JAMA Sub -Journal: BRCA1/2 mutations are related to 7 kinds of cancer!Or will be inherited to the child ...
Author:Cancer Channel of the Medical Time:2022.07.20
*For medical professionals for reading reference
Breaking cognition!
In the 1990s, researchers discovered that BRCA1 and BRCA2 were pathogenic genes for genetic breast cancer and ovarian cancer syndrome. In addition to promoting the development of genetic testing, based on this gene pathogenic variation related to homologous recombinant repair defect mechanisms, researchers have developed a polygonosine di -phosphate polymerase (PARP) inhibitor. With BRCA1 and BRCA2 pathogenic variations were discovered in patients with prostate and pancreatic cancer, and PARP inhibitors' good effects on these cancers, the application boundaries of BRCA1 and BRCA2 gradually widen.
Recently, a large -scale case -in -law study found that the type of cancer related to the pathogenic variation of BRCA1 and BRCA2 far exceeded the previous analysis of breast cancer, ovarian cancer, prostate cancer, and pancreatic cancer. Related, the results were published in Jama Oncology.
Screenshot of the thesis homepage
BRCA1/2 mutations are also biliary cancer,
The risk of esophageal cancer and gastric cancer increases by 3-16 times!
Researchers used the Japanese biological sample library to conduct a large -scale sequencing research on 14 common cancer types for 6,3828 patients (average age 64, 42%for women) and 37086 participants. Study estimates the risk of each type of cancer, and determines the clinical characteristics related to the state of the carrier of the pathogenic mutant. At the same time, it also investigates the effectiveness of family medical history in the detection of patients with pathogenic variations.
1. Biliary cancer
Surprisingly, the risk of BRCA1's pathogenic mutations caused the risk of gallbladder cancer to risks by 16 times (OR, 17.4; 95%CI, 5.8-51.9)!
BRCA1 pathogenic mutation rate of biliary cancer patients is 1.1%. According to the increase in cancer in relatives, pathogenic variations are enriched among biliary cancer carriers.

The correlation between BRCA1 and BRCA2 disease mutations and 14 cancer type risks

14 types of cancer types and contrasts of BRCA1 and BRCA2 pathogenic mutations

Based on 7 types of cancer types of family history analysis patients BRCA1 or BRCA2 joint carrier frequency
The cumulative risk of biliary cancer at the age of 85 at the age of 85 is 11.2%(95%CI, −1.1%to 22.1%)

Absolute risk of bile duct cancer estimation
2. esophageal cancer
BRCA2 disease mutations are significantly related to the risk of esophageal cancer risks by nearly 5 times (OR, 5.6; 95%CI, 2.9-11.0).
Patient's BRCA2 pathogenic mutation rate is 0.7%.
The cumulative risk of esophageal cancer at the age of 85 at the age of 85 (95%CI, 1.7%-8.5%) at the age of 85.

Absolute risk of esophageal cancer estimation
3. Stomach cancer
BRCA1 (OR, 5.2; 95%CI, 2.6-10.5) and BRCA2 (OR, 4.7; 95%CI, 3.1-7.1) pathogens increase the risk of gastric cancer by 4 times. BRCA1 and BRCA2's diseased occurrence rates of gastric cancer patients are 0.3%and 0.9%, respectively.
BRCA1 pathogenic mutations at the age of 85 were 21.3%(95%CI, 6.9%-33.4%), and BRCA2 was 19.3%(95%CI, 11.9%-26.0%)
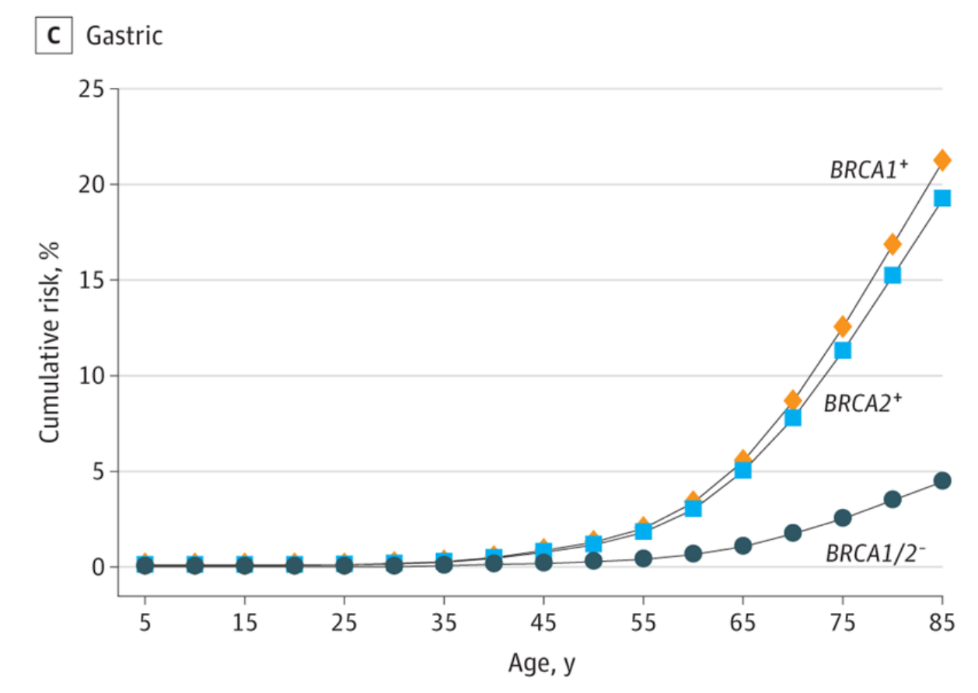
Absolute risk of gastric cancer estimation
4. Breast cancer
BRCA1 (OR, 16.1; 95%CI, 7.1-36.7) and BRCA2 (OR, 10.9; 95%CI, 7.0-17.1) have increased the risk of female breast cancer by 15 times and 10 times. BRCA2 has raised the risk of male breast cancer to 68 times (OR, 67.9; 95%CI, 19.2-239.8)!
Male breast cancer patients with pathogenic mutation BRCA2 are high (18.9%), but BRCA1's carrying rate is not high (1.89%). BRCA1 and BRCA2's diseased occurrence rates of female breast cancer patients are 1.3%and 2.5%, respectively. According to the increase in cancer in relatives, pathogenic mutations are enriched among patients with female breast cancer.
For the cumulative risk of the 85-year-old carrier of the diseased and sudden change, breast cancer is "topped" in BRCA1 and BRCA2, of which BRCA1 is 72.5%(95%CI, 20.4%-90.5%), and BRCA2 is 58.3%(95 (95 %CI, 38.3%-71.9%), which means that more than half of the pathogenic leaders will suffer from breast cancer before the age of 85.

Absolute risk of breast cancer estimation
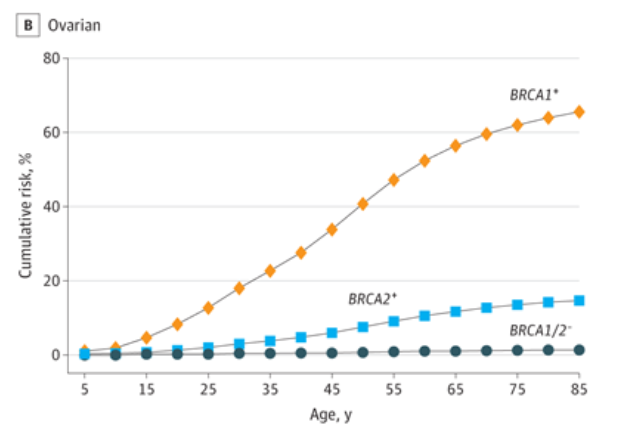
5. Ovarian cancer
BRCA1 (OR, 75.6; 95%CI, 31.6-180.6) and BRCA2 (OR, 11.3; 95%Ci, 5.6-23.0) disease mutations increased the risk of ovarian cancer 75 times and 11 times.
In addition to breast cancer, the second is patients with ovarian cancer (BRCA1, 4.86%; brca2, 3.42%). According to the increase in cancer in relatives, pathogenic variations are enriched among patients with female ovarian cancer.
Carrying BRCA1 pathogenic variation, at the age of 85, its cumulative risk of ovarian cancer was 65.6%(95%CI, 12.8%-86.4%), and BRCA2 was 14.8%(95%CI, 4.6%-23.9%). Absolute risk of ovarian cancer estimation
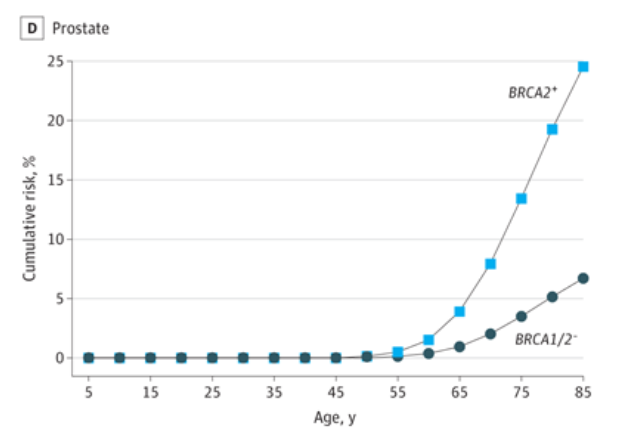
6. Protestant cancer
The increase in the risk of prostate cancer is mainly related to BRCA2 pathogenic mutations, and the risk has increased by 3 times (OR, 4.0; 95%CI, 2.5-6.5).
Patient's BRCA2 pathogenic mutation rate is 0.7%.
The cumulative risk of prostate cancer at the age of 85 at the age of 85 is 24.5%(95%CI, 6.9%-38.8%), and has a high "BRCA2 list" list, only after breast cancer.
Absolute risk of prostate cancer estimation

7. pancreatic cancer
BRCA1 (OR, 12.6; 95%CI, 3.7-42.8) and BRCA2 (OR, 10.7; 95%CI, 5.1-22.6) pathogens increase the risk of gastric cancer by 12 and 10 times the risk of gastric cancer.
BRCA1 and BRCA2's diseased occurrence rates of BRCA1 and BRCA2 are 0.7%and 2.3%, respectively.
The cumulative risk of gastric cancer at the age of 85 at the age of 85 was 16.0%(95%CI, 3.9%to 32.1%), and BRCA2 was 13.7%(95%CI, 3.7%-22.8%).
Absolute risk of pancreatic cancer estimation
The study also found that 4128 patients (6.3%) had more than one type of cancer. With the increase of the type of cancer, the carrying rate of the two pathogenic mutations is on the rise: the porting frequency of the BRCA1 pathogenic variation is 0.44%, 0.85%of the two types of cancer, and 0.69%of the three types of cancer; in BRCA2 They are 0.97%, 1.40%, and 1.74%, respectively.
Among the 14 cancers, the pathogenesis of diseased and sudden carrying rate of various cancer patients is diagnosed

The results of this large -scale case comparison show that the pathogenic mutations of BRCA1 and BRCA2 are related to as many as 7 cancer types. Among them, BRCA1 pathogenic mutations and five types of cancer -ovarian cancer, female breast cancer, biliary cancer, gastric and pancreatic cancer; BRCA2 pathogenic mutations and 7 cancers -female breast cancer, gastric cancer, ovarian cancer, male The risk of breast cancer, pancreatic cancer, prostate cancer and esophageal cancer.
It can be seen that the type of cancer related to the pathogenic variation of BRCA1 and BRCA2 may be wider than the scope determined by the analysis of major European people. The discovery of these risks and analysis of the associated with the family history of cancer and clinical phenotypes may broaden or even rewrite the application guide for genetic testing, treatment schemes and PARP inhibitors of each cancer type.
PARP inhibitors are developed based on the mechanism of homologous reorganization repair defects related to the causal variation in BRCA1 and BRCA2. PARP inhibitors have now been found in the treatment of prostate and pancreatic cancer that is rich in pathogenic and enriched. Researchers recognize that the BRCA1 and BRCA2 gene detection should be expanded, but further research needs to be expanded to what scope is expanded. If the clinical trials of PARP inhibitors in these three cancer types (biliary cancer, esophageal cancer, gastric cancer) can confirm its clinical effectiveness, the necessity of this expansion will be greatly increased.
Expand: Except "Star" mutant BRCA1/2,
This gene mutation is also worthy of vigilance!
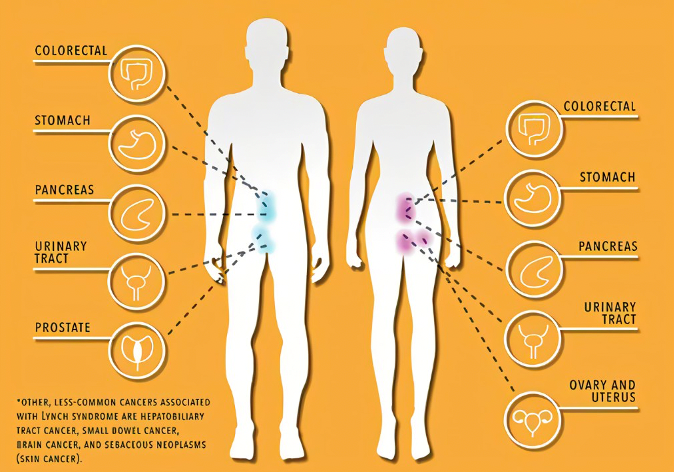
Link Syndrome (LS) is a kind of ingredients in genetic tumor syndrome. Embryo variants are suffered by 4 error -mixed fixing genes (MMR), or epithelial cell adhesion molecular (EPCAM) genes, causing lack of MSH2 expression. cause.
Compared with normal people, patients with LS patients suffer from colorectal cancer (52%to 82%vs.5.5%), endometrial cancer (16%to 60%vs.2.7%), and other risks of cancer such as gastric and ovarian cancer Obviously rising. Among them, LS accounts for about 2%to 4%of all patients with colorectal cancer, which is the most common genetic colorectal syndrome.
Picture source: Dana-Farber Cancer Institute
Foreign research statistics have found that the incidence of LS in the crowd is as high as 1/279, indicating that the disease is a common genetic tumor susceptible syndrome [3], but it is far from the synthesis of hereditary breast cancer-ovarian cancer synthesis Focus on a considerable attention. At present, all LS patients know that they do not exceed 1.2%of the diagnosis, miss the early diagnosis of LS, and then perform strict cancer monitoring and/or preventive surgery to prevent LS -related cancer opportunities. [4]
LS's previous identification and diagnosis mainly depends on family history. The international Amsterdam diagnostic standard requires more than 3 cases of LS -related tumor patients in the family department, but this standard has certain limitations in domestic application. Therefore The standard of the Chinese crowd Lynch syndrome is used for clinical diagnosis [5].
The Chinese LS family standard is patients with ≥2 patients with colorectal cancer with ≥2 cases of tissue pathology. Two of them are the relationship between parents and children, children, brothers and sisters (first -level blood relatives), and meet the following conditions: (((((one level of blood relatives): ( 1) ≥1 patients with multiple colorectal cancer (including adenoma); (2) ≥1 cases of sector cancer incidence <50 years; (3) ≥1 cases of LS related intestinal malignant tumors (including LS Gastric cancer, endometrial cancer, small bowel cancer, ureteral and renal pelvic cancer, ovarian cancer and hepatobiliary system cancer). For patients who meet the above standards, they should conduct LS -related gene screening and conduct targeted follow -up monitoring of the type of pathogenesis.
Picture source: consensus of Chinese family hereditary tumor clinical diagnosis and treatment experts
references:

[1]Momozawa Y,et al.Expansion of Cancer Risk Profile for BRCA1 and BRCA2 Pathogenic Variants.JAMA Oncol.2022 Jun 1;8(6):871-878.doi:10.1001/jamaoncol.2022.0476.PMID:35420638;PMCID : Pmc9011177.
[2] https://www.medscape.com/viewArticle/976993?src=
[3] Win, Aung Ko, et al.cancer epidemiol biomarkers prev. (2017): 404-412.
[4] Hampel H, de La Chapelle A.The Search for Unaffected Individuals with Lynch Syndrome: Do the Ends Justify the Means? Cancer Prev Res (Phila); 1940-6207.capr-10-0345.pmid: 21205737; PMCID: PMC3076593.
[5] Consensus on the Association of Clinical Diagnosis and Treatment of Chinese Family Hereditary Tumor (2021) (4) -Cathery of family hereditary colorectal cancer [J]. Chinese Oncology Clinical, 2022,49 (01): 1-5
Frontier of the tumor you want
Please pay attention to the doctor station 注
1. Scan the QR code below
2. Click to download the app

3. Open the doctor station app and click on the upper right corner

4. Find the tumor in the channel
And follow

Download the doctor's station app and subscribe anytime, anywhere ~
The first release of this article: the medical world tumor channel
Author of this article: lily

Audit expert: Yu Jiangyong Beijing Hospital
Editor in charge: Sweet
- END -
How much does Pingtan know?

recentlyNon -Heritage Festival activityKaisen in the town of TaiwanBest carved, sa...
Seeing people and seeing life, let the non -heritage really "live"

Not long ago, the results of the 2021 Chinese Non -Heritage People publicity activ...