How to do CTDNA?What precautions?ESMO super full guidance
Author:Cancer Channel of the Medical Time:2022.08.03
*For medical professionals for reading reference
The ESMO Precision Medicine Working Group supports CTDNA to guide clinical practice of advanced tumor.
At present, liquid biopsy technology is showing a rapid development, and circulating tumor DNA (CTDNA) test is one of the detection targets. Although the clinical practical evidence of CTDNA is increasing, if it is carried out in clinical practice, it is necessary to confirm the analysis results and the clinical correlation, and the standards of evidence support in terms of detection quality.
Recently, in the international authoritative magazine Annals of onCology, experts from the European Cancer Internal Science Association (ESMO) Precision Medical Working Group issued a report of CTDNA applied to the clinical practice of tumor and conducted related recommendations.

Screenshot of the thesis
CTDNA test report specification
The content of the CTDNA test report depends on the expected use of the CTDNA detection type and detection. In addition to the recommendations of the general clinical molecular laboratory, the elements of the CTDNA test report have been listed in Table 1, and can be queried on the following URL:
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.annonc.2022.05.520
Table 1: CTDNA test report specification

Recommendation of CTDNA detection technology
The blood collection time of CTDNA detection should be carefully selected according to clinical conditions, because different factors will affect the release of CTDNA (for example, the process of treatment, complication and surgery). The detection of CTDNA-micro residual disease (MRD) after surgery should be performed at least 1 week after surgery. For large healing surgery, it may take 2 weeks or longer. For CTDNA tests for the purpose of classification of advanced cancer genes, blood collection should be avoided when actively treating effective or without progress to minimize false negative results.
The selection of blood sample collection tubes is mainly based on sample processing time and detection methods, so you should choose carefully.
If the plasma sample does not extract CTDNA temporarily, it should be stored for a long time at -80 ° C, and the temperature change should be controlled to minimize, and repeated freezing fusion should be reduced as much as possible.
Pseudoma (actually exists in tumors but not detected) is an important problem for CTDNA detection. It may be that the level of plasma CTDNA is low, insufficient detection sensitivity, or "non-shedding tumor (Non-shedding" (that is, the tumor itself is not released CTDNA).
CHIP is a common cause of false positives in CTDNA detection. Therefore, it is recommended to perform synchronous detection and analysis of plasma CTDNA and white blood cell DNA when conducting tumor inhibitory genes such as DNA repair genes, and then eliminate Chip mutations.
CTDNA may detect the pathogenic germ variation (such as BRCA1, BRCA2, PALB2) of the disease -induced genes of cancer, and the detection of such variations requires a verified detection method for return detection to confirm that it is system variation and embryo Mutations.
In the future, clinical gene typing detection should be applied to assessing tumor purity in order to predict reliability of unlocked results and reliably conduct real -negative predictions. This can be achieved through biological information analysis, such as detecting an alternative tumor instead of CHIP. Derivative mutations have sufficiently high -level gene ratio, or orthogonal purity analysis.
Recommendation of special tumor parts
Because CTDNA detection in metastatic central nervous system tumors and primary brain tumors is less sensitive, liquid biopsy is not suitable for such patients for geneticism. Just think about trying.
Recommendations for advanced cancer gene typing
Only when the liquid biopsy has very high analytical and clinical specificity, and the positive results have predictive value, it may affect the selection of standard treatment schemes, can it be considered routinely in the clinical practice of advanced tumors.
Based on liquid biopsy has the advantages of rapid issues. Therefore, for most advanced tumor patients, it is recommended to choose liquid biopsy as an alternative option for tissue genetic types, especially those invasive tumors that take a certain time to get the test results, such as such as the detection results, such as, for example Recent non -small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). In addition, when the tissue biopsy is not available or the patient is not suitable for organizational geneticism, liquid biopsy can also be selected.
Whether it is initial treatment or back -line therapy, the specimen should be collected during the progress of the tumor for liquid biopsy. This is due to the sensitivity of CTDNA detection when the tumor responds to the treatment response to the treatment.
For the genetic types of advanced cancer, the choice between real-time (RT) -PCR, digital (D) PCR and NGS detection in clinical practice should be based on the availability, reimbursement, and the "1 category of targeted targeted categories of categories and each tumor type. The quantity of genetic mutation is determined.
Carefully interpret the pathogenic variation of high -lying cancer susceptible genes (such as BRCA1, BRCA2, PALB2), and should be used to determine systems and embryo variations.
In view of the clinical sensitivity and negative prediction values of CTDNA, CTDNA results for not detectable mutations should be prompted for return tumor tissue testing. If an expert can confirm that there is sufficient CTDNA purity in the sample (the overall CTDNA level or the allele of the detected mutation is analyzed), there may be no return tumor tissue testing. Due to the low sensitivity of CTDNA detection to genetic fusion and copy number variation, these mutations should be detected in the tissue when conditions permit.
All oncologists should have the opportunity to contact MTB (molecular oncology expert committee) to ensure the correct interpretation of the results by receiving education as soon as possible, and discuss difficult cases to ensure proper decisions.
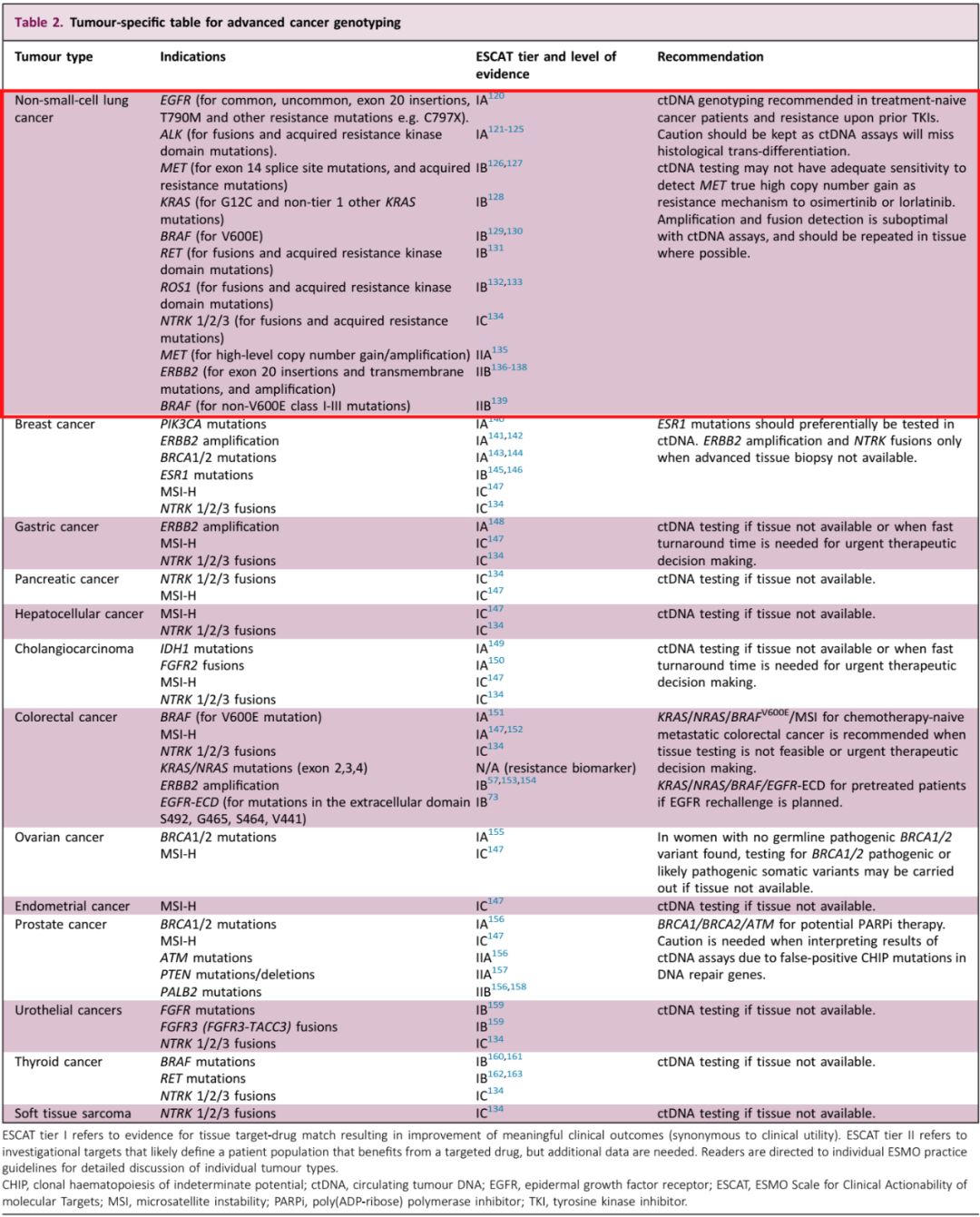
Table 2: CTDNA test recommendation for different advanced cancer gene classification
Recommendation of late NSCLC CTDNA testing:
not
1. Recommend initial treatment and previous TKI treatment patients to perform CTDNA testing;
2. CTDNA detection may miss the transformation of historical transformations and should be cautious;
3. For the increase in the number of copies of Oshitinininib or Lalotininini, the number of copies of MET, the sensitivity of CTDNA detection may not be enough;
4. CTDNA detection amplification and fusion effect is not good, and it should be repeatedly tested in the organization as much as possible.
Recommendations for advanced cancer CTDNA dynamic monitoring
There is no sufficient evidence to indicate that CTDNA needs to be detected regularly during treatment. Although the dynamic changes in early CTDNA were closely related to the prognosis, and it may be found to be resistant to drug resistance a few months before clinical progress. However, there is currently no sufficient evidence that the adopting intervention measures based on these discoveries can improve the prognosis. In the future, random intervention in clinical research may be performed to evaluate the effectiveness of CTDNA monitoring.
Early cancer MRD/MR test recommendation
A number of clinical effectiveness studies have shown that for early cancer after healing treatment, optimized and verified CTDNA-MRD testing methods can be used to predict future recurrence risks.
In the absence of evidence of forward -looking clinical trials, there is currently no evidence that MRD/MR testing can be used to guide clinical treatment or safe dehuminar.
references:
[1] J. Pascual, G.ATTARD, F.-C. Bidard et al. Esmo Recomgends on the user of circulating tumour dna assays with a cancer: a report from the esmo preculation money.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.annonc.2022.05.520
not
First of this article: Rare target ecosystem in the medical community
Organize this article: Tumor Baby
Editor in charge: Sharon
- END -
Ten questions about fertility health knowledge
July 11 is the 33rd World Population Day. The National Health and Health Commission has determined the Chinese theme of the World Population Day as life is supreme, guarding the future. Under the co
Jindingling Center, Tianxin District, Changsha City to carry out the elderly health propaganda Zhou righteous consultation activities

July 25-31, 2022 is the fourth Elderly Health Publicity Week in the country. In or...