"China Greenhouse Gas Bulletin 2020" was released!Global carbon dioxide concentration continues to rise!
Author:China Meteorological Administr Time:2022.09.29

Today, the China Meteorological Administration released the "2020 China Greenhouse Gas Bulletin (Tenth Issue 10)". This echoes the "2020 WMO Greenhouse Gas Bulletin" released by the United Nations World Meteorological Organization (WMO) and reports the situation of major greenhouse gas monitoring data in 2020 in China.
1. Monitoring and analysis of Chinese greenhouse gas concentration
Under the framework of the World Meteorological Organization, the China Meteorological Administration coordinates the high -precision observation of greenhouse gas and related trace components in China. Essence Since 2016, my country has launched three carbon dioxide in the rail satellite. In 2018, it began to carry out online observation of air -carried greenhouse gas in situ observation tests. In 2021, the China Meteorological Administration formed a national greenhouse gas observation network including 44 national meteorological observation stations and 16 provincial meteorological observation stations. As of now, the three -dimensional observation capacity of greenhouse gases with integration of sky, air, and earth has been initially formed.
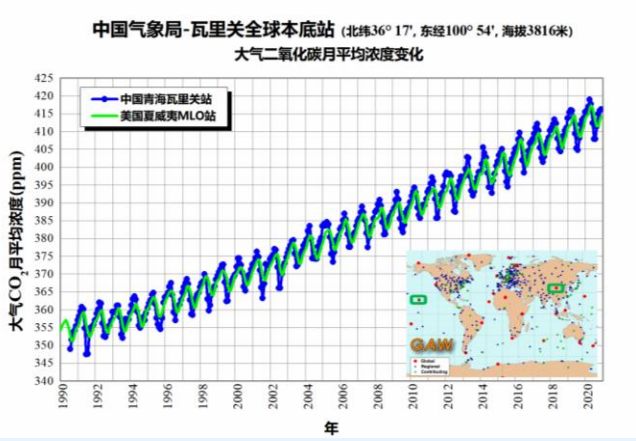
At present, the China Meteorological Administration has 7 national atmospheric base stations to carry out greenhouse gas business observations, namely Qinghai Wari Pass, Beijing Shangdianzi, Zhejiang Lin'an, Heilongjiang Longfengshan, Hubei Jinsha, Shangri -La, Yunnan, and Akdala, Xinjiang. The Variguan National Atmospheric Base Station is one of the 32 atmospheric base stations around the world. In 2020, the concentrations of carbon dioxide, methane and nitrogen oxide observed by the Virguan National atmosphere were 414.3 ± 0.2 PPM, 1944 ± 0.7 PPB, and 333.8 ± 0.1 PPB, respectively. The increase is about 2.5 ppm from 2019, which is the same as the global increase. In 2020, the CO2 and CH4 concentrations of the 6 regions in my country have increased their trend compared with 2019.
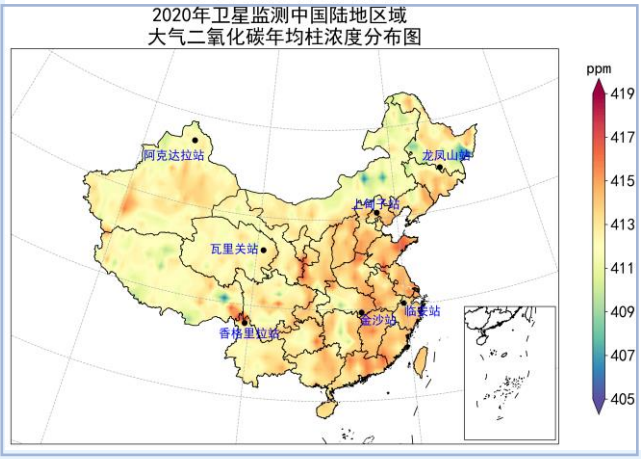
Second, global greenhouse gas concentration monitoring and analysis
The greenhouse gas mainly includes the carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), nitrogen oxide (N2O), hexarium fluoride (SF6), hydrofluorized carbide (HFCS), and whole fluoride carbonide (PFCS) ), Tsimonial Nitrogen (NF3), and the limited ozone layer of the "Montreal Protocol". The World Meteorological Organization/Global Atmospheric Monitoring Network (WMO/GAW) is responsible for coordinating the systematic observation and analysis of the large temperature room gas and related trace ingredients. The large temperature room gas concentration network monitoring and analysis is the scientific evaluation report of the "UN TMB Special Committee (IPCC)", the "UNFCCC), WMO and the UNEP" Ozone loss scientific assessment of ozone loss scientific assessment (UNFCCC) " Report "data sources and scientific foundations.

Since 1990, the concentration of the atmospheric CO2, CH4, N2O concentration (above) and its growth rate (figure below) in the above blue dots in the Blue Dot in the Blue Dot of the Red Line is the linear fitting curve above; the red line is the red line; Points represent the monthly growth rate, the gray column is the annual average carbon dioxide
On October 25, 2021, WMO released the Global Greenhouse Gas Bulletin 2020. The large temperature room gas concentration data adopted by the communiqué comes from WMO/GAW, Global Gas Gas Advanced Test (AGAGE), etc. The communiqué said: The global atmospheric gas concentration continues to break through the historical records since the observation of the instrument. The concentrations of carbon dioxide, methane and nitrogen oxide reached 413.2 ± 0.2 PPM, 1889 ± 2 PPB, 333.2 ± 0.1 PPB, and the carbon dioxide concentration of the atmosphere was 2020. The increase is about 2.5 PPM, which is higher than the average increase in the past ten years (2.4 PPM). The concentration of global atmospheric methane and nitrogen oxide also reached a new height in 2020, with an increase of 11 PPB and 1.2 PPB, respectively. According to the results of the Greenhouse gas index of the National Oceanic Atmospheric Bureau (NoAAA): radiation forced by the long -life greenhouse gas caused by the long life of the atmospheric long life increased by about 47%compared to 1990, and the contribution of carbon dioxide was more than 80%.
In the future, the China Meteorological Administration will further enhance observation capabilities, form a full -factor greenhouse gas based on the comprehensive element gas of the world's main latitude bands in 16 key areas of climate in my country and radiates the backbone network of the global latitude band, and enhance the global atmospheric CO2 and CH4 wide coverage, high accuracy, high time and space, high time and space Resistance business observation capabilities, based on my country's independent satellites, combined with various star -carrying detection methods, improve the global greenhouse gas monitoring level, and provide scientific monitoring support for the smooth realization of my country's carbon peak target and carbon neutralization goals.
Produced by China Meteorological Administration Xuanke Center (China Meteorological News Agency)
Edit: Yang Aoqing
Review: Duan Hao Shu Cui Guohui

- END -
The development of smart fisheries, what "black technology" has it applied to fish farming?

Those who know smart agriculture must know unmanned farms, and friends who like fi...
Nanning High -tech Zone provides "three guarantees" to help talents employment and entrepreneurship
Nanning High -tech Zone actively implemented Nanning City's ten measures to strongly support the 2022 college graduates to come and stay for employment and entrepreneurship, earnestly be a good servic...