Are you curious where curious?
Author:Institute of Physics of the Ch Time:2022.09.18
Anterior
Our behavior is driven by curiosity all the time. Curiosity is essential for human exploration and understanding of the world's world, but what is curiosity? How does it happen? Professor Dani S. Bassett from the University of Pennsylvania studied human information behavior from a complex network perspective, and found that in the behavior data of people browsing Wikipedia, it contains a curious mechanism.
Research field: curiosity, complex network, human behavior
Guo Ruidong | Author
Xu Enzheng | Reviewing School
Deng Yixue | Edit
1. The way to browse Wikipedia,
Exposure your curiosity mode
The so -called Curiosity refers to the behavior of not being driven by the current external needs, but a search knowledge driven by the heart. Through the information obtained by curiosity, it may provide you with novelty and challenging stimuli in the future and promote personal happiness.
Previous research divided curiosity into two categories, namely busybody and information hunter. The former is characterized by "distraction" and "never settle in anywhere". TA will browse various information, but it will not return to the theme that I have seen before, and it will not be linked according to the picture; the information hunter is just the opposite. Always pursue a set of information, from one concept to another closely related concept.
Different people will have different models when they present curiosity, and over time, different types of curiosity will lead to different types of information accumulation. The roamers 'information storage is more diverse than information hunters, but information hunters' information is stored in less themes contains greater depth.
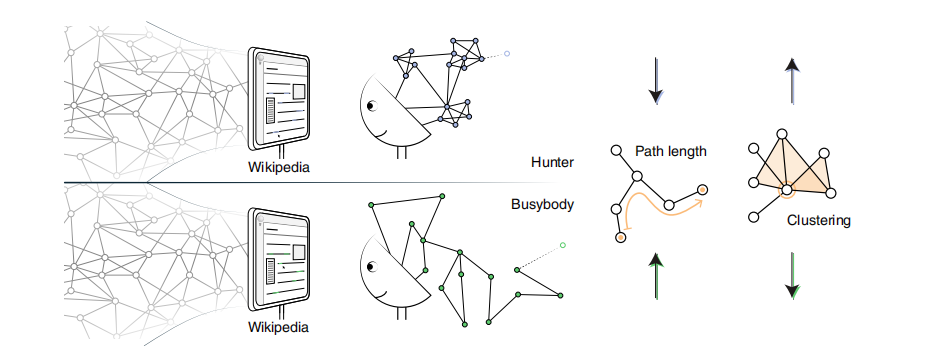
Figure 1: The two curiosity styles of information hunters and roamers are distinguished.
From the perspective of network science, each information is regarded as a node, and the similarity between information is regarded as a connection. Then the two curiosity models will generate networks with different characteristics. The average value of the shortest path between the two points of the information hunter's network is small, and the aggregation coefficient is high. The opponent of roaming is the opposite.
In the relevant research, 149 were tried in the experiment, and for 21 consecutive days to browse the Wikipedia interface for 15 minutes per day to obtain the above -mentioned knowledge network. The researchers seek the information of the participants, and expressed the knowledge network according to the semantic similarity between the pages. The higher edge weight represents the higher degree of similarity contained in the two nodes connected by the side.

Figure 2: The knowledge network composed of Wikipedia interface browsed by the subject
The subjects filled out the questionnaire before participating in the experiment. Through the questionnaire, the degree of curiosity of individuals was also known as the curiosity of depriving driver due to the lack of specific information -driven curiosity. The theory comes from the psychology world, pointing out that the curiosity of people is due to the poor information. Individuals have different sensitivity to the difference in information. Some people feel that they do not understand and uncomfortable, and some people have a blind eye to the existing information. The results point out that the more sensitive the information deprives information, the closer to the information hunter to browse information, the higher the cluster coefficient and the shorter path length between nodes.
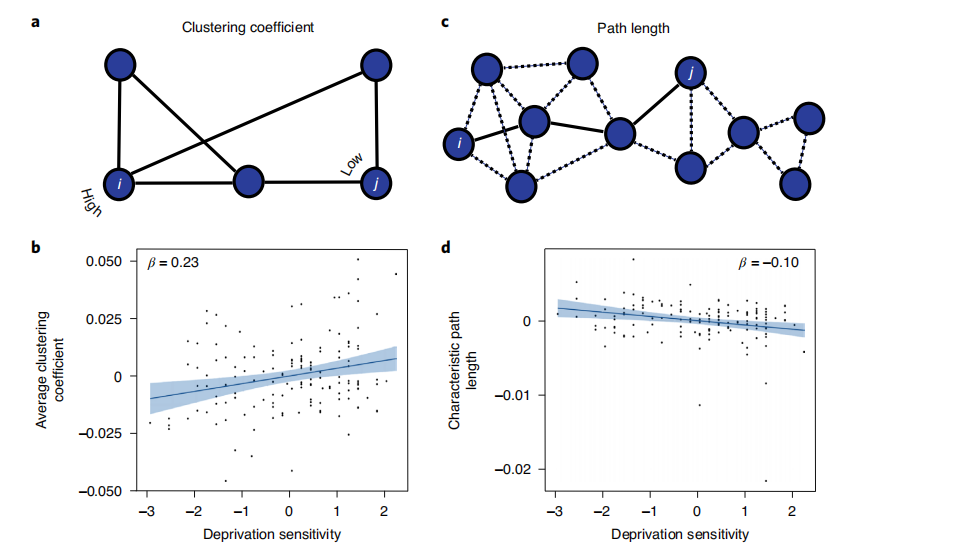
Figure 3. Different information deprivation of sensitivity and (A, B) average gathering coefficient, and (C, D) representing scattered dots of the length of the representative path
The interpretation of curiosity in psychology also includes pursuit of sensory stimuli. The study analyzed the daily diary of the trial to determine how much it pursued the sensory stimulus, and then divided the 21 days of the test browse Wikipedia into three stages. It was found that when pursuing sensory stimuli, the curiosity of individuals tended to the "roamers" type, as shown in Figure 4.

Figure 4: Personally, at different stages, according to the degree of pursuing sensory stimuli, the average node weight of the knowledge network formed with (b), (C) the aggregation coefficient, and the length of the length of the (d).
2. What drives humans to produce curiosity
Based on the same batch of data, the researchers later tried to analyze the changes in the topology characteristics during the generation of the knowledge network, and discovered the mechanism of curiosity.
2.1. Fill in the lack of information
The interpretation of curiosity of this study is the information gap, that is, the reason why people are curious is that human knowledge of the world can tolerate the uncertainty of the limited number. Exposed to a small amount of information before can make people pay attention to the existence of the knowledge gap and make the uncertain level exceeding one acceptable threshold. This increasing uncertainty prompts people to find information to fill the knowledge gap and solve unknown problems.
The verification of the theory comes from the topology cavity in the map theory. The topology cavity can be understood as the gap between the two unconnected nodes. Filling makes nodes located in the gap in a critical position in the network. In the context of curiosity research, nodes in the gap can be regarded as poor information. By comparing the dynamics and zero models of the topology of the topological cavity in the network, researchers have verified that the difference in information difference can indeed explain the cause of curiosity. The number of topology cavity is only higher than the zero model on the Internet. It is pointed out that even if we get more information, the connection between the familiar concepts is still not found.
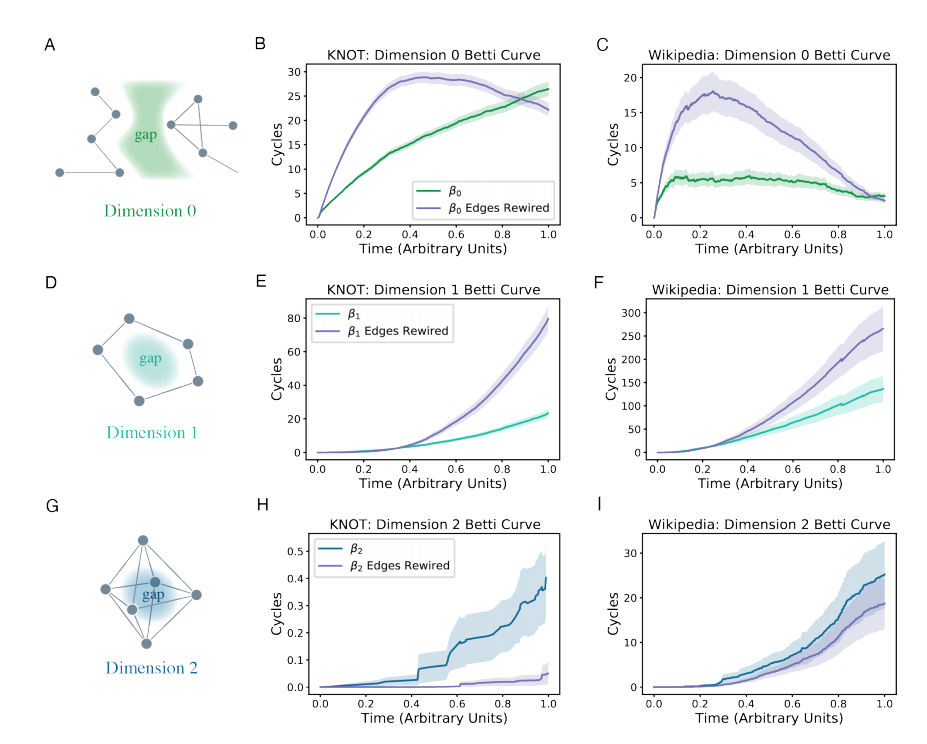
Figure 5: In different dimensions (see A, D, G), the information difference is located in the structure hole of the knowledge network. In the knowledge network (see B, E, H) built by individuals to view Wikipedia, compared with the zero assumptions formed by random re -connection, the number of top topology empty cavity in the real network increases first The number of topology cavities in the 2nd dimension is significantly more random. Figure C, F, and G correspond to the number of topology cavity under different dimensions during the construction of the collective level of knowledge network, respectively. Collective may be easier to fill these cavities (the differential network of individual knowledge compared to the different models of the zero model) than individuals), because the field of cross -disciplinary sectors in the scientific field is inspired to connect different knowledge sub -fields 2.2. Model compression compression.
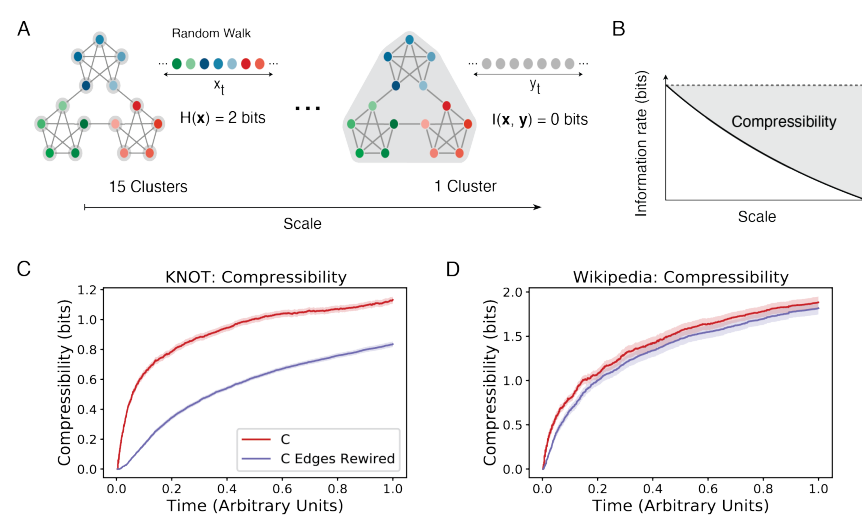
Another explanation of curiosity is that through exploration, it can build a more streamlined model for the world. For example, after reading a lot of Song poles, the poets are divided into two graceful and magnificent factions. The advantage of doing this is that it is easier to store new information. In terms of quantitatively, it is randomly walking in a 15 -node network (shown in Figure 6A). The information entropy corresponding to the sequence is 2 bit. Information entropy is turned into 0 bits. At this time, the reduction of information entropy can be regarded as the income brought by model compression. The less the number of clusters, the more benefits brought by the compression.
Figure 6: The revenue brought by the compression of the quantitative model, it is found that when the knowledge network is constructed, the income brought by the knowledge network of individuals (Figure 6C) and groups (Figure 6D) exceeds the assumptions. The hypothesis brought by the model compression driver.
The above two interpretations of curiosity have their own shortcomings. In the false setting of information, learners only pursue the growth and integrity of knowledge. Under the explanation of compression income, the curiosity follows the curiosity to work hard to reveal the potential organization of the world. However, in a more complex environment, with the emergence of new unknown things, the unknown boundary expands rapidly, and the responsibility to be curious is not only effectively adding or abandoning information, but also to acknowledge the value of what we already have. Essence However, the above two explanations only pay attention to the value of new information, and do not consider the benefits brought about by changes between the existing information.
2.3. Build a flexible and stable knowledge network
As a result, the author provides a new explanation about curiosity, defining curiosity as a balance between local internal rigidity (Rigidity) and global external flexibility during the knowledge network construction process. Rigidity and flexibility are a mechanical concept that requires interested objects to the physical space. Assuming that the knowledge network is embedded in the space of Europe, the network has multiple degrees of freedom. Flexibility can be regarded as the ability to change the network without changing its topology.
Rigidity and flexibility are two concepts from mechanical networks. The network in Figure 7A has rigidity, and the network of Figure 7B has flexibility. By combining rigid and flexible network modules, it can generate Figure C such as local rigidity and global flexibility. Through the heavy company between nodes, 338 nodes and 672 edges can also be generated. The network is stable locally and has a high degree of freedom in the overall perspective.
FIG

The indicator D, which represents the global flexibility between nodes, is significantly higher than the random connection network in the construction of individual and collective knowledge networks, so that the driving force for curiosity is to build a global knowledge network, as well as personal attention to personal attention Considering the ability to know things according to the newly obtained information. The theory regards curiosity as a practice of building a flexible knowledge network.
Figure 8: Curious support evidence of the theoretical theory of the heart conformity. Figure B and C indicate that the acquisition of individual unique information has led to frequent reshaping of conceptual relationships based on context. Figure D and E indicate that in the collective knowledge network, the evolution of interested mechanical characteristics cannot be distinguished from their evolution in zero model data.

Compared with and summarized the above explanation of curiosity, at first people think that curiosity is either to fill cognitive vacancies. For example, they feel that they lack the knowledge of ancient poetry and read the works of ancient people, or to satisfy sensory stimuli. Later, people's curiosity was to be able to build a simplified model of the world, such as dividing Song Ci into two types: bold and euphemistic; new research proposed a new explanation of curiosity, that is, people pursue new information to make the old information about the old old information about the old old information about the old old information about the old. The model of information can be more flexible. For example, by reading more Dongpo poems, I realize that Su Shi should neither be simply attributed to the pride or graceful faction. The evidence of the study pointed out that the mechanism of curiosity obtained is diverse and driven by the various mechanisms described above.
3. Curiosity study inspired artificial intelligence
Previously, the psychological research of curiosity was mostly qualitative analysis, and based on tools provided by network science, the research first studied curiosity and driving mechanism behind quantitative ways. By using curiosity as the process of knowledge network construction, these studies provide computational, theoretical -based measures, such as topological cavity, compressed, and constructive freedom. Experiments in the laboratory can also be used in real scenes. The important development direction in the future includes the most suitable curiosity type of each network measurement to the most suitable curiosity, and expand the current sub -type classification to adapt to the new network theoretical perspective. Through multi -dimensional review of curiosity, the study expands the classification of traditional psychology for curiosity. With these findings, relevant personnel can make suggestions for the formulation of education policies by guiding the exploration of different types of curiosity driven by different types of curiosity, and can also be used to improve user retention and satisfaction.
The research based on the browsing behavior of the relatively small samples under the control of the experiment. With the popularity of streaming media, in the knowledge community such as Zhihu, massive users' spontaneous exploration behavior can help scientists in a more real scene in a more real scene. Below, explore the curiosity model presented in different circumstances, and make more interesting and meaningful discoveries through the association with user attributes, such as gender, age, education level.
Furthermore, curiosity is not only related to humans, but also related to artificial intelligence. For example, compression is initially proposed as an internal learning signal that guides enhanced learning. The study provides several candidate indicators -such as the number of topological cavity, network compression, and constructive flexibility — it can be used as a suitable mission -based task setting signal.
Increased learning requires that intelligence must be balanced between development and exploration in interaction with the environment. In many real worlds, external rewards are very rare and even at all, so naturally they cannot reliably guide their behavior. In this sparse reward environment, the inherent motivation similar to curiosity can still promote exploration behavior and further improve task performance. The design of strengthening the internal (or curiosity) reward signal of learning is an important area for further research. It may benefit from the insight into the calculation of human behavior, such as the main conclusions obtained in the study.
Reprinted content only represents the author's point of view
Does not represent the position of the Institute of Physics of the Chinese Academy of Sciences
If you need to reprint, please contact the original public account
Original title: Where does curiosity come from? Knowledge network data reveals the various mechanisms of curiosity
Source: Jizhi Club
Edit: Garrett
- END -
The Industrial Site of the Industrial Site will be held
On August 17, the press conference of the industrial site (Baoding) Industrial Dev...
Western Industry University was exposed to the real murderer by the Internet. What is the "specific invasion office office"?

The Specific Invasion Office is like a digital channel worker who follows the call...