2022 WCLC lung cancer research progress, interpret the prognostic value of installment on lung cancer stages
Author:Cancer Channel of the Medical Time:2022.08.08
*For medical professionals for reading reference
Sort out the research progress of lung cancer worthy of attention at the 2022 WCLC conference.
The International Cancer Cancer Conference (WCLC) is a multidisciplinary oncology conference dedicated to lung cancer and other chest malignant tumors. Together, the cutting -edge treatment of lung cancer and other breast malignant tumors is committed to reducing the burden on patients, families and society of lung cancer. The WCLC conference in 2022 attracted the attention of experts and scholars in the world, and the latest cutting -edge progress was overwhelming.
In the process of occurrence and development of lung cancer, the early, middle, and evening stages of the occurrence and development of lung cancer are different in the morning, middle, and evening. The principles of tumor treatment at different stages are different, and the prognosis is different. In 2015, IASLC updated the staging system of the lung cancer, and formulated the 8th edition of the international lung cancer TNM staging standard. According to the stages of different stages of tumor development, the principles and methods of treatment can be determined. The staging of lung cancer is also one of the key factors that are related to the prognosis of patients. This article organizes the summary content related to the prognosis in the 2022WCLC conference in the 2022WCLC conference [1-3].
Conside the T3/T4 non -small cell lung cancer extra category T
(Summary number: MA04.03)
NSCLC is defined as T3 and T4 on the same lung lobe or different lung lobes on the same lung lobe. This definition is based on the anatomical location of the additional nodules without considering other prognosis factors. From 2009 to 2014, a study included 4711 patients with T1-4, N0-2, and M0 NSCLC who underwent completely cutting surgery, of which 145 patients had additional nodules (T3-ADD) in the same lung lobe, 174 There are additional nodules (T4-ADD) on different lung lobes on the same side of patients. Studies adopt multi -factor Cox regression model and tendency scoring matching analysis (PSM) General survival (OS).
The results show that through multi-factor COX analysis, and further pass PSM verification, OS of patients with T3-ADD is better than T3 patients (HR, 0.693; 95%CI, 0.526-0.912; P = 0.009), OS of patients in the T3-ADD group of OS group与T2b患者的OS相当(HR,0.949;95%CI,0.724-1.245;p = 0.703),T4-Add患者具有广泛不同的预后,以及单个肿瘤直径最大(& 3cm vs. ≤ 3 cm, HR, 1.701; 95% CI, 1.166-2.482; P = 0.006). OS of patients with T4-ADD (≤ 3 cm) is better than T4 patients (T4-ADD [≤ 3 cm] vs. T4, HR, 0.629; 95% CI, 0.455-0.869; P = 0.005), T4-ADD (≤ 3 cm) Patients are equivalent to the OS and T3 patients (T4-ADD [≤ 3 cm] vs. T3, HR, 0.830; 95% CI, 0.610-1.129; P = 0.119). OS and T4 patients in patients with T4-ADD (& 3 cm). The results of the study show that patients with NSCLC patients with the same leaf (T3-ADD) and same different leaf (T4-ADD, maximum tumor diameter ≤3cm) are combined with nodules, and in the upcoming TNM installment system, it should be further further Verify and consider redefining T2B and T3.
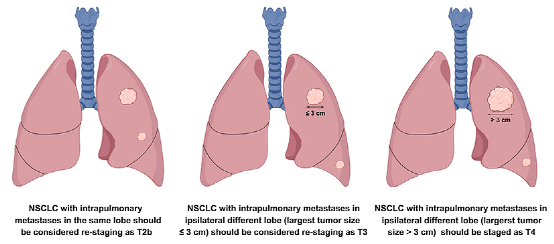
Figure 1. T2B, T3, T4 staging redevelop
The effect of T3 definition features on the long -term survival of T3N0M0 non -small cell lung cancer removal
(Summary number: MA04.05)
Although the 8th edition TNM installment system has improved on the basis of the 7th edition, the T3 category in the installment system still has heterogeneity. A study evaluated the long -term survival of patients with NSCLC patients classified as T3N0M0 based on different T3 tumor characteristics, aiming to determine the method of improving the prognosis of installments.
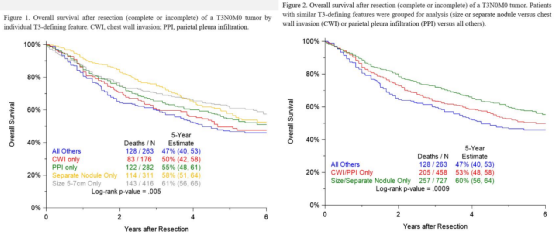
Researchers have inquired about the IASLC database of primitive T3N0M0 NSCLC patients. The main queries are OS based on the characteristics of individual T3 characteristics and resection integrity. Among the 1448 T3n0m0 tumors, 1187 (82.0%) tumor feature single can be judged as T3. The incomplete resection rate of T3 tumor combined with chest wall infiltration (CWI) and pleural wall infiltration (PPI) was 9.8%and 8.4%, respectively. The incomplete resection rate of T3 tumor size & 5 and ≤ 7 cm is the lowest, with 2.9%.
A single T3 definition characteristics are related to the significant differences between OS. When a group of tumors with similar survival and complete resection rates, patients with a size or in the same lung lobe have a separate nodule (SN) tumor patients in the same lung lobe 5 after resection 5 after removal. 5 OS is better than tumor patients characterized by CWI or PPI (60% VS 53%, P = 0.017). The results of the research show that the significant differences in the 5 -year OS are related to the size of tumor size, SN, PPI, and CWI T3 definition. Segment the T3N0M0 tumor, or consider the existence of CWI or PPI when distinguishing the IIA staging, which may improve the accuracy of the prognosis of tumor staging. Figure 2. Prognosis of patients with different characteristics
The incidence and predictive factors of unknown brain metastasis in Period ⅠA non -small cell lung cancer patients
(Summary number: MA04.09)
For NSCLC patients with a clinical diagnosis, the clinical routine does not recommend the use of brain MRI for pre -processing and evaluation of brain metastases. However, the incidence of brain metastases in this patient group is unclear. To this end, a study uses two large American clinical databases to check the incidence and predictive factors of brain metastases in phase IA NSCLC patients.
Researchers selected T1N0 NSCLC patients from the National Cancer Database (NCDB) and National Lung Cancer Screening Research (NLST). NLST is a random multi -center test. Compared with the current and smoking elderly lung cancer radiology screening methods, it includes data from the lung cancer confirmed by 1971 biopsy. The incidence of brain metastases that meets the standards of the standard is first evaluated in NCDB, and then evaluated separately in NLST to report that patients with liver, lung or bone metastases are excluded from this analysis. In the NCDB queue alone, multi -factor logistic regression evaluates factors related to the increase of the possibility of brain metastases.
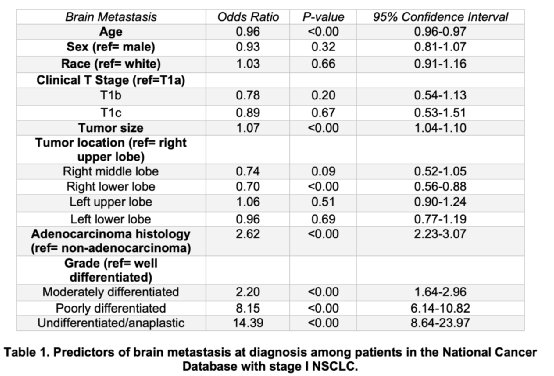
The results showed that the NCDB group was included in 121338 patients with T1N0 NSCLC, and NLST was included in 618 patients with T1N0 NSCLC. The incidence of brain metastases during diagnosis was 1.9% (n = 2531) and 2.6% (n = 16). In the multi -factor adjustment and analysis of the NCDB queue, the staging is the most closely related factors related to brain metastases; compared with the well -differentiated tumor patients, the probability of brain metastases in patients with unlimized tumors is 14 times that of good tumor patients (OR 14.4.4 , [8.64-23.97], P <0.001). In the NCDB group of patients with unimincharized adenocarcinoma, the incidence of brain metastases was 4.3%during diagnosis, and even higher than 4.1%of patients with T2 tumor patients. The United States usually recommends MRI screening for patients with T2 tumor. Other factors related to the increase in brain metastases include adenocarcinoma tissue and tumor size, and the position of the right lower lobe tumor is related to the reduction of brain metastases. Researchers pointed out that the incidence of brain metastases in patients with T1N0 NSCLC cannot be ignored. The incidence of brain metastases of patients with NCDB and NLST is 1.9%and 2.6%, respectively. Small tumors of lymph nodes, especially patients with low -differentiated and unlimited adenocarcinoma, may be necessary to use brain MRI before treatment.
Table 1. Predictive factors for patients' brain metastases during diagnosis
This material is supported by Astrikon, for medical professionals for reference
Approval number: CN-100217 Expired Date: 2023-8-3
references:
[1] Hang Su, haojie si, xiaofengxie, et alconsides t classification for T3/T4 non-Small Cell LUNG CANCER with AdDitional Nodule (s). MA04.03.
[2] Edouard Marquesa, VANESSA J. CILENTO, Dori Giroux, ET Al.t3 Defining Features Influence Long Term Survival AFTER Resection of T3N0M0m0m04.054.05.
[3] Malaika Syeda Zaidi, Alexandra Potter, Leah Backhus, Et Al.The Incidence and Predictors of UnsusPected Brain Metastases in Patients with Stage IA NSCLC.MA04.09.09.
*This article is only used to provide scientific information to medical people, and does not represent the viewpoint of this platform


- END -
Beijing yesterday added local \"4+4\"
From 0:00 on June 7 to 24, 4 new cases of confirmed cases in Beijing (including 1 asymptomatic infected cases were transferred to the diagnosis case) and 4 asymptomatic infections, and no suspected
The third batch of aid medical teams in Shandong Province sent the Tibetan medical team to Tibet to support the epidemic prevention and control
Data-version = 0 data-vwidth = 1920 data-vHeight = 1080 transcoding = 1 / Qilu.com · Lightning News, August 17th, on August 17, Shandong Province selected the third batch of medical teams c