2022 WCLC hotspot -local advanced NSCLC related research progress
Author:Cancer Channel of the Medical Time:2022.08.14
*For medical professionals for reading reference
The cutting -edge research progress of the WCLC conference in 2022 is the first to see!
About 1/3 of non -small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients were already in the III stage during the first diagnosis. However, despite the active use of standard treatment, the clinical ending of patients with local advanced NSCLC is still poor. The survival (OS) rate is about 20%[1]. Most patients finally recur after the treatment, and more than 60%of the recurrence manifestation is a distant transfer. Therefore, the exploration of related indicators such as the prognosis of tumor treatment has become a clinical research hotspot.
The 2022 World Lung Cancer Conference (WCLC) was held in Vienna, Austria, August 6-9, 2022. This article compiled three studies related to local advanced NSCLC disease risk prediction and treatment [2-4], which is now shared with readers.
NADIM II Studies: CTDNA levels before treatment can significantly predict OS and PFS [2]
(Summary number: MA06.03)
According to the NADIM II test reported by the American Clinical Oncology Society (ASCO) in 2022, compared with individual chemotherapy, neoosure Nivo Platinum Platinum Chemotherapy has improved the pathological relief of patients with phase IIIA patients ( The PCR) rate has not increased the incidence of high -level adverse events, and the surgical rate is increased. The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has recently approved patients with neoading NIVO combined chemotherapy to remove patients with NSCLC (stage IB tumor ≥4cm or lymph nodes -positive IIIA). However, clinically, there are currently lack of indicators that can predict the progress of the disease and the risk of death.
NADIM II studies are included in the removed clinical period IIIA (based on AJCC 7th edition) NSCLC, ECOG PS 0-1, and there is no known EGFR/ALK mutation. Before the treatment, all patients collected the circulatory tumor DNA (CTDNA) in the plasma sample and conducted a second -generation sequencing (NGS) analysis. After that, these patients were randomly received neo-assisted therapy of NIVO 360mg+200mg/m2+karplatin (AUC = 5). Every 21 days (+/- 3 days) was a cycle, 3 cycles, and then surgery; /m2+card platinum (AUC = 5) treatment, every 21 days (+/- 3 days) is a cycle, a total of 3 cycles, and then surgery. After surgery, patients with a pathological assessment were confirmed to be R0, which began to assist NIVO (480mg Q4W) at the 3-8 weeks (+7 days) after the operation, which lasted for 6 months.
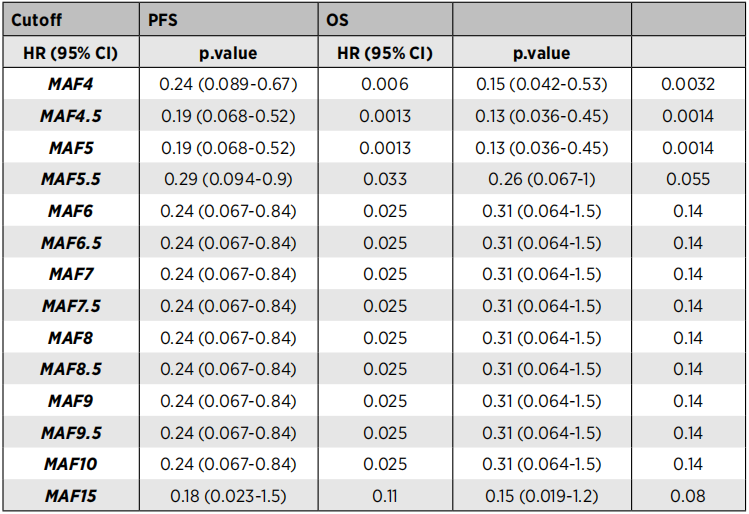
Among the plasma samples obtained from 54 patients, 52 cases (91.4%) were detected (91.4%) detected the baseline CTDNA and found that the size of the tumor was significantly related (P = 0.006). In addition, the CTDNA level before treatment is significantly related to no progressive survival (PFS) and OS (Table 1). Compared with patients with high CTDNA levels, PFS (HR = 0.19, 95%CI: 0.07-0.52, P = 0.013) and OS (HR = 0.13, 95%CI: 0.04-0.45, PF = 0.001) Significant improvement.
The results show that the baseline CTDNA level can effectively predict patients with high risk of disease and high risk of death, and can assist in formulating corresponding follow -up treatment.
Table 1. The risk ratio (HR) of PFS and OS at different baseline CTDNA levels (HR)
ESPATUE research long -term follow -up data update [3]
(Summary number: MA06.08)
In 2015, the ESPATUE test results showed that for the surgical resection III NSCLC, patients with chemotherapy and surgical resection were similar for 5 years, and the treatment effect was good (eberhardt et al, J Clin Oncol 2015). With the rapid development of lung cancer, more and more III phase NSCLC patients have experienced long -term survival (LTS). The new treatment principle of immune examination point inhibitors (CPI) shows a certain impact on LTS of patients with different lung cancer. Therefore, the data set of the ESPATUE test needs to be re -evaluated to find the best local treatment method. The current researchers followed up with all the patients who still survived in the trial until January 2022, and the LTS data was updated based on the follow -up results, and different treatment strategies and risk of competition were reported.
ESPATUE Studies were selected as 246 patients from January 2004 to January 2013. These patients received 3 courses of cisplatin+paclitaxel induction chemotherapy and 45GY radiotherapy+cisplatin+Changchun Ruibin synchronous chemotherapy treatment. 161例患者(65%)经多学科讨论评估可行手术切除,这些可手术切除的患者被随机分到继续接受65-71Gy的放化疗组(A组,n=80)或手术组(B组, n = 81).
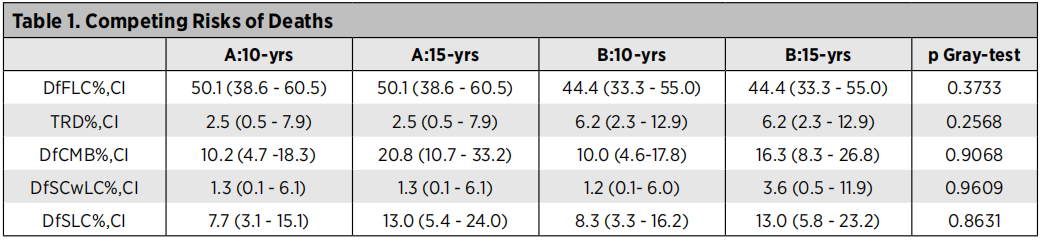
At the last follow -up (January 2022), 37 of the 246 patients were still survived, the median follow -up time of the patients still survived was 129 months, 15 patients survived in group A, and 16 patients in group B survived. The 5-year OS rate after random grouping is group A [43.8 (32.7-54.2)], group B [43.2 (32.3-53.6)]; 10 years OS rate is group A [28.3 (18.8-38.5)], Group B [ 29.9 (20.2-40.3)]; P = 0.70. The 5-year PFS rate after random grouping is group A [30.0 (20.4-40.2)], group B [29.2 (19.7-39.4)]; 10 years of PFS rate is group A [23.3 (14.6-33.1)], Group B [ 19.8 (11.8-29.4)]; P = 0.94. Table 2 summarizes the risk of competitive death in the two groups: first lung cancer death (DFFLC), the treatment of related death (TRD), the death death (DFCMB), non -lung cancer secondary cancer death (DFSCWLC), and secondary lung cancer death (DFSLCCCCC (DFSLCCC) To.
Table 2. Risk of competition death
The LTS rate of patients with Phase III NSCLC shows the encouraging 5 -year OS, PFS rate and 10 -year OS, and PFS rate. In addition, there is no significant difference between the two during surgery or chemotherapy as a radical local treatment. Both treatments are very good treatment methods, both can be used as good treatment strategies. At the same time, competitive death risk analysis shows that in DFFLC, TRD, DFCMB, DFSCWLC, and DFSLC, there are no clear signals between the two groups. DFCMB and DFSLC are proved to be the main long -term risk indicators of patients with local advanced NSCLC. These important phase III data can be used as baseline information, compared with future feasible treatment plans including CPI immunotherapy.
A deep learning model can effectively predict MPR in NSCLC new assisted immunotherapy [4]
(Summary number: MA06.09)
In NSCLC patients, a large proportion of patients cannot achieve the main pathological relief (MPR) through neoading immunotherapy. A multi -center queue studies the use of CT images to build and verify a deep learning model to predict the MPR of NSCLC patients receiving new assisted immunotherapy.
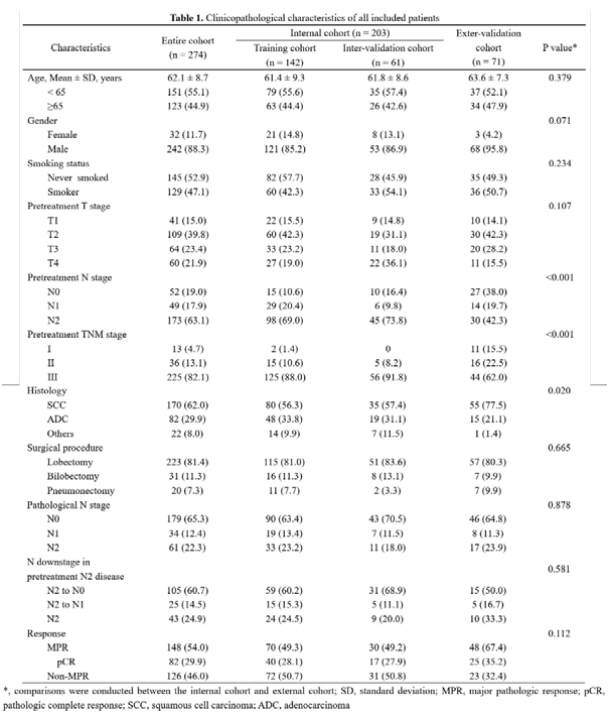
The study was included in the Shanghai Luke Hospital of Tongji University, from January 2019 to December 2021, Shanghai Luke Hospital, Ningbo Huamei Hospital of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, the First Affiliated Hospital of Nanchang University, and Shaw Run Hospital of Zhejiang University Medical College. A total of 274 patients undergoing athletic surgery later collected the baseline characteristics and chest CT images within 2 weeks before the treatment of new assisted treatment. Among them, the patients of the Shanghai Lung Hospital were divided into the training queue (142 cases) and the internal verification queue (61 cases) at a ratio of 7: 3. All patients in other centers were assigned to the external verification queue (71 cases).
The results of the study showed that more than half of patients (54.0%, n = 148) were evaluated as MPR. In the internal verification queue and external verification queue, the deep learning model distinguishes the under area (AUC) of the curve of MPR, respectively (95%CI: 0.58-0.86) and 0.72 (95%CI: 0.58-0.85). After integrating clinical features into deep learning models, the combined model obtained in the internal verification queue (AUC: 0.77, 95%CI: 0.64-0.89) and the external verification queue (AUC: 0.75, 95%CI: 0.62-0.87) Satisfied performance.
Table 3. The clinical pathological characteristics of all patients in the group
Figure. Deep learning model and AUC of a combination model
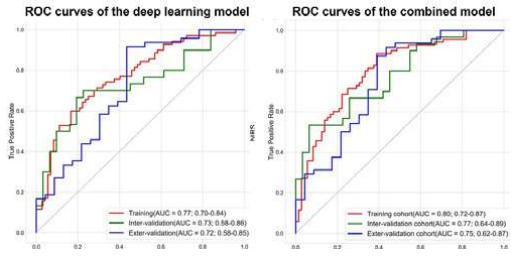
The study first discussed the predictive value of deep learning on the efficacy of NSCLC new assisted immunotherapy, and the deep learning model proposed can effectively predict the MPR of NSCLC patients receiving new assisted immunotherapy.
This material is supported by Astrikon, for medical professionals for reference
Approval number: CN-100529 Expired Date: 2023-8-8
references:
[1] Sonam Puri, Andreas Saltos, Bradford Perez, et al. Locally Advanced, Unresectable Non-Small Cell LUNG CANCER.
[2] A.ROMERO, R.serna, E.NADAL, ET AL. Pre-Treatment CTDNA Levels Significantly Predicts of OS and PFS in Nadim II TRIAL. 2022WCLC. MA06.03.
, Y.She, J.Deng, C.Chen. Deep Learning for Predicting Mpr to Neoadjuvant Immunotherapy in NSCLC. 2022WCLC. MA06.09.
*This article is only used to provide scientific information to medical people, and does not represent the viewpoint of this platform


- END -
Minhang's latest notice: Screening on weekends!Why does the outlet staff nucleic acid be single

Shanghai Minhang again issued a full -member nucleic acid screening noticeOn the m...
Beijing Fengtai Society +1, today's release meeting focuses on returning to school, examinations, holidays and other issues

On June 25, Beijing held the 376th press conference of the prevention and control ...