Good medicines first, worry -free -Osicinib first -line treatment has benefited more, and multiple drug resistance mechanisms have solved solutions!
Author:Cancer Channel of the Medical Time:2022.09.06
*For medical professionals for reading reference
In -depth analysis of Osicinini -to -line treatment mechanism and solution, so that the first -tier treatment is "worry -free."
In recent years, with the development of precision medicine, more and more lung cancer -driven genes have been discovered. Among them, EGFR mutations are the most common driving gene mutations in patients with non -small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) in my country, existing about half of patients. Fortunately, the emergence of EGFR-TKI has brought hope for long-term survival to patients with late NSCLC patients in EGFR mutations. Especially the three generations of EGFR-TKI Oshitinib can not only be used for the first/second-generation EGFR-TKI resistance, but also set up a new standard for the first-line NSCLC treatment of EGFR mutations for the effect and security of the first/second-generation EGFR-TKI, and Recommended unanimous recommendations at home and abroad as a preferred plan.
However, as other targeted therapy drugs, the first -line treatment of Oshitinib will inevitably occur after about 19 months. This also caused some clinicians to worry about the use of Oshitininib in the front line, worried that "no medicine can be available" after drug resistance. In fact, the clinical clinical understanding of the Osdini drug resistance mechanism is becoming more clear, and there is already a corresponding treatment strategy after drug resistance, so that clinicians have "worry -free" on the first -line treatment of Olkininib.
Survival benefits are significant. Osicinib is an EGFR mutation NSCLC first -line treatment preferred
With the announcement of the comparison of many EGFR-TKI and chemotherapy head comparison, the EGFR-TKI has established the status of EGFR-TKI to become EGFR mutations NSCLC first-line standard therapy. However, although the first generation of EGFR-TKI can significantly extend the non-progressive survival period (PFS), the total survival period (OS) has no significant benefit; the second generation of EGFR-TKI Aafinib, although compared to compared A generation of EGFR-TKI has significantly extended PFS, but OS benefits have not been expected [1]. It can be seen that the efficacy of the EGFR mutant NSCLC first -line therapy still needs to be further improved.
With the announcement of Flaura's research results, Oshitinib established a new standard for the first -line treatment of EGFR mutations NSCLC. Flaura research is a phase III clinical trial of random, control, multi-center, and double-blindness. It explores the first-line local advanced or positive local advanced or positive part of the treatment The main endpoint of NSCLC is PFS evaluated by researchers, and OS is the key second point.
The results of the study showed that the median PFS for the first-line treatment of Oshitinib was 18.9 months. Compared with the generation EGFR-TKI, it was significantly extended for 8.7 months, which reduced the risk of patients' disease progress or death by 54%(HR = 0.46, 95%95% CI: 0.37-0.57), and all sub-groups benefit significantly [2]. In addition, the median OS of Oshitinib for 38.6 months has broken through the survival bottleneck of the EGFR mutant NSCLC first -line targeted therapy [2]. It is worth noting that the Flaura research control group allows cross -use Olininib (65%of patients in the control group receives second -line treatment, 47%of which receives Olkinib). In this case It is not easy [3].
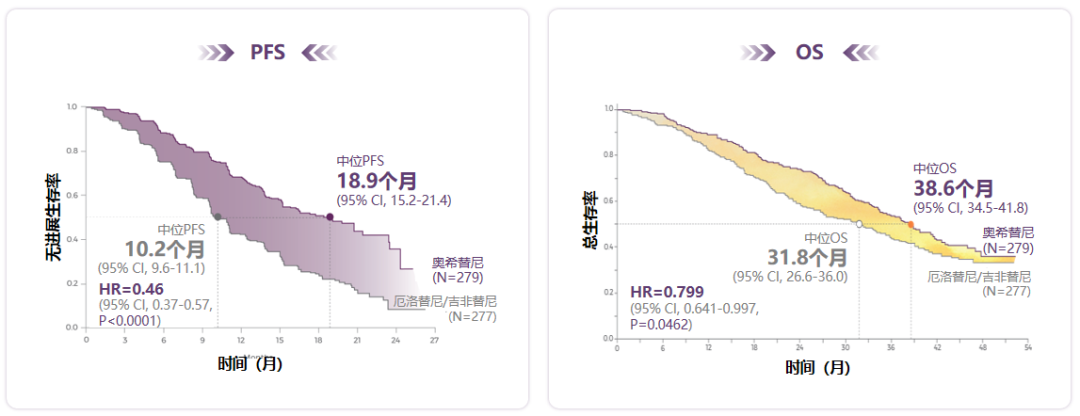
Figure 1. Flaura study showed that the first -line therapy for Oshitinib was significantly extended to the medium -ranked PFS and OS
Osicinib first -line treatment can also significantly reduce the progress or death risk of the central nervous system (CNS) of the central nervous system (CNS MPFS: NR VS. 13.9 months, HR = 0.48), reducing the emergence of new CNS lesions (12% vs vs VS VS VS 30%). Moreover, among patients with baseline brain metastasis, Oshitinib first -line treatment can also significantly extend the median PFS (15.2 months vs.9.6 months, HR = 0.47) [4,5].
In addition, the first -line treatment of Oshitinib has good security. In the case of Osimininib exposed longer (20.7 months VS 11.5 months), Oshitinib still shows good tolerance and lower incidence of adverse events, and the quality of life of patients has also improved [2,3,6].
With excellent efficacy and safety, the National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN), the European Cancer Internal Science (ESMO), and the China Clinical Oncology Society (CSCO) and other domestic and foreign authoritative guidelines have unanimously recommended Oshidinini as the standard for EGFR mutations NSCLC First-line treatment plan [7-10].

Figure 2. Osicinib is the standard first -line treatment of EGFR mutation NSCLC
The mechanism of the first -line treatment of Oshitinib has gradually become clear, and the response strategy is becoming increasingly richer.
The long survival benefit of the first -line treatment of Oshitinib is beyond doubt, but for the treatment of EGFR mutations NSCLC patients, clinicians must not only consider the front line, but also comprehensively consider the whole process management. Therefore, it is essential to identify the drug -resistant mechanism for the first -line treatment of Oshitinib and develop corresponding treatment strategies.
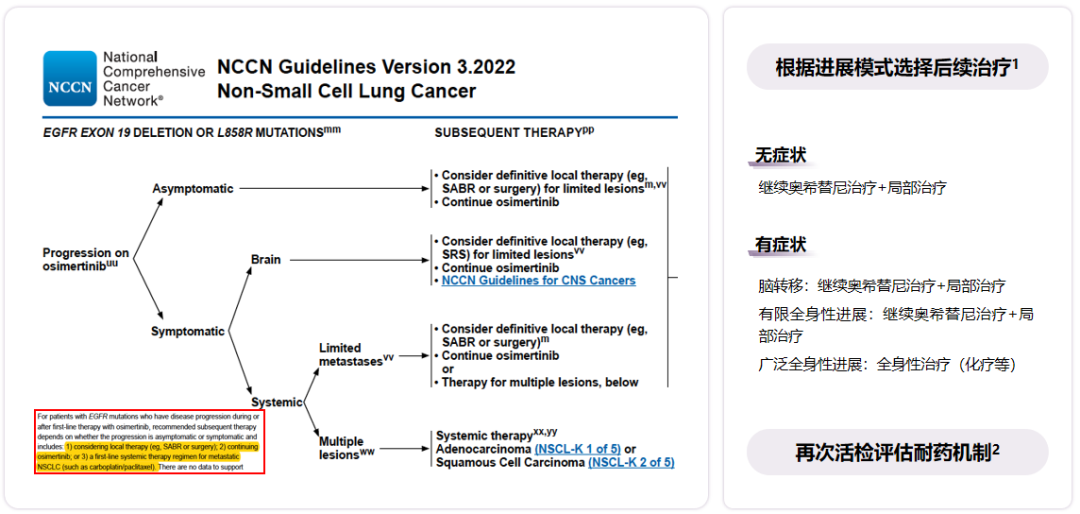
The National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) Guide recommends that after Oshitinib for treatment, follow -up treatment is selected according to the progress mode. For asymptomatic progress, symptoms of brain metastases, and symptoms of limited systemic (outside the skull) progress, you can consider continuing to continue Osicinib therapy+local treatment; for the progress of multiple lesions of the whole body, it is recommended to use it. Systemic treatment [7]. For patients who need to replace the whole body treatment, a biopsy and evaluation mechanism should be performed again, and then the follow -up treatment should be guided [9]. FIG
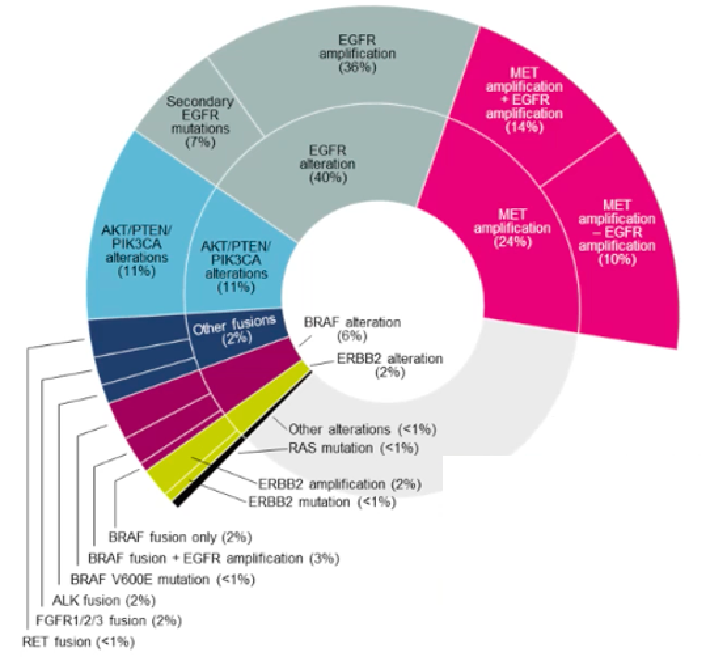
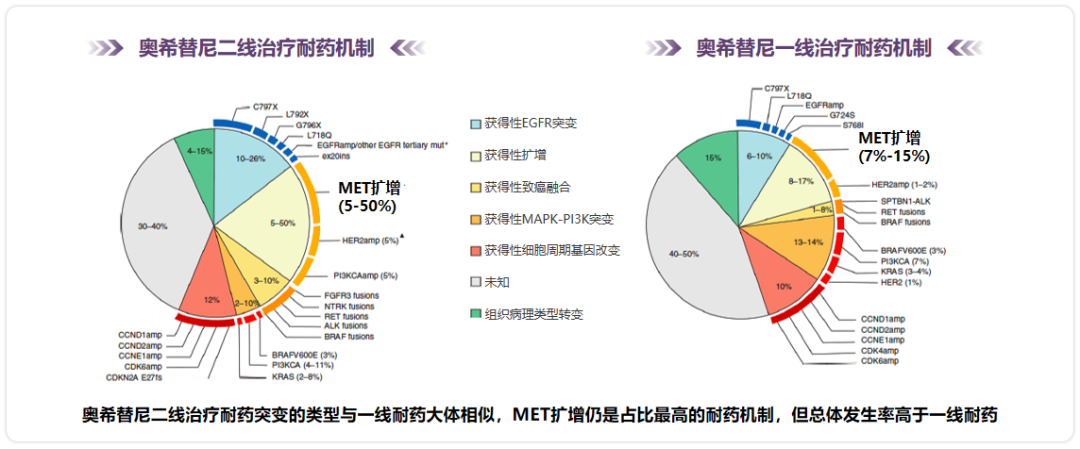
There are currently many research on the drug -resistant mechanism for Osicinib first -line treatment. In the ORChard Studies, patients or plasma samples of tumors or plasma samples after the first line of Oshitininini were analyzed by the second -generation sequencing (NGS) detection to analyze the patient's resistance mechanism to understand the patient's resistance gene spectrum. It was found that the incidence of MET amplification was 24%, which is the most common drug tolerance mechanism; the incidence of EGFR amplification and secondary EGFR mutations (C797X, L718X) was 36%and 7%, respectively; The incidence rate is 11%; the incidence of BRAF fusion or reunion is 5%; other potential target mutations are relatively rare: ERBB2 amplification/mutation 2.3%, ALK fusion 1.7%, FGFR1/2/3 fusion 1.7%, 1.7%fusion, 1.7%, 1.7%, 1.7%, 1.7%, 1.7%, 1.7%, 1.7%, and 1.7%, and 1.7%fusion, 1.7%fusion, 1.7%, 1.7%, 1.7%, 1.7%, and 1.7%, and 1.7%, FGFR1/2/3, 1.7%, 1.7%, and 1.7%fusion. RET fusion is 0.6%, RAS mutations 0.6%, Braf V600E 0.6%; and MET amplification, BRAF fusion, and ERBB2 amplification are mutually exclusive [11].
Figure 4. In the ORChard Studies, the Osicinib first -line drug -resistant frequency of the tumor tissue NGS detection
There are certain differences in the mechanism of resistance to first and second -line Oshitinib for treatment. A summary of the retrospective summary of the drug -resistant mechanism of tumor tissue or blood analysis after the treatment of Oshitinib (analysis and research as a clinical trial of the number of patients in the number of patients ≥15), and found that the types and types of drug resistance of Oshitinib for drug resistance mutations were found. The front -line resistance is generally similar. MET amplification is still the most proportion of drug -resistant mechanism, but the overall incidence is higher than the first -line drug resistance [12].
Figure 5. Aohitinib second -line treatment is slightly different from the drug -resistant mechanism of first -line therapy
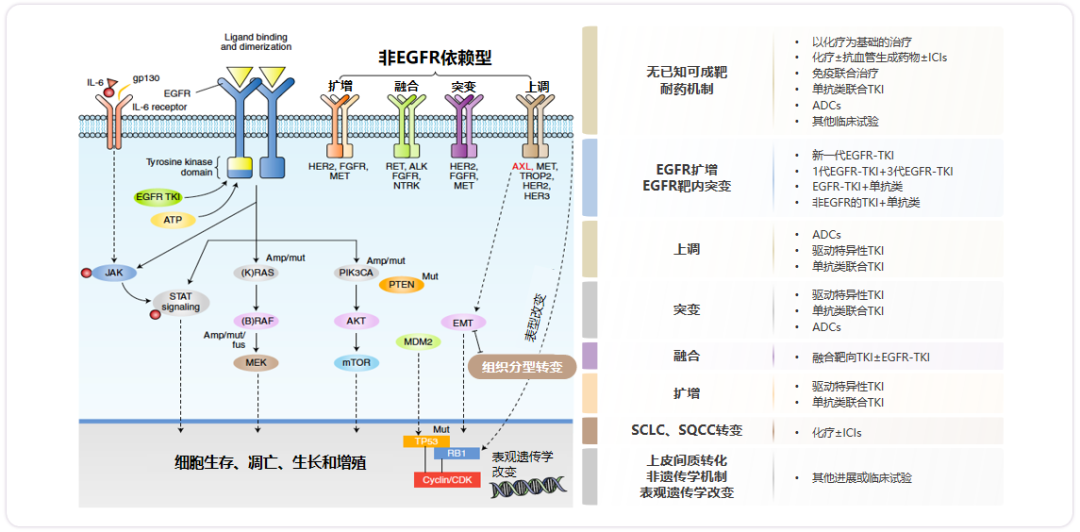
For the common reasons for the first -line treatment of Oshitinib, multiple research results have provided effective solutions. A review published by Nature Cancer in 2021, a summary of the corresponding potential treatment strategies for different EGFR-TKI drug resistance mechanisms [13]. As shown in Figure 6, for the internal mutations of EGFR targets, you can choose a new generation of EGFR-TKI, first generation EGFR-TKI+three generations EGFR-TKI, EGFR-TKI+monoclonal or non-EGFR TKI+monoclonis, such as C797S and T790M. Mutations can consider using the first generation of EGFR-TKI+three generations of EGFR-TKI; for non-EGFR dependent drug resistance, you can choose to drive special TKI, monoclonal combined TKI or antibody coupling drugs (ADCS). For example -TKI combined with MET-TKI; for the conversion of small cell lung cancer/squamous cell carcinoma, you can consider using chemotherapy ± immune examination point inhibitors (ICIS); for no known mechanism for targeting the target, the current treatment options are also getting more Rich, including chemotherapy -based therapy, chemotherapy ± anti -vascular generated drug ± ICIS, immunomotive combined therapy, monoclonal combined TKI, ADCS, and other clinical trials.
Figure 6. potential treatment strategy of EGFR-TKI drug resistance
All in all, although the drug -resistant mechanism for the first -line treatment of Oshitinib is heterogeneous, with the development of medical technology and the continuous exploration and research and development of various new drugs and new plans, there are already solutions available after Oshitinib to resist. Essence
Expert comment: Drug resistance! Promoting Ositinib to the front line can bring greater survival benefits
Flaura research shows that the first-line treatment of three generations of EGFR-TKI Oshitinib can significantly improve the survival benefits of EGFR mutations in advanced NSCLC, and it has become a first-line standard solution recommended by many domestic and foreign authoritative guidelines. For Osicininib for treatment, the current guidelines are recommended to choose subsequent treatment strategies based on the drug resistance mode, and at the same time recommend the biopsy after drug tolerance to detect the drug -resistant mechanism. For patients with a clear resistance mechanism, there are currently a variety of selective TKI and ADC drugs to show better curative effects, which can provide options for subsequent treatment. For patients without a clear resistance mechanism, immune combined therapy shows that certain survival has obtained a certain amount of survival. In addition, a variety of new treatment methods and EGFR-TKIS combination solutions also show better anti-tumor activity, which may become potential strategies in the future. It can be seen that Oshitininib has no longer "no medicine" after resistance. Moreover, some studies have shown that among the patients who use first/second-generation EGFR-TKI treatment in the real world, the second line has the opportunity to receive only 23.7%of patients treated three generations of EGFR-TKI treatment [14]. Therefore, moving the three generations of EGFR-TKI to the first-line medication may bring longer survival benefits to patients with EGFR mutations NSCLC.
Expert Introduction
Professor Liu Xiaoqing

The Fifth Medical Center of the PLA General Hospital, chief physician, professor, and deputy chairman of the deputy chairman of CSCO small cell lung cancer expert committee
Standing Committee Member of the China Anti -Cancer Association Lung Cancer Professional Committee
Deputy Chairman of the Professional Committee of Precision Medicine and Tumor Rehabilitation
Deputy Chairman of the Cancer Association of Cancer Internal Medicine of China Medical and Healthcare
Central Military Commission health expert
references:
[1] .sebastian m, et al. EUR Respir Rev.2014 Mar 1; 23 (131): 92-105.
[2] .soria jc, et al. N English. 2018 Jan 11; 378 (2): 113-125.
[3] .ramalingam ss, et al. N English. 2020 Jan 2; 382 (1): 41-50.
[4] .thanyanan reUngwattana, et al. J clin oncol 2018 AUG 28; JCO2018783118.
[5] .j vanteenkiste at esmo asia 2017.
[6]. Natasha B Leighl, ET Al, Eur J Cancer. 2020 Jan; 125: 49-57.
[7]. NCCN. Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Version 3. 2022.
[8]. ESMO Guidelines Committee, Ann Oncol (2018) 29 (SUPPL 4): IV192 – IV237, Updated Version 15 SePtember 2020.
[9] .csco, non -small cell lung cancer diagnosis and treatment guide, 2021.
[10]. Chinese Medical Association Oncology Branch, Chinese Medical Magazine, 2021, 101 (23): 1725-1757.
[11] .r. J. Hartmaer, et al, 2022 ACR, Poster# LB078/3.
[12] .leonetti a, et al., Br J Cancer. 2019; 121: 725-737.
[13] .passaro a, et al. Nat carncer. 2021 APR; 2 (4): 377-391.
[14] .Seto T, et al. Oncol theer. 2018 DEC; 6 (2): 203-215.
*This article is only used to provide scientific information to medical people, and does not represent the viewpoint of this platform


- END -
[Notes on September 5] Notice of Yanbian Prefecture on the epidemic of new coronary virus pneumonia
At 0-24 on September 4th, there were no new local diagnosis cases in Yanbian Prefecture, and there were no asymptomatic infections.Remind the general public that those who have recently occurred in th
Cross -efficiency Sichuan outbreak prevention and control also pays attention to maternal and infant safety at the same time
Cover reporter Zhou JiayiIn order to do a good job of the safety of maternal and i...