How to perform effective intervention measures for elderly young muscle obesity?
Author:Popular Science Hunan Time:2022.09.11
Generally, the normal range of normal adult BMI is 1.5-23.9kg/m2, while the normal range of BMI in the age of 65 is 20.0 ~ 26.9kg/m2. Among them, the constitution index is referred to as BMI, BMI (KG/M2) = weight (kg)/height (M2), which is the most commonly used indicator and recognized standard for judging obesity. For example, Uncle Li's height and weight of 70 -year -olds are 170cm and 65kg, respectively, and the BMI value is 22.5kg/m2, which is a normal range. Well, when BMI is a normal range and does not cause less muscle obesity. The answer is negative. Figure-1 is the normal range of BMI, but the area of body fat and visceral fat is significantly higher than the normal range, but the weight of skeletal muscle and low grip is significantly lower than the normal range. Therefore, for the elderly, in addition to evaluating the appropriate BMI value, you should also pay attention to the weight and / or physical index value to determine that fat and thin must consider muscle and fat ratios, that is, body components.
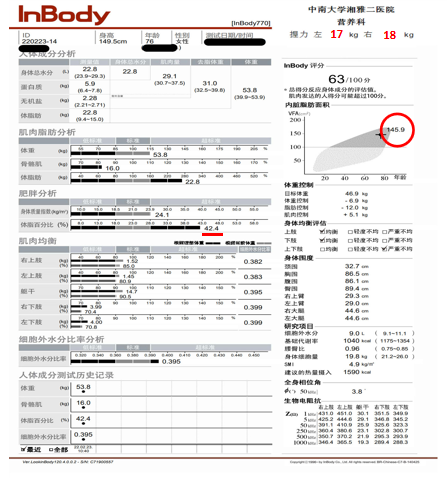

Figure -1 The elderly young muscle obesity with normal BMI values
Studies have shown that after the age of 25, the muscle weight has gradually declined. After 40 years of age, the decrease rate reaches 8%, and after 70 years of age, the decrease rate reaches 15%. Therefore, for the elderly, please do not blindly pursue low weight. Forty fat and suitable muscle mass are ideal. At present, the commonly used muscle mass detection methods mainly include dual -energy X -ray absorption measurement method (DXA). The clinical application characteristics are the first choice and widely used; biological impedance (BIA), clinical application characteristics are not directly measured, cheap, portable, portable, portable, portable, portable, portable, portable, portable, portable, portable, portable, portable, portable, portable, portable, portable, portable, portable, portable, portable, portable, portable, portable, and portable. Widely used; electronic computer fault scanners (CT) and magnetic resonance (MRI), clinical application characteristics are gold standards of non -invasive assessment, but not commonly used).
Elderly and muscle obesity refers to the common syndrome of the elderly with age -related skeletal muscle strength, decreased quality, dysfunction, and obesity. Its clinical characteristics are muscle reduction and fat increase. At present, the prevalence of low muscle obesity in the elderly in China is 4%to 20%. Today, there is no clear diagnostic standard for young muscle obesity. Most scholars believe that in different people use different methods to evaluate fat accumulation and skeletal muscle content diagnostic clues. Little muscle obesity is the result of the common effects of age, gender, disease control, lifestyle, and social family. Among them, diet and physical activity reduces a major pathogenic effect in young muscle obesity. With the increase of age, due to the decrease in diet, especially protein intake plus physical activity, muscle loss (that is, muscle reduction) plus fat increase (that is, obesity), leading to minor muscle obesity. Little muscle obesity may cause falls and fractures, metabolic diseases (diabetes, metabolic syndrome), cardiovascular disease (hypertension, heart disease, and center), and the quality of life and independence decreases, which leads to premature death.
Can young muscle obesity measure effective intervention measures? Generally, muscle mass maintenance is affected by two aspects: on the one hand, positive regulation factor (part of hormones, physical activity, and reasonable protein intake), and on the other hand, negative regulatory factor (age, partial hormone, inflammatory factor, etc.). It can be seen that the establishment of a lifestyle -based lifestyle management can promote muscle synthesis.
For obesity elderly people, the use of energy replacement diets in the short term can reduce the weight and fat of obesity, but the intake of sufficient nutrients should be ensured. Once again, it is not recommended to choose a very low energy diet, that is, the daily energy supply is ≤800 kcal. Because the elderly people have potential synthetic metabolism resistance, the elderly need higher protein intake to stimulate the synthesis of protein. It is recommended to suffer from less muscle obesity. KG.D, and diet protein should be balanced to each meal, at least 25 ~ 30g of protein per meal, which must ensure the quantity and quality to stimulate muscle protein synthesis. It is important to keep in mind that patients with kidney dysfunction are disabled. In addition, the elderly for the elderly in the elderly of the younger muscular obesity can supplement 2g (calculated in the EPA dose) N-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids or eat sea fish twice a week, 150 ~ 200g each time, but for those with hyperuricemia, pay attention Purine problem. In order to prevent the adverse effects of weight loss on bone metabolism, it is recommended to supplement 800 ~ 1000IU vitamin D per day. As far as vitamins and trace elements are concerned, it is recommended to consume 500 grams of fresh vegetables per day, 200 ~ 350 grams of fresh fruits and 15 grams of nuts. If the above -mentioned recommended intake cannot be achieved, consider 1 daily supplementary composite trace nutritional supplement. Of course, due to the limitation of the elderly, the target intake cannot be achieved, and considering the comprehensive and balanced intestinal nutritional preparations with oral or tube feeding channels.
Finally, as far as the exercise intervention strategy of less muscle obesity is concerned, the principle is to do with force, step by step, avoid bump/fall, and formulate an individualized exercise solution. Common anti -resistance exercises include stretch bands, dumbbells, sitting legs, etc.; aerobic exercise has fast walking, jogging, swimming and door balls. Because the elderly suffer from a variety of basic diseases, it is recommended to carry out appropriate exercise training programs under the guidance of exercise rehabilitation divisions.
In short, reasonable weight and good muscle conditions are the health foundation of the elderly, and good muscles maintain dependence on reasonable nutrition and scientific movements, and reasonable nutrition depends on balanced diet, high -quality protein, vitamin/trace elements, etc.Edit: Liu Qian
Popular Science Hunan specially invited correspondent: Tang Hanfen Tan Yan, Health Education Propaganda Center, Hunan Province
Popular Science Hunan special expert: Tang Hanfen, chief physician of the Department of Nutrition Department of Xiangya Second Hospital of Central South University
- END -
The latest notice of Hebei!End on October 20 ...

On August 31, the Hebei Provincial Department of Agricultural and Rural Affairs is...
[Health Hall] "Wake up the brain to prevent strokes" broadcast at 17:25 today

Expert Zhao Ruizhen: Director and Chief Physician of the Third Affiliated Hospital...