Inventory of people in the car HMI design due to factors
Author:Everyone is a product manager Time:2022.06.17
Editor: With the continuous development of smart cars, the status of HMI has become higher and higher, and car manufacturers pay more and more attention to user experience. The author of this article mostly take stock of the factors contained in the car HMI design from the four four of the sensory, cognition, decision -making and automation. Interested friends take a look.

Driving is an information processing activity. During the driving process, the driver continues to obtain information and process information from various sensory channels, so as to make decisions and take appropriate action to control the vehicle movement. This article will take you from the four parts of sensory, cognition, decision -making, and automation ...
1. Sensors
1. Vision
(1) Vision
The ability of the eye to distinguish the object is called vision, and the vision is divided into calmness and dynamic power. The calmness is the vision of the driver when the driver is still, and the dynamic vision is the vision of the driver during the car movement. When people with normal vision observing distant objects, the dynamic vision has increased rapidly with the increase in speed. If the speed of 60km/h is 60km/h, you can see the traffic symbol at 240M; when the speed is 80km/h, you can only see clearly clearly clearly clearly. Traffic logo at 160M. In addition, according to the NHTSA2010-0053, the driver's sight cannot leave the road ahead for too long, and 2 seconds are recognized safety time limit.
(2) Vision
Vision refers to the scope that can be seen on both sides of the viewing point on both sides of the eye. The size of the field of vision is related to the speed of the vehicle. As the speed increases, the driver's field of vision is significantly narrower. If the speed is 40km/h, the field of vision is 90 ° ~ 100 °; when the speed is 80km/h, the field of view is 60 °. Useful Field of View (UFOV) refers to the interval diameter of the continuous movement of the eyes between different viewing centers. In this perspective, the goals can be seen. UFOV has proven to collide with the vehicle collision risk and obstacles. The tendency of collision and falling is related.
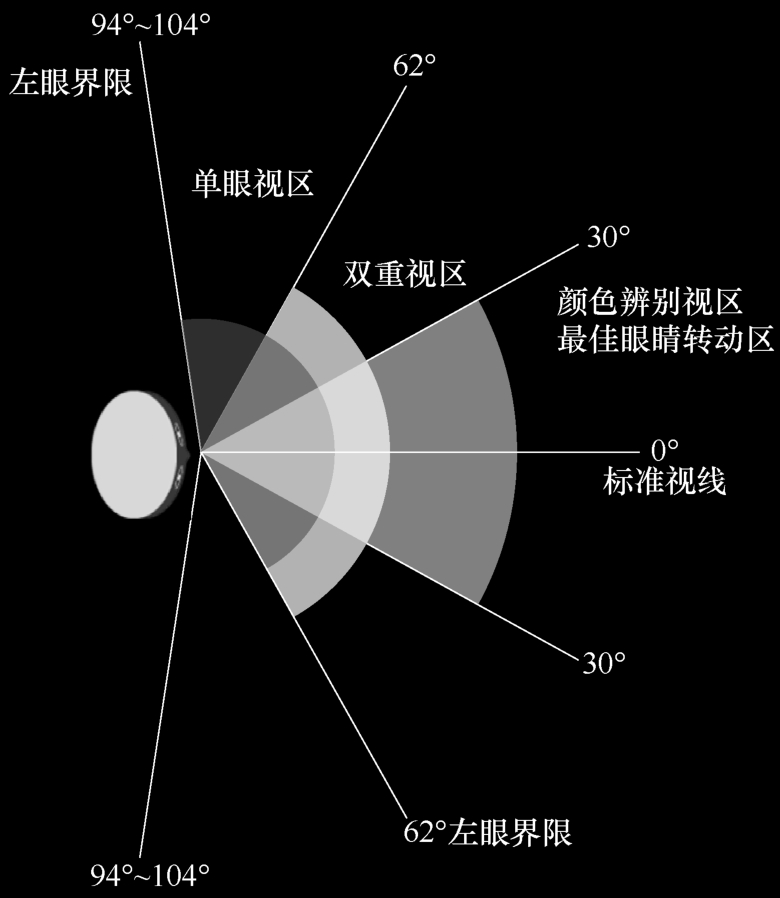
Human Eye Vision Scope
(3) Color
Human identification and feeling of different colors are called color. People have different reactions to different colors. For example, red light is easy to visually visible and stimulated, making people alert people; yellow light has the highest brightness, the most reflected light intensity, and it is easy to evoke people's attention; People are calm and security. Therefore, the red light is used as a ban on banking in the traffic engineering, yellow light is a warning signal, and green light is used as a traffic signal.
Baidu car networking visual specification
2. Hearing
When the visual channel of human drivers is occupied, the hearing interaction can wake up and guide the driver's attention. The types of sound symbols can be divided into simple sound, earmark sound, symbolic sound, and voice information.

Simple sounds can attract the attention of the driver, and the combination of visual interaction can shorten the driver's reaction time. The earmark sound is suitable for conveying the prompt information, which can be applied to a low degree of danger. Simple sound and ear labels need to be learned in advance, otherwise it may lead to an error reaction.
The symbol of sound is context, and it can promote the understanding of the driver's understanding of emergencies, but it is more interference and a low degree of friendship. The voice information carried by voice messages will lead to a slower response speed, but with the improvement of the intelligence level of the vehicle, voice messages can meet the high demand for information details.

Xiaopeng Auto Voice Assistant Little P
3. Touch
In the car, most operations and information input, etc., are done by hand before voice interaction. The design of many keys on the car is also to facilitate the driver's "blind operation": without the eyes, you can complete the input of the information with just touch. At present, under the trend of large -screen smart cockts, many manufacturers have added tactile click feedback on the touch screen.

In addition, as a warning reminder, compared with the visual and auditory prompt method, related studies have shown that the visual prompts are the lowest, and the tactile prompt method is more disturbing. Therefore, in a very urgent driving scenario, you can use tactile prompts to maximize the vigilance of the driver.
2. Cognitive Cognition
1. Attention
During safe driving, the driver's attention is a very critical factor. You need to understand a new concept in visual attention, focusing on the area of interest, AOI). AOI refers to an external physical area. In this area, people can find information associated with the corresponding tasks. The distance between the two AOI determines how much visual effort is made, called information capture effort. In the actual driving scenario, the advantage of looking up to show HUD is to shorten the distance between the road AOI and the central control screen AOI.
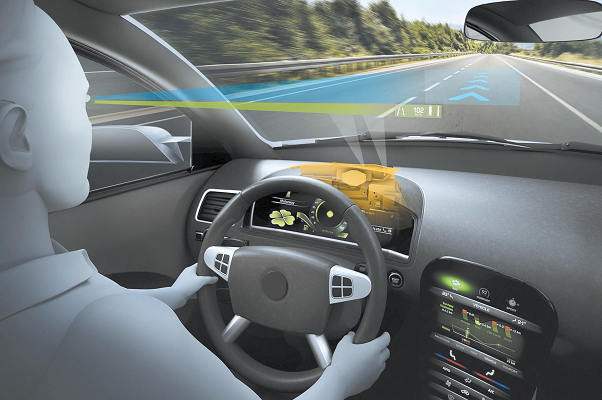

AR-HUD
Our visuals usually have two parallel processes: they automatically group the similar content in the external environment, and at the same time use selective attention to find the information we want to pay attention to. Therefore, when displaying information, the relevant information organic combination is important for more effective visual search.

Format tower principle
The perception of the sound is dominated by two attention: one is differentiation, such as listening to different sounds at the same time; the other is selective attention, such as we focus on a certain sound. People generally distinguish the sound (recognition) sounds through several different sound elements, including syllables, height, sound space position and timing. The sound design in the cockpit needs to be clearly identified to the driver's main information and secondary information. Weilai Automobile 5.1 speaker configuration

2. Memory
Human memory can be divided into work memory and long -term memory. Work memory is a relatively active memory, temporary, and used to store new information. It has high requirements for attention. Long -term memory is our long -term storage about the phenomenon of this world and how we do things. In safe driving, work memory is more important.
In work memory, language information is stored in text and voice; spatial information is stored by sound space positioning and image. When a short text information needs to be conveyed to the driver, the best way is to pass the voice, so that the information will not be lost when the auditory sense is received when the information is received. Visual retention is long. However, if it is a relatively long information, it can still be written for a long time in writing, or repeated voice information.
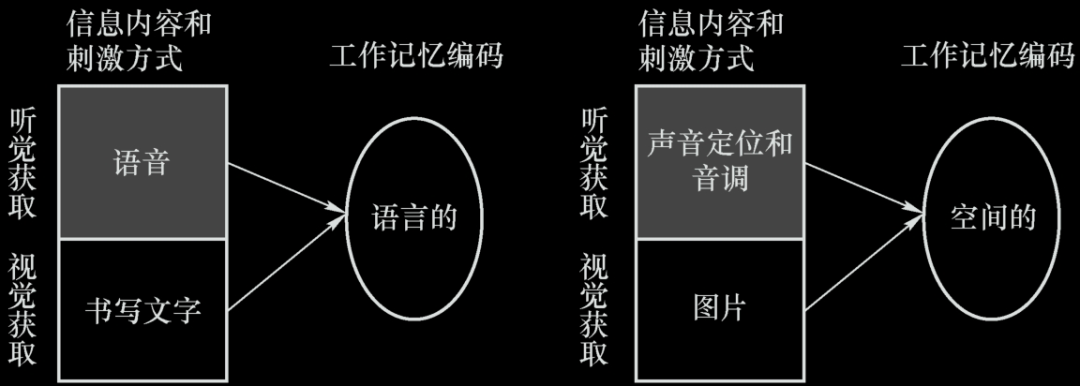
How much people can remember at the same time are also related to each matter occupied. Do not require users to remember more than 5 numbers or letters at the same time.

3. Work load
Workload refers to the workload of the human body within a unit time. Driving work load refers to the information processing capabilities of the driver on the influence of the road, traffic, and the environment, and more refers to the psychological load of the driver.
For a skilled driver, highway driving is a scene where he is familiar with him. He also has extra psychological resources to complete other tasks, such as calling and operating vehicle interfaces. And if an accident or road construction occurs in front, he needs to change the aisle or drive out of the highway, then the demand for these tasks on his psychological load will reach the critical point. At this time, if there is a call, he may not answer it.
NASA-TLX working load meter
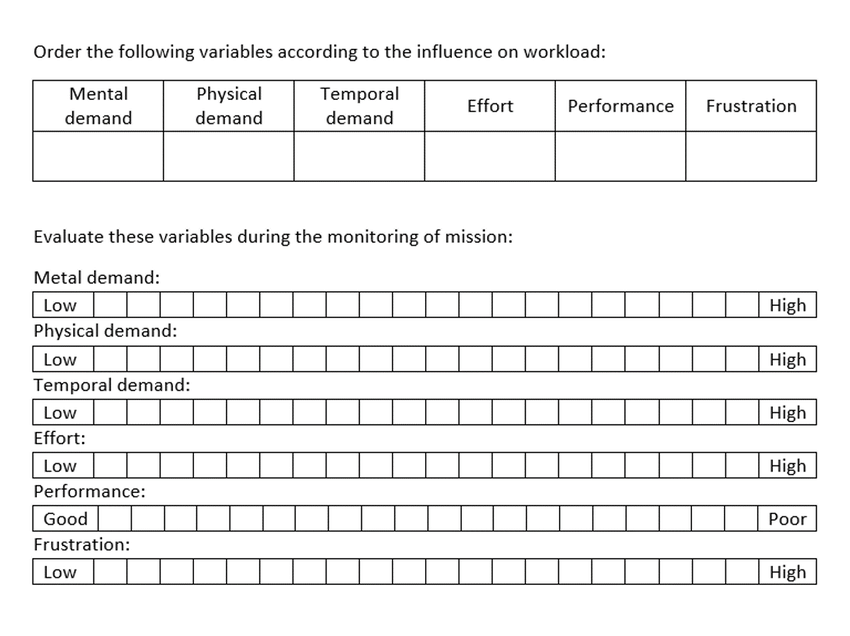
3. Decision Decision
1. SRK behavior theory
Behavioral-based behavior models are divided into three different levels based on the complexity of people's work according to the complexity of cognitive participation. The operation can also be called instinct.
For example, the old driver can drive the vehicle proficiently, and the eyes, the eyes, and the hands and feet are tacit. The corresponding interfaces are mostly state interfaces, such as the safety of the vehicle and the speed of the vehicle. The operation based on the rules (RBB), operate in accordance with various rules, such as keeping lane lines and compliance with traffic laws, it belongs to such operations. The guide -type interface, such as driving operation prompts, collision time.
Based on Knowledge-Based Behavior (KBB), the problems they face are relatively complicated and require a lot of knowledge, analysis and judgment. In the interface design, it is necessary to provide as much information as possible to help the driver's thinking.
AR-HUD RBB guide information
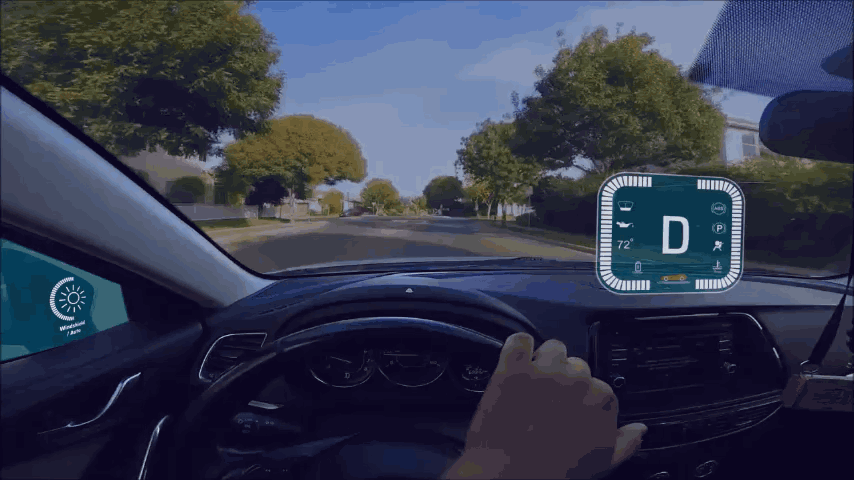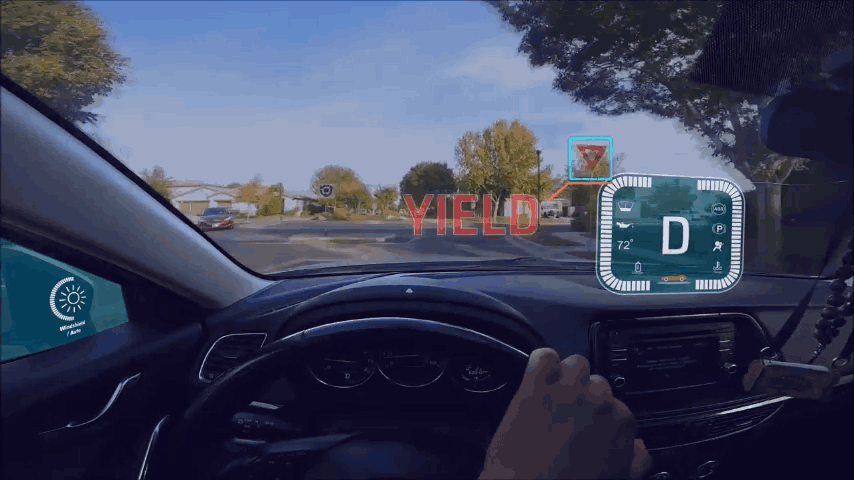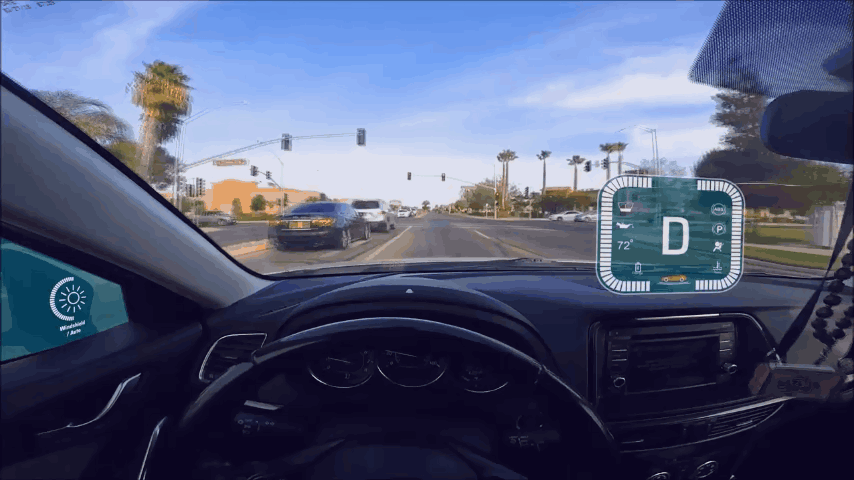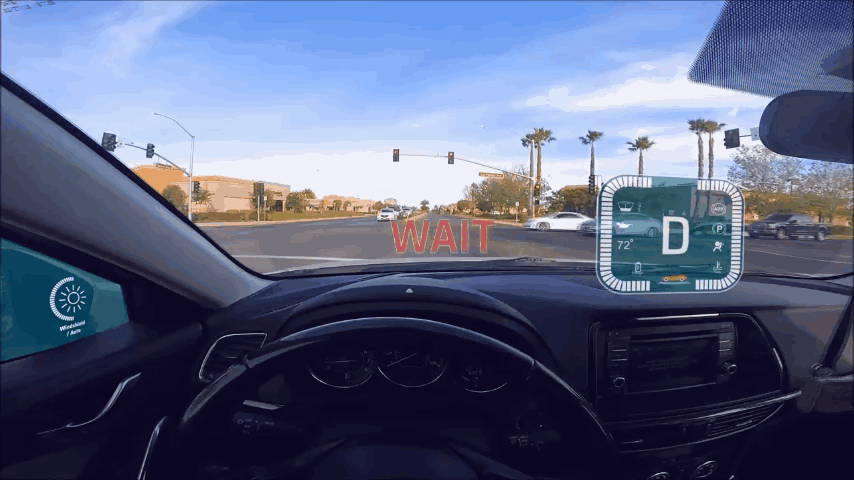
2. Situation consciousness
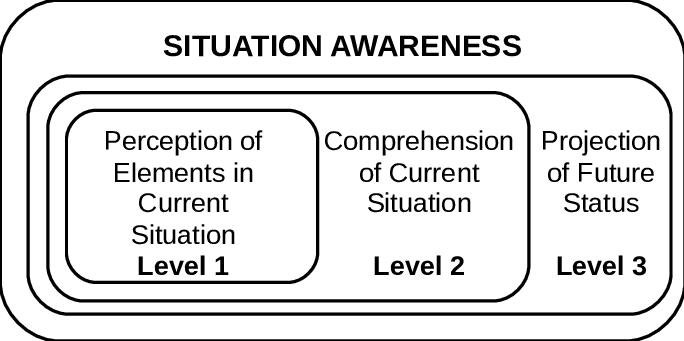
Situation Awareness (SA) is what the driver is aware of what is happening around him, understands the meaning of relevant information, and what the information means to the future.
Scenario consciousness is divided into three stages: perception, understanding, and prediction. The perception stage can provide the driver with the basic information of the current state, goals, intentions and plans. To understand the process of reasoning and the constraint restrictions and choices considered. During the prediction stage, the driver provides the possibility of prediction, prediction, success or failure of the future state.
Three stages of context consciousness
Fourth, automated automation
1. Fantastic
Driving distinction means that the driver's attention is transferred from safety driving activities to other competitive activities, which is easy to occur under the conditions of assisting driving.
When the level of automation is L3, the driver does not need to supervise the road conditions, and the driver can participate in some non -driving sub -tasks, such as using mobile phones to chat and watch videos. This will reduce the awareness of the driver's scenario. You need to understand the previous situation in order to make response measures. This has led to a long period of time and decreased decision -making ability. The system no longer trusts, and the sense of autonomous driving experience is worse.
Designing the receiving behavior in the background of autonomous driving, the designer needs to focus on the situation when the driver is not in the OUT-OF-the LOOP.
Autonomous driving auxiliary system receiving prompt

2. division of labor
Automation systems need to clarify their respective division of labor in interaction with people. What tasks can be completed, what task is done by the system. If the information processing and decision -making process of the automation system does not communicate with people, people will be in the dark and can't touch it. Therefore, the feedback design of the automation system is very important.
In addition, division of labor can also be between road users. With the development of Vehicle to Vehicle (V2V), you can understand their intentions through vehicle communication. For example, in the process of ramp merging, it can be better connected and avoided. 3. Trust
"Trust" is very important in automated human -computer interaction. The relative relationship between the two mainly includes three types: proper trust, insufficient trust, and excessive trust. Approndriate Trust refers to the consistent level of the driver's subjective trust as the level of objective trust. Insufficient trust (Under-Trust) means that the driver's subjective trust level is lower than the level of objective trust in the system. Over-Trust often has the ability of the driver to overestimate the ability of the autonomous driving system and abuse automated functions.
Smart car confidence signal
4. Acceptance

Compared with trust, acceptance is a more underlying factor, and trust is based on acceptance. Acceptance refers to people's willingness to use new information technology. It can be understood in terms of usefulness and ease of use. Useability is the measurement of the driver's usefulness of the automation system, and the ease of use is to how much the driver thinks the automation system is used. One of the ways to increase acceptance can be achieved through anthropomorphic and emotional appearance characteristics to provide natural and emotional interaction feelings.
Weilai Automobile Voice Assistant NOMI
5. Summary

Smart cockpit provides rich functions and convenient operations for drivers and passengers. It is very important to understand the bottom layer of human factors. The design of the car HMI design always implies the influence of human factors ...
Reference materials:
"People -oriented Smart Car Interactive Design HMI"
Yang Xue. Car-HUD road security reminder information interface design principles study research
Gabbard J L, SWAN, D HIX, ET Al. An Empirical User-Based Study of Text Drawing Styles and Outdoor Background TEXTURES for Augmented Reality
Baidu.
DOT HS 812 360, Human Factors Design Guidance for Driver-Vehicle Interfaces
Endsley M R. Toward a Theory of Situation Awareness in Dynamic Systems
Chen, J y c, Barnes m j, et al. Situation awareness-base transparench
This article was originally published by @TAPHUB knocking on the workshop. Everyone is a product manager. Reprinting is prohibited without permission
The title map is from Unsplash, based on the CC0 protocol
- END -
Ministry of Industry and Information Technology: It will introduce the standards related to autonomo
At the China Ten Years theme press conference today (14th), Xin Guobin, deputy minister of the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology, responded to my country's autonomous driving related i...
Motor vehicles occupy the walkways and fire channels exposure!
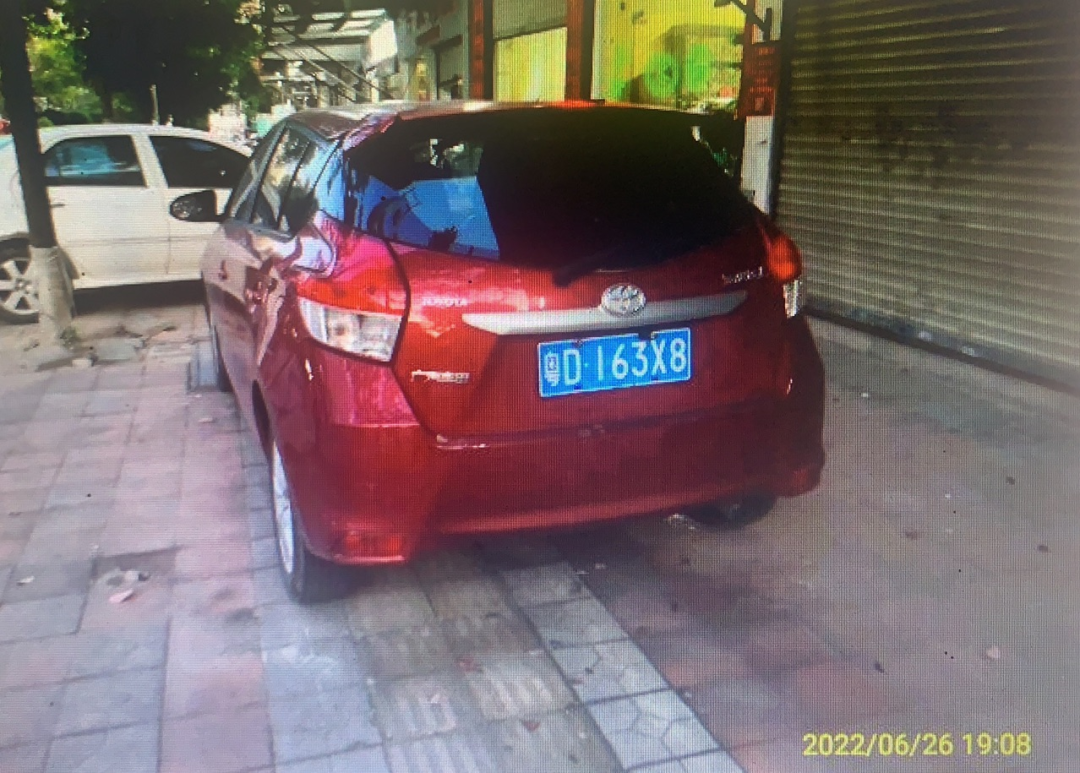

License plate number: Guangdong D163X8Owner name: Shen*CongIllegal time: June 26, ...