2022 WCLC radiotherapy collection!What are the latest progress of NSCLC radiotherapy combined with whole body treatment?
Author:Cancer Channel of the Medical Time:2022.08.28
*For medical professionals for reading reference
In 2022, WCLC radiotherapy advanced progress!
In the treatment of patients with non -small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), radiotherapy is an important local treatment method. For patients with advanced NSCLC patients, systemic treatment is the main treatment method. However, in the process of clinical practice The residual lesion, so local radiotherapy is still indispensable. In recent years, some studies have shown that immunotherapy and radiotherapy have synergistic effects. Radiotherapy may enhance the systemic anti -tumor response of immunotherapy. However, whether the combination of radiotherapy and other systemic treatment methods can improve the prognosis of patients with advanced NSCLC.
The 2022 World Lung Cancer Conference (WCLC) was held in Vienna, Austria on August 6-9. In response to the application of radiotherapy in NSCLC, this article organizes three related research with readers!
Properties of lung cancer bone metastasis risk radiotherapy-forward-looking vertical research from India
(Summary number: MA09.03)
A forward -looking and vertical study from India reports the results of the asymptomatic bone metastasis (BM) patients who receive radiotherapy, and observe the patterns and sustainability of pain reactions and changes in the quality of life [1].
From June 2020 to October 2021, this forward -looking study included BM patients confirmed by lung cancer with lung cancer confirmed by tissue. Most patients use conventional radiotherapy to proclaim the pain brought by BM. The main endpoint is the pain reaction of 2 weeks and 4 weeks, and the secondary end point is the pain reaction of 3 months and 6 months. In the study, the digital pain scales were used to record the pain scoring of the patient, and the dose of opioid analgesic drugs was converted into oral morphine equivalent dosage (OMED). Until the patient's pain progress or death is used to measure painless survival (PFS). In addition, the QLQ-C30 and BM22 recording patients' quality of life were used to use the European Cancer Treatment Research Organization (EORTC) life quality.
The study continued to include 125 patients in a row, most of them NSCLC (95%), men (67%), and non -smoke (77%). Most of the dissolved lesions (83%) are in the middle shaft (77%). 47%of patients discovered the positive driving gene and received TKIS treatment. 70%of patients received conventional radiotherapy of the single field. The most commonly used dose was a single 8GY. In the baseline examination, the average pain score was 5.5 (SD ± 2.46), and the average OMED was 17.5mg/day (SD ± 18.8).
The results of the study show that after radiotherapy, the complete relief (CR) rate of 2 weeks (n = 86), 4 weeks (n = 85), 12 weeks (n = 67) and 24 weeks (n = 47) is 9%, respectively, respectively, respectively, respectively, respectively, respectively. 19%, 36%, and 38%, the partial relief (PR) rates were 37%, 48%, 42%, and 32%, respectively. 70%; the rate of uncertain reactions (IR) was 45%, 27%, 21%, and 25%, respectively, while the pain progress (PP) rates were 8%, 6%, 1.5%, and 4%, respectively. The demand for opioid drugs was significantly reduced in 3 months and 6 months, with an average OMED of 11 (± 15.2) and 6 (± 11.6) mg/day, respectively.
In the positive queue of mutation, the median duration of the pain reactions is significantly higher (7.8 vs 4 months, P = 0.003), the radiotherapy rate is 13.6%, the median time is 4.4 weeks, the PFS rate of pain is 3 months and the PFS rate is 3 months and the PFS rate is 3 months and 82%and 69%were 6 months. Radio radiotherapy tolerance is good, no II or more severe acute or advanced toxicity. At 3 months, the quality of life of patients included pain, emotional function, fatigue, insomnia, and overall health, and the scores have been significantly improved. In addition, the symptoms and functions of BM22 have also showed that 60%of patients have absolutely improved significantly statistically significantly.
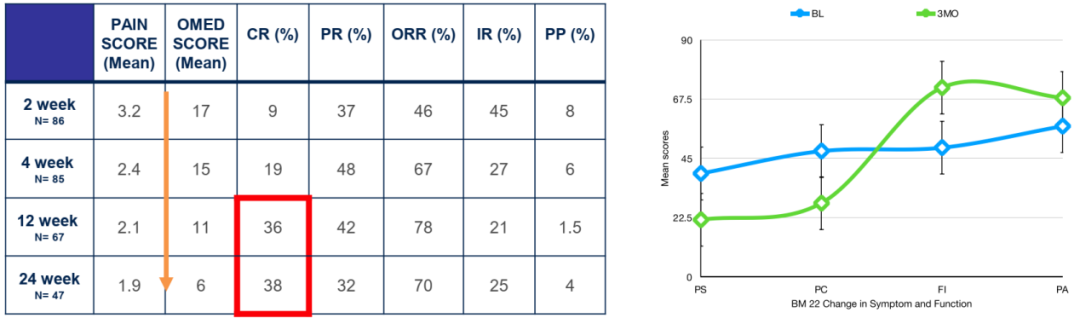
Figure 1. Main research results
(BL: baseline; 3MO: 3 months; PS: Pain sites; PC: Pain nature; FI: dysfunction; PA: social psychology)
This forward -looking study shows that for patients with asymptomatic BM in lung cancer, conventional radiotherapy can obtain excellent and lasting overall relief rates, and significantly improves the quality of life of patients. However, the result also reminds that in patients with positive gene mutations, which patients should be determined to receive radiotherapy again, and they may need to be more suitable for high -dose radiotherapy.
PD-1 inhibitor and chemotherapy combined with or non-combined radiotherapy for the first time NSCLC [2]
(Summary number: MA09.04)
In recent years, immunotherapy has become a standard front -line treatment plan for late NSCLC. Some studies have shown that immunotherapy and radiotherapy play a synergistic role in local and distant tumor control. However, the data for the late NSCLC of the first -line immunotherapy+chemotherapy+radiotherapy is still relatively small. This study retrospectively analyzed the patients with a single center received PD-1 inhibitors immunotherapy+chemotherapy patients with advanced NSCLC patients, and according to whether they received radiotherapy, they divided the patients into two groups to observe the first-line immunotherapy+chemotherapy combined radiotherapy (ICRT group) and immunotherapy The efficacy and safety of +chemotherapy group (ICT). The study was included in 135 patients, of which 65 of them received PD-1 inhibitors combined with chemotherapy and radiotherapy, while the other 70 patients only received immune+chemotherapy. The medium interval between radiotherapy and PD-1 inhibitors immunotherapy is 5 days (range of 0-96 days).
The results showed that compared with the ICT group, the median PFS (16.5 vs 10.4 months, P = 0.043) and median OS (not reaching VS 21.0 months, P = 0.030) of the ICRT group patients were significantly extended.
Figure 2. Kaplan-Meier analysis of PFS (A) and OS (B)
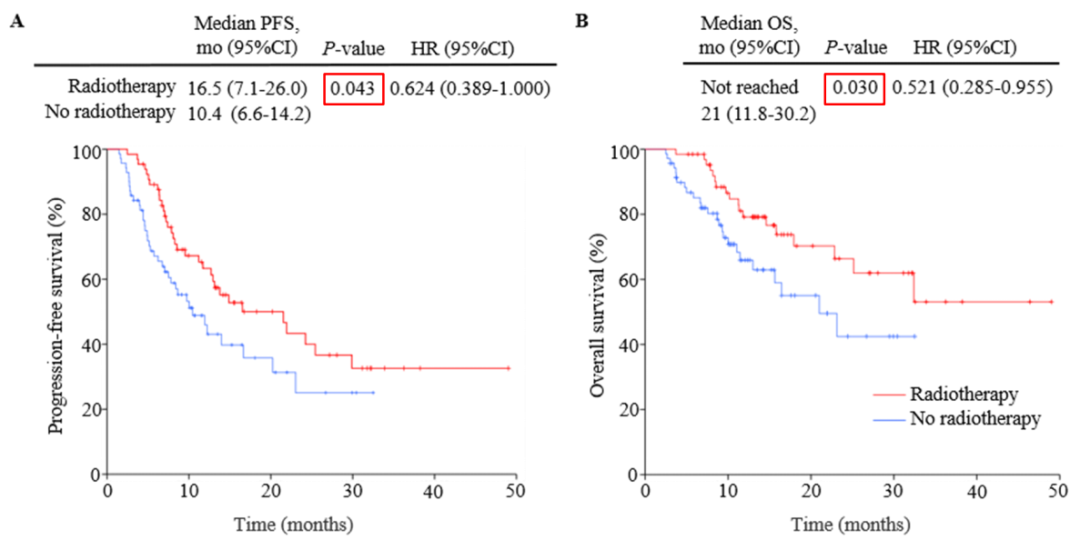
Single variable COX regression analysis found that the increased radiotherapy is PFS (HR = 0.617, 95%CI: 0.385-0.989, P = 0.045) and OS (HR = 0.512, 95%CI: 0.277-0.947, P = 0.033). factor.
In terms of safety, the patient's tolerance is good, and the total incidence of adverse events between the ICRT and the ICT group is similar. A patient with a patient in the ICRT group stopped immunotherapy due to severe immune-related pneumonia. The incidence of adverse events related to level radiotherapy was 3.1%.
The results of the study suggest that adding radiotherapy on the basis of the first-line PD-1 inhibitor immunotherapy and chemotherapy can improve the prognosis of patients with advanced NSCLC and toxicity to tolerance. More forward -looking research can be carried out in the future to explore the application of immune+chemotherapy and radiotherapy in the first -line treatment of NSCLC.
Immunotherapy efficacy of patients with radiotherapy improvement stage and stage IV non -small cell lung cancer patients [3]
(Summary number: MA09.08)
Radiotherapy may enhance the systemic anti -tumor reaction of immunotherapy. Researchers performed a retrospective analysis to explore whether radiotherapy can improve the immunotherapy results of Phase III or stage IV non -small cell lung cancer patients. This study conducted in Enze Medical Center included 259 patients with NSCLC confirmed by tissue pathology from December 1, 2018 to December 31, 2021. These III or phase IV NSCLC patients are suitable for receiving fabricab, and some patients receive radiotherapy at a specific time. Radiotherapy includes conventional radiotherapy (64.8gy/30F and 54GY/25F) and stereo -oriented systemic radiotherapy SBRT: 50Gy/5F and 60GY/8F). The end point of the study is the PFS rate and OS rate.
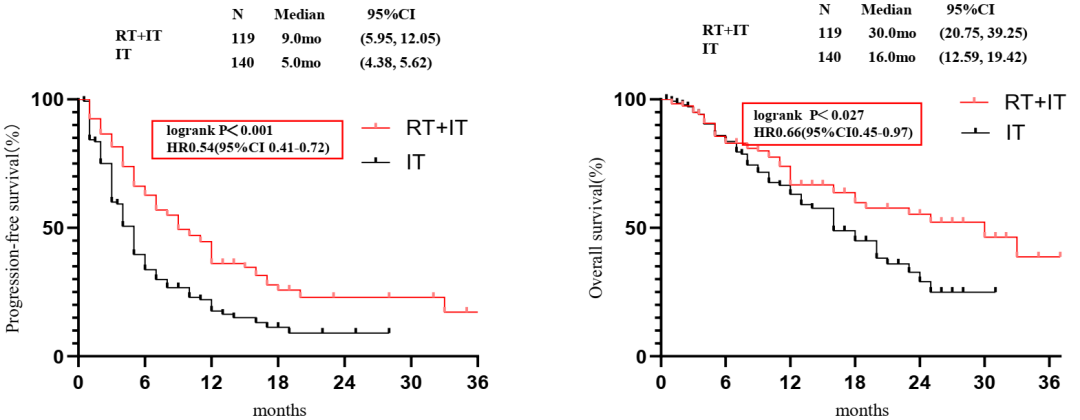
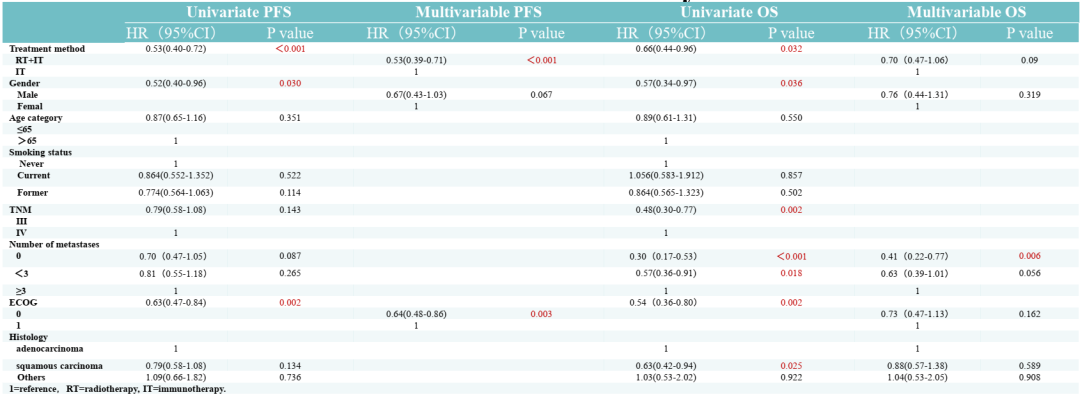
140 of the 259 patients who were included in the study received immunotherapy and 119 cases were under immunized radiotherapy. There is no difference in the baseline variables between the treatment group, including gender and age, smoking status, TNM installment and number of metastasis, and ECOG grading and histological studies.
The results of the study show that the PFS of the overall population is 6 months (95%CI: 5.03-6.97), of which PFS of patients receiving individual immunotherapy and immunotherapy radiotherapy are 5 months (95%CI: 4.38-5.62), respectively. And 9 months (95%CI: 5.95-12.05; P <0.001). The median OS of the overall crowd is 20 months (95%CI: 15.27-24.73), of which patients who receive individual immunotherapy and immunotherapy add radiotherapy are 16 months (95%CI: 12.59-19.42) and 30 A month (95%CI: 20.75-39.25; P = 0.027).
Figure 3. General population PFS and OS results
Single variable analysis shows that ECOG = 0 (P = 0.03), men (P = 0.002), radiotherapy (P <0.001) are related to better PFS rates. Multi-variable analysis shows that radiotherapy (HR = 1.89, 95%CI: 1.41-2.54, P <0.001) and ECOG = 0 (HR = 1.55, 95%CI: 1.16-2.07, P = 0.003) is an independent prognosis factor, The PFS rate has increased significantly.
In addition, single -variable analysis shows that ECOG = 0 (P = 0.002), women (P = 0.036), III stage (p = 0.002), squamous cell carcinoma (P = 0.025), and no metastasis (P = 0.01) and OS The rate is significantly improved. The multi-variable analysis shows that there is no metastasis (HR = 2.42, 95%CI: 1.29-4.54, P = 0.02) is an independent prognostic factor, and the OS rate has increased significantly; radiotherapy (HR = 1.42; 95%CI: 0.95-2.14,, 0.95-2.14, P = 0.09) also related to the higher OS rate.
Table 1. Single variable and multi -variable COX analysis results of PFS and OS
The study prompts that increasing radiotherapy in immunotherapy is significantly related to the improvement of NSCLC patients. However, in the future, forward -looking studies are still needed to further confirm the efficacy and safety of the first -line treatment of immune combined radiotherapy. This material is supported by Astrikon, for medical professionals for reference
Approval number: CN-101262 Expired Date: 2023-8-24
references:
[1]A. Agrawal, A. Tibdewal, T. Tahmeed, N. Mummudi, J.P. Agarwal,et al.Response of Palliative Radiotherapy in Bone Metastasesof Lung Cancer - Results of Prospective Longitudnal Study from India.2022WCLC. MA09.03.
[2] P. Ding, y. huang, f. tong, l. Chen, L. Wen, R. ZHANG, S. Cheng, x. DONG, ET Alt-Line PD-1 inhibitors and Chemotherapy Combined with Without Radiotherapy in Advanced Non-Small-Cell LUNGCANCER.2022WCLC. MA09.04.
[3] S. Li, K. Chen, M. Chen, Y. Meng, H. Yang, ET Al.radiotherapy Improves Outcomes to Immunotherapy in Patients with Stage III and Iv NSCLC. MA09.08.
*This article is only used to provide scientific information to medical people, and does not represent the viewpoint of this platform


- END -
What time stays up late?Can I make up for the consciousness of staying up late →

Does staying up late will affect the quality of sleep?actuallyIt's not sleeping la...
[Health and Health] Note!The cervical spine is most afraid of these 4 words. Chinese medicine has summarized 6 small cervical movements for you, and it is practiced ~

inContent source: China Traditional Chinese Medicine Reporter: Wang DiThe problem ...