The top international journals are published!Chinese scientists have discovered the four major "valves" to regulate the Qinghai -Tibet Plateau greenhouse gas emissions
Author:Cover news Time:2022.09.27
Cover reporter Chen Yanzhang
On September 27, the reporter learned from the Chengdu Institute of the Chinese Academy of Sciences that researchers Chen Huai were invited to publish a review in the top international journal "Nature Reviews Earth & Environment". The carbon and nitrogen cycle changes and driving mechanisms on the Qinghai -Tibet Plateau are described, pointing out that the development of grassland sustainable management, ecological engineering and green technology will inhibit the emissions of greenhouse gas emissions of the Qinghai -Tibet Plateau and help maintain the carbon exchange function of the Qinghai -Tibet Plateau.

Researchers are setting up in the field
Adjust greenhouse gas emissions
Improve the "carbon storage" of the Qinghai -Tibet Plateau
It is understood that the Qinghai -Tibet Plateau ecosystem plays an important ecological function, including soil and water conservation, global biodiversity protection, regional climate, and carbon exchange. Many processes in the nitrogen cycle have changed, which in turn has changed its carbon fixed function. What changes have taken place in the carbon nitrogen cycle of the Qinghai -Tibet Plateau and how to achieve its sustainable carbon fixing function? The research on the main factor affecting the carbon nitrogen cycle of the Qinghai -Tibet Plateau is urgent.
The Qinghai -Tibet Plateau is an important carbon bank in my country. More than 90%of carbon is stored in the soil. Studies have shown that the Qinghai -Tibet Plateau soil carbon reserves (1 m) are higher than 48 billion tons, and the carbon reserves of 3 m soil are as high as 73.6 billion tons. At present, the warming and dampness of the Qinghai -Tibet Plateau will help the growth of the plateau plant. The Qinghai -Tibet Plateau will also become greener. To a certain extent, the plant -solid carbon ability is enhanced. Generally speaking, the annual carbon net absorption of the natural ecosystem of the Qinghai -Tibet Plateau is about 44 million tons.
Taking the wetlands and water bodies of the Qinghai -Tibet Plateau as an example, especially the long -term monitoring of the researcher Chen Huai and his team, it is the main source of methane emissions of the Qinghai -Tibet Plateau, accounting for more than 90%of the entire plateau methane emissions. Although the improvement of grass methane absorption capacity partially offsets the increase in methane emissions, the data shows that methane discharged by the Qinghai -Tibet Plateau still maintains about 0.96 million tons each year. How to better suppress greenhouse gas emissions and enhance the carbon fixing function of the ecosystem?
Through further thinking and organizing the research team of the nearly 20 Qinghai -Tibet Plateau carbon nitrogen cycle models and experimental research, the research team finally discovered that the four important "valves" in the Qinghai -Tibet Plateau biochemical cycle: the temperature limit of the growth of plant growth, the nitrogen of the ecosystem system Restrictions, carbon restrictions on soil microorganisms, and soil moisture restrictions on drought semi -arid ecosystems.
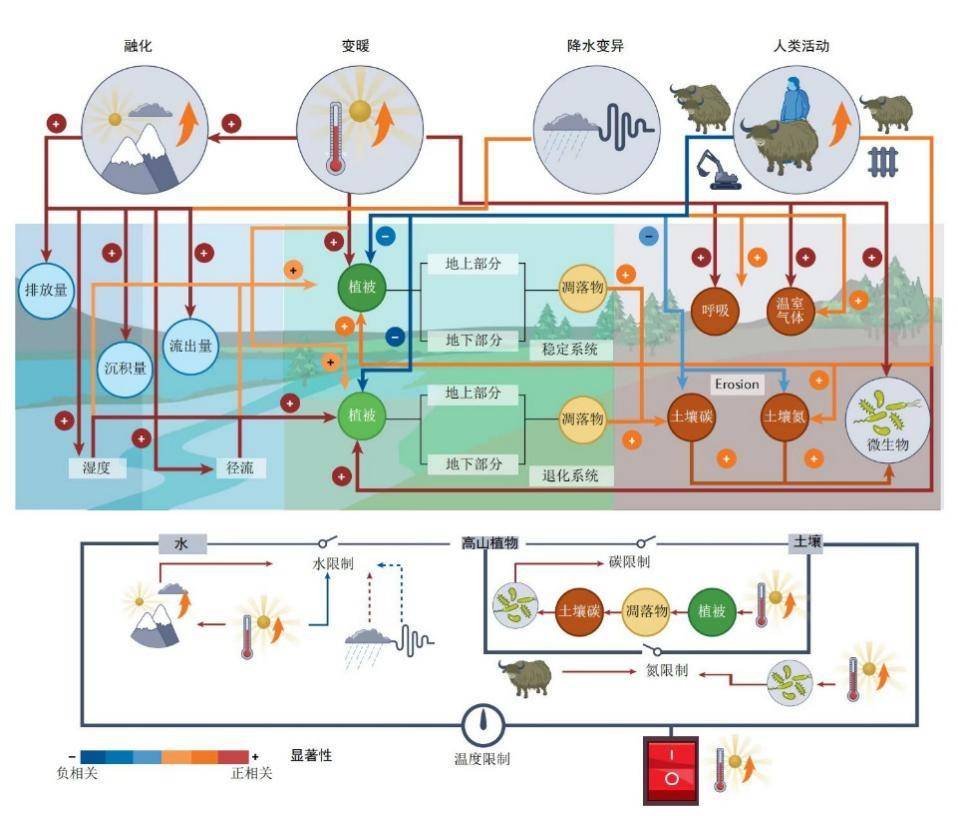
Four important "valves" and driving factor in the Qinghai -Tibet Plateau biochemical cycle
Four "valves"
Provide direction for the ecological management of the Qinghai -Tibet Plateau
The article shows that climate warming directly alleviates the temperature limit of the growth of plateau plants and promotes plant growth. The increase in plant growth will also increase the biomass (carbon) allocated to the underground, which will alleviate the carbon restrictions of soil microorganisms to a certain extent. Coupled with the impact of the temperature increase effect, the activity of soil microorganisms is further enhanced, especially the enhancement of the activity of nitrogen cycle -related microorganisms, which will alleviate the nitrogen restrictions of the ecosystem. In addition, for the dry semi -arid ecosystem restricted by soil moisture, the intensification of soil moisture variability may alleviate the restrictions on soil moisture, thereby determining the direction and strength of these ecosystems to the global changes.
At the same time, climate change and human activities have led to melting glaciers and frozen soil. The heating simulation experiment shows that the non -degraded permanent frozen soil, the plant productive forces in its ecosystem increased with the temperature, and the productivity of degenerate frozen soil plant decreased with the temperature increase. Waiting for greenhouse gas emissions to increase significantly, it will also increase the water -based greenhouse gas emissions affected by thawing.
In addition, mild or moderate grazing reduces the ground biomass of the grass by feeding, but to a certain extent increases the underground biomass of the grass, and at the same time enter the grass -rich feces to the grass, which still helps maintain the grass soil carbon carbon carbon carbon. Nitrogen reserves. On the one hand, severe grazing and severe frozen soil melting increased soil erosion and organic carbon mineralization. On the one hand, the input of plant carbon was reduced, resulting in a large amount of losses in the Qinghai -Tibet Plateau soil carbon and nitrogen.
In the future, continuing to experience the tendency of warming and increased precipitation, the Qinghai -Tibet Plateau will be greener and more produced as a result. Function, on the one hand, the decomposition of the frozen soil carbon library makes it risk of changing from carbon stems to carbon source. In addition, the "Overall Plan for the Protection and Repairing Major Ecological System Protection and Repairing (2021-2035)" in the "Qinghai -Tibet Plateau Ecological Barrier Ecological Protection and Repair Major Project" is one of the nine major projects of the plan. More positive and reasonable recovery and carbon reduction measures, including sustainable grassland management, ecological engineering and green technology development. These measures will inhibit the discharge of gas emissions of the Qinghai -Tibet Plateau greenhouse, which will help maintain the maintenance and sustainable development of the Qinghai -Tibet Plateau.
Studies have pointed out that in order to support sustainable, scientific -based Qinghai -Tibet Plateau ecosystem management and ecological compensation policies, it is urgent to conduct detailed census and estimates of carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus reserves of the entire plateau. Experimental research network; urgently need to carry out phosphorus cycle and mechanism research on the Qinghai -Tibet Plateau ecosystem, and improve the process -based multi -scale ecosystem models that cover the scenario of human activities.
- END -
New business opportunities of payment institutions: fluttering and rushing to overseas cross -border e -commerce

The popularity of cross -border e -commerce has made domestic payment institutions...
Explore the magic space mechanics world, 2022 Fangshan science reporter's second live broadcast was successfully held

In 2022, the second event of Scientific Little Reporter+Exploring Fangshan was suc...