"Common" in "Rare" -hpot of EGFR EX20INS treatment?
Author:Cancer Channel of the Medical Time:2022.09.02
*For medical professionals for reading reference
Quick GET EGFR EX20INS disease burden and treatment progress
//
For patients with non -small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), EGFR common mutation sites EX19DEL and 21 outer l858R mutations currently have a variety of targeted drugs, but EGFR EX20Inins, the third common mutation site EGFR, used to be "long -term attack Not broken. "
Why must you "overcome" the target? What is the progress of treatment? What else is worth further exploring?
EGFR EX20INS is the third common EGFR mutation type, and clinically, such patients may be higher than the number of literature reports. The highest frequency of EGFR mutations in lung cancer is the lack of mutations (DEL19) and No. 21 outer L858R mutations (known as classic mutations or common mutations), which accounted for more than 80%of all EGFR mutations [1]. EGFR EX20Ins account for about 2%of all NSCLC adenocarcinoma mutations, and 6%-10%of all EGFR mutations in NSCLC cases [2-11] (Figure 2).
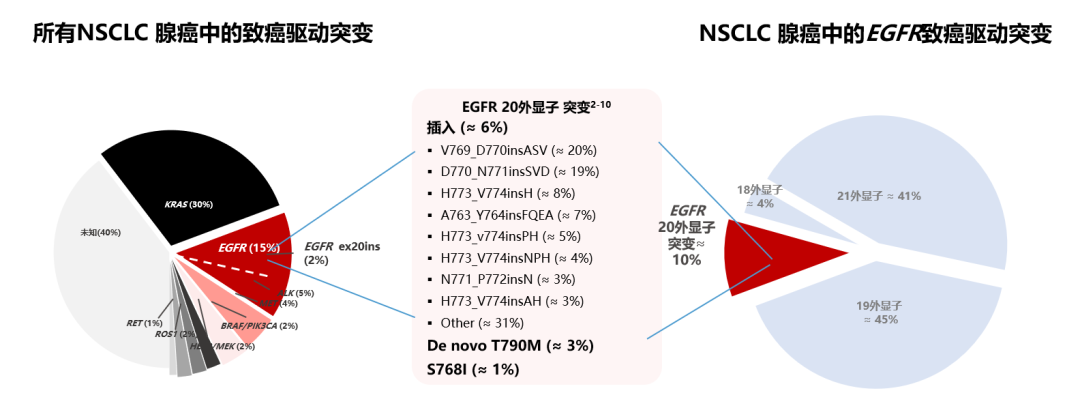
Figure 2. The distribution of EGFR mutations and EGFR EX20Ins [2-11]
Limited to the level of testing, clinically, patients with EGFR EX20INS may be far higher than the proportion of literature reports.
Compared with EGFR classic mutations, the prognosis of patients with EGFR EX20INS is even worse
Performance 1: Short survival period, shorter than common EGFR mutation survival period
A retrospective real world queue study of a 3014 EGFR mutant NSCLC patients in a group showed that the 5 -year real world total survival (RWOS) of EGFR EX20Ins and common EGFR patients was 8%and 19%, respectively. It is 16.2 months (95% CI, 11.04-19.38 months), and 25.5 months (24.48-27.04) [After adjustment HR = 1.75 (1.45-2.13); P <0.0001] [12].
In another queue study, 1086 cases of EGFR classification were admitted to the group. As a result, it also showed that: The EGFR EX20INS patient (16.5 months) was similar to the survival period of wild patients (20.0 months), but more common than common EGFR mutant lung cancer (33.0 months) has a short survival period [13] (Figure 3).
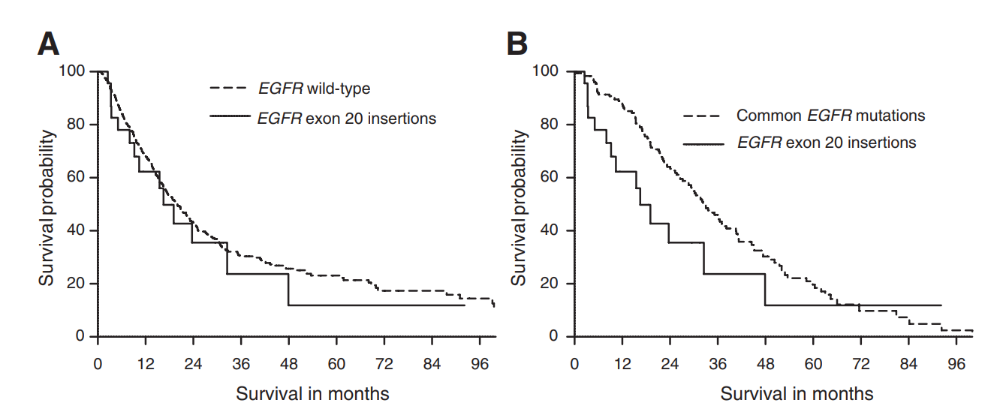
Figure 3. Comparison of the median survival of patients with EGFR EX20Ins
Performance 2: High risk of death
From the retrospective study of a large Korean sample at the ELCC conference in 2022, 53 patients with EGFR 20INS patients were analyzed, of which 62.3%received first -line platinum -containing chemotherapy, and 24.5%received first -line TKI treatment. The results show that whether it is first -line platinum -containing chemotherapy or first -line TKI treatment, the efficacy of EGFR EX20In NSCLC patients is not ideal. The risk of death of EGFR EXON 20INS NSCLC patients is twice that of common mutations in EGFR (HR = 2.16; P <0.001) [P <0.001) [) [P <0.001) [) [P <0.001) [ 14].
Performance 3: Discontinue time (TTD) and the shortage of the next treatment (TTNT) short
In the Korean retrospective research mentioned above, the data also shows that TTD (HR = 2.47; P <0.001) and TTNT (HR = 4.32; P <0.001) are also significantly shorter [14].
What is the current treatment status of patients with EGFR EX20INS?
Status 1: EGFR EX20Ins subtypes are diverse, and there is a heterogeneity for the treatment of traditional EGFR-TKI [15]
EGFR EX20Ins have a variety of sub -types, and the sensitivity of different subtypes to treatment is different. It can be divided into four sub-groups according to the structure, which is used to predict EGFR-TKI efficacy [15] (Figure 4).
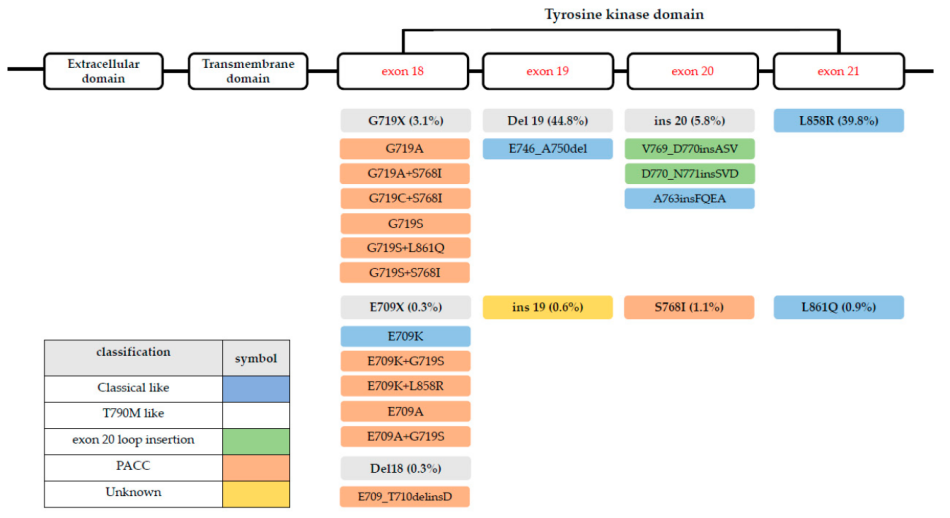
Figure 4. EGFR EX20INS has a variety of subtypes, and the sensitivity of different subtypes to treatment is different
This classification method can better define the mutation group according to drug sensitivity:
Classic prototypes are sensitive to all three generations of EGFR-TKI;
α-C spiral (amino acid 761-766): Insert subtype is sensitive to the approved EGFR inhibitors (such as A763_Y764INSFQEA), and insertion mutations in the LOOP ring area have a poor treatment effect;
The relief rate of insertion mutations in the near -end structure area is higher than that of the P Ring remote insertion type.
Status 2: Existing problems related to EGFR EX20INS mutation detection
Gene detection is a key link for NSCLC treatment management, and it is especially important to identify specific sequence sub -types. However, due to the diversity and complex structure of EGFR EX20Ins, the detection rate is very low.
The most commonly used detection methods include polymerase chain reactions (PCR) and next -generation sequencing (NGS). Among them, PCR is easy to detect and requires relatively large tissue samples to insufficient ability to detect molecular heterogeneous mutations such as EGFR EX20Ins [16]. Foundation Medicine data shows that PCR missed 51.4%of mutations compared with NGS [17]. NGS is a diagnostic tool for identifying molecular heterogeneous sequences. It has higher sensitivity and stronger reliability, so it is more valuable. Although as the "Sequential Swipe Technology's Clinical Application of Chinese Experts (2020 Edition)" as a "second -generation sequencing technology (2020 version)" is given priority recommendation detection methods, the application of NGS in patients with EGFR EX20INS NSCLC in China is still unclear in clinical practice [16].
Status 3: Authoritative Guide Recommended Starting Treatment Reference NSCLC Systematic Treatment Strategy
Chemotherapy is still the standard first -line treatment of the world. NCCN and CSCO's starting treatment reference NSCLC systematic treatment strategies have not yet been recommended for specific treatment schemes (Figures 5 and Figure 6). More first -line targeted treatment strategies still need to be explored.
Figure 5. 2022 V1 NCCN non -small cell lung cancer diagnosis and treatment guide [18]
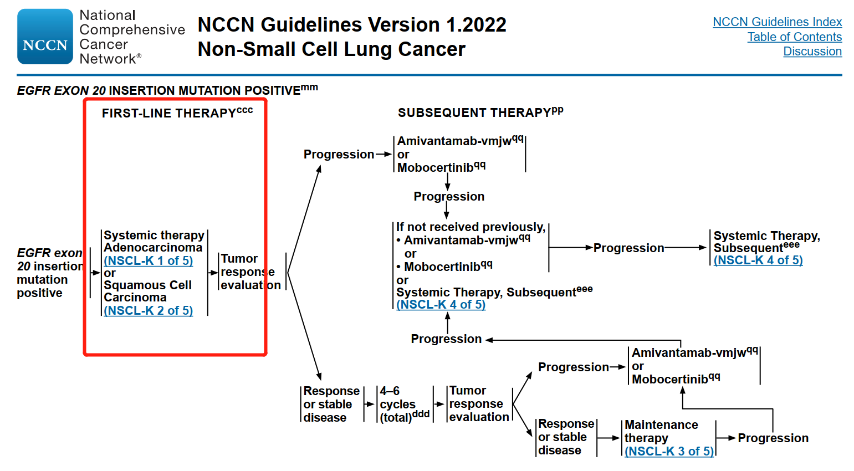
Figure 6. 2022 CSCO non -small cell lung cancer diagnosis and treatment guide [19]

The previous traditional treatment benefits have limited benefits, and there have been milestone progress.
Prior to the advent of targeted targeted drugs, the treatment schemes that EGFR EX20INS patients can choose include chemotherapy, traditional EGFR-TKI, and immunotherapy.
Chemotherapy and immune tumor treatment
The combination of chemotherapy and chemotherapy is the most commonly used first -line therapy for EGFR EX20INS NSCLC, but the effect is not ideal [17]. According to the US cancer electronic medical records Flatouronhealth database as of February 2020, the combined schematic and chemotherapy joint plan accounted for about 60%of the entire treatment method, and the total relief rate (ORR) was close to 20%(n = 57). Survival (PFS) is 4.5 months-5.7 months [17].
When immune tumor therapy is used as a single medicine first -line plan, the ORR confirmed is only 9.1%, the PFS is 3.1 months (n = 11), and when the second -line treatment is ≥ second -line treatment after the treatment of platinum, the PFS is 2.2 months. (N = 20); When traditional EGFR-TKI is used as a single-line first-line plan, ORR is only 2.7%, PFS is 3.3 months (n = 37). When the second-line treatment of platinum was treated, the ORR was 10.0%, and it was 10.0%. PFS is 3.4 months (n = 10) [17].
Traditional EGFR-TKI
The results of a real-world data META analysis showed that the PFS used for EFGR-TKI for first-line therapy is 3.0 months (95% C1: 2.0,3.8), and OS is 16.4 months (95% CL: 1.6,19.77 ); EFGR-TKI is used for the estimated PFS for backline treatment. The PFS is 2.1 months (1.9,3.0), and OS is 14.1 months (12.9,15.3) [20] (Table 3).
table 3. Summary analysis of EGFR-TKI IL and ≥2L PFS, OS, OS
Milestones Progress -Latest targeted therapy: ORR has been significantly improved, MOS is more than 2 years [17]

For a long time, chemotherapy, traditional EGFR-TKI, and immune tumor treatment have limited benefits. Patient's survival ending is poor. The treatment of EGFR EX20INS NSCLC patients is facing considerable challenges.
The relatively mature targeted drugs for EGFR EX20INS include: Mobocertinib (Mobositinib) and amivantamab. They were granted breakthrough therapeutic drug qualifications by the US FDA in 2020 for previous treatment of platinum chemotherapy or post -disease progress. EGFR EX20INS transferring NSCLC adult patient.
Current research data show that new targeting drugs can significantly improve the ORR of these patients, MOS for more than 2 years [17] (Table 4).
Table 4. For the clinical data summary of the pharmaceutical clinical data of the mutant -positive NSCLC, the EGFR outer appende 20 [20]
summary
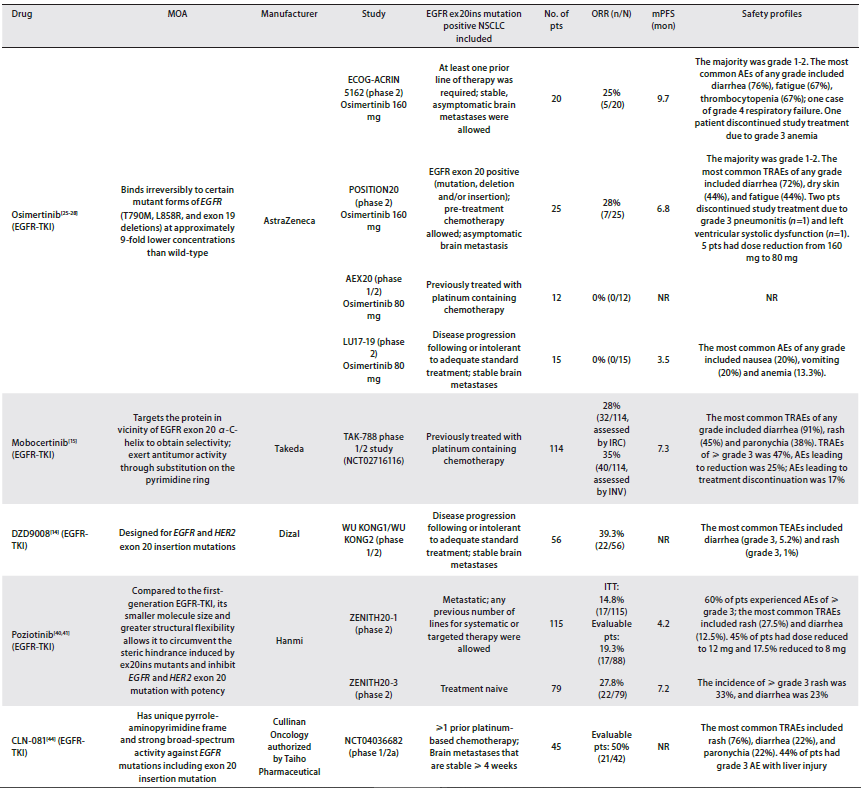
In short, the EGFR EX20Ins NSCLC is high heterogeneous, poor prognosis, is not sensitive to traditional treatments, and has not met in high clinical needs. In recent years, EGFR EX20In NSCLC targeted therapy has made milestone progress, including the first new EGFR-TKI Mobicinibinib and EGFR/MET bIPC AMIVANTAMAB, etc. , Relatively large samples (Mobosyinib Research N = 114, AMIVANTAMAB Study N = 81) in EGFR EX20In NSCLC confirmed that it brought continuously in the clinical sense and created more possible treatment options for patients.
references:
[1] .fang w, huang y, hong s, et al. EGFR EXON 20 Insertions and Response to Osimertinib in Non-Small-Cell LUNG CANCER [J]. BMC Cancer, 2019, 19 (1): 595 [2 2) ] .Chan Ba, hughes bg. Targeted theracy for non-Small Cell LUNG CANCER: Current Standards and the Promise of the Future. Transl LUNG CANCER res. 2015; 4 (1): 36-54. Doi: 10.3978/J.ISSS .2218-6751.2014.05.01
[3]. AnOXNARD GR, LO PC, Nishino M, et al. Natural history and molecular characteristics of lung carboring egfr exon 20 insertions.j thorac oncol. 2013; 8 (2): 179-184. .0b013e3182779d18
[4] .Chong Cr, Jänne Pa. The Quest to Overcom Resistance to EGFR-TARGED TheRAPIES in Cancer. Nat Med. 2013; 19 (11): 1389-1400. Doi: 10.1038/nm.33888
[5]. Crossland v, et al.The Frequency and Spectrum of Egfr EXON 20 Insertions in NSCLC: a Global Liticture Review.j Thorac Oncol 2018; 13 (10 SUPPL); S612-S613; S612-S613;
[6] .gazdar Af, Minna JD. Inhibition of egfr Signaling: All Mutations are not created equal. Plos med. 2005; 2 (11): e377. Doi: 10.1371/placed.002037777
[7].Gazdar AF. Activating and resistance mutations of EGFR in non-small-celllung cancer: role in clinical response to EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Oncogene. 2009;28 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):S24-S31. doi:10.1038 /onc.2009.198
[8]. Jorge Se, Kobayashi SS, Costa Db. Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR) Mutations in LUNG CANCER: Preclinical and Clinical Data. /1414-431x20144099
[9].Kobayashi Y, Mitsudomi T. Not all epidermal growth factor receptor mutations in lung cancer are created equal: Perspectives for individualized treatment strategy. Cancer Sci. 2016;107(9):1179-1186. doi:10.1111/cas. 12996
[10].Lee JK, Shin JY, Kim S, et al. Primary resistance to epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer harboring TKI-sensitive EGFR mutations: an Exploratory Study. Ann Oncol. 2013; 24 (8): 2080-2087. Doi: 10.1093/Annonc/MDT127 [11] .Afa K, CHAFT JE, EGFR EXON 20 Insertions , molecular heterogeneity, and clinicopathology characteristics.
[12].Bazhenova L, Minchom A, Viteri S, Bauml JM, Ou SI, Gadgeel SM, Trigo JM, Backenroth D, Li T, Londhe A, Mahadevia P, Girard N. Comparative clinical outcomes for patients with advanced NSCLC harboring EGFR exon 20 insertion multi-common egfr mutations. LUNG CANCER. 2021 DEC; 162: 154-161. Doi: 10.1016/J.LUNGCAN.2021.10.020.
[13]. AnOXNARD GR, Lo PC, Nishino M, et al. Natural history and molecular characteristics of lung caring egfr exon 20 adse 0b013e3182779d18
[14]. Yoon S, Lim Sm, Jung Ha, Et Al. Clinical Characteristics, Treatment Patterns and Outcomes of Egfr Exon 20 Inseer EGFR Mutations in Korean AnsclclclcLCLCLC PATIENTS. 2022 Elcc 5P.
[15] .hou j, li h, ma s, et al. EGFR EXON 20 Insertion Mutations in Advanced Non-Small-Cell LUNG CANCER: Current Status and Perspectives. Biomark res. Doi: 10.1186/S40364-022-00372-6.
[16].Kwon CS, Lin HM, Crossland V, et al. Non-small cell lung cancer with EGFR exon 20 insertion mutation: a systematic literature review and pooled analysis of patient outcomes [published online ahead of print, 2022 May 27] . Curr Med Res pin. 2022;1-34. doi:10.1080/03007995.2022.2083326[17].Kitadai R, Okuma Y. Treatment Strategies for Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Harboring Common and Uncommon EGFR Mutations: Drug Sensitivity Based on Exon Classification, and Structure-Function Analysis. Cancers (Basel). 2022; 14 (10): 2519. Doi: 10.3390/Cancers14102519
[18]. NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in onCology-Non-Small Cell LUNG CANCER, Version 2 [J].
[19]. China Clinical Oncology Association Guide Working Committee .2022 CSCO Non -small Cell Cancer Diagnosis and Treatment Guide [J]. People's Health Press.
[20]. Yang Xue, Zhao Jun. EGFR outer appende 20 inserted the clinical research progress of mutant positive NSCLC treatment [J]. China Lung Cancer Magazine, 2022, 25 (5): 14.
Approval number: VV-MEDMAT-71717
Approved date: July 2022
statement:
This information aims to help medical professionals better understand the latest progress in the field of related diseases. The content of the information released on this site does not mean that it agrees with its description and view, only to provide more information. If the copyright issue is involved, please contact us, we will deal with it as soon as possible.
For medical and health professionals, we can understand the use of information. These information cannot replace professional medical guidance in any way, nor should they be regarded as diagnosis and treatment suggestions. If such information is used to understand the purpose other than information, Takeda does not assume relevant responsibilities.
As of July 28, 2022, Mobocertinib has not been approved by the China National Drug Administration (NMPA). The above information is only for medical and health professionals to understand academic progress. Takeda does not recommend except for the instructions.
*This article is only used to provide scientific information to medical people, and does not represent the viewpoint of this platform


- END -
What should I do if I have a cold but have been coughing? What should I do?

A friend told Huazi that he had a heavy cold some time ago, and he kept coughing f...
Jiayuguan City's notice on the second round of regional nucleic acid testing
Friends of residents:In order to resolutely block the transmission of epidemic conditions, cut off the epidemic dissemination chain to ensure the health and life safety of the people, after studying t