used rodents to repeat self-through the research model as a research model to explore the neurosphere mechanism for stereotypes to regulate emotions. Researchers found that excited growth of Somatitin-POSITIVE Neurons (SSST) in the medial paradate nucleus (MPL) in the middle of the brain. The optical fiber calcium signal shows that the activity of the MPLSST neurons has a strong correlation with Mao Mao's behavior. This type of neurons will regulate the start and maintenance of the bonding behavior. Inhibiting MPLSST neurons will not only significantly reduce repeated self -rational hair under the induction of stress, but also cause damage to the ability to relieve the anxiety and relief of mice. In addition, activating MPLSST neurons is significantly associated with positive emotional costs, generate a reward effect, and drives reinforcement.
The researchers performed a spatial transcription group sequencing analysis of the brain sheet containing the MPL brain area, and found that the SST and PTH2 genes encoded the SST and PTH2 genes encoded the nerve peptide were found. The spatial transcription, fluorescent in situ hybridization, and electrical records further confirmed that the SST neuron in the MPL is the excited neuron of the release of glutamic acid, and about half of them release the neurotipptide SST and PTH2.
The input of negative emotions related to the central almond core CEA to MPLSST neurons will directly participate in the self -rational behavior induced by stress stimulation. At the same time, VTA, the stamped area of the middle brain, an important coding rewarded brain area, will accept the domination of MPLSST neurons. MPLSST neurons and VTADA neurons (DA) form excitement single -debris connections. Activating MPLSST neurons can record a large number of dopamine releases in dopamine in the downstream projection position point NAC of the downstream projection position of the VTADA neurons. By characterizing related upstream and downstream connections, the researchers have verified the important role of CEA-MPLSST-VTADA in the neurotranscene of the neurotransmid. Emotional neural circuit mechanism.
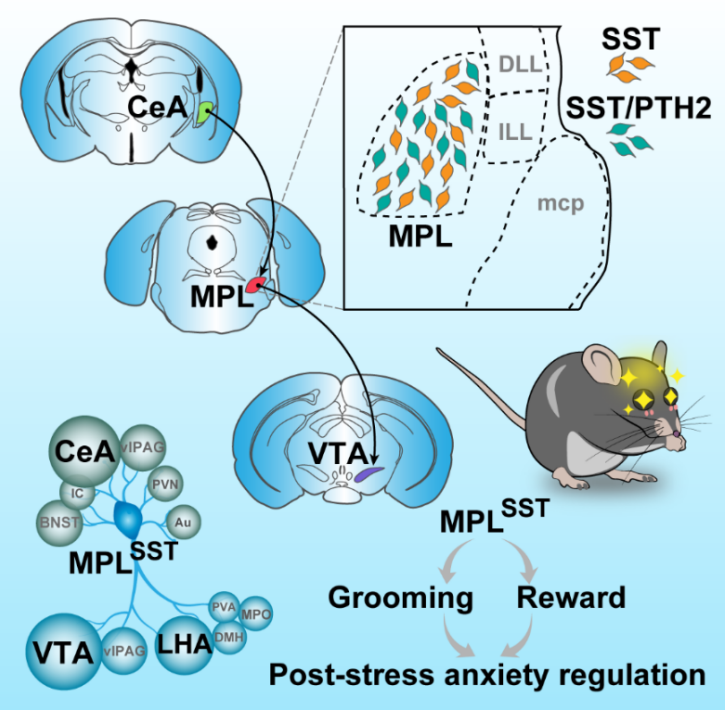
In summary, this study reveals the neurosphere mechanism that interacts between stereotypes and emotional regulation, and provides a reference for understanding the neurosphere mechanism related to human BFRBS diseases. The innovative nature of this study is reflected in: 1) discovering a neurotransurbon that controls stereotype repeated behaviors; 2) Discover neurons clusters that control stereotyped repeated behaviors at the same time; 3) found that the neuron cluster that controls the repeated behavior of repeated behaviors becomes becoming Connecting pressure and rewarding point.
Dr. Sun Jingjing, Dr. Yuan Yuan graduate student, and Dr. Wu Xiaohua were the first author of the paper. Researcher Huang Ju was the author of the communications.
In recent years, the research team of researchers in Huang Ju focused on the research on the function of instinctual behavior and emotional regulation, apparent genetic regulation, and disease -related proteins. Related research results have previously been published in Science (2018), Cell Reports (2020), and Cell Reports (2021), which provides us with a new perspective of neurological mechanism behind instinctual behavior and emotional regulation.
Original link:
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2022.08.010


- END -
Li Junjiang: Use superb medical skills to help obese patients with beautiful "butterfly changes"
Recently, Li Junjiang, director of the three ward of gastrointestinal hepatotespillary and biliary surgery of Shangqiu City, received a special child full -moon wine invitation, which was sent by Xiao
From December 1st, these medicines must not be sold on the Internet!
The State Administration of Market Supervision announced the Measures for the Supe...