Liu Li et al.-EMR: The diversity of microorganisms and its adaptation mechanism of the extreme environment of Mars-class in the Chaidama Basin
Author:Institute of Geological Earth Time:2022.09.08


The success of the first Mars detection task of "Skywen No. 1" marks that my country's planet detection has entered a new journey. Mars is one of the most likely to have life in the solar system except the earth. Finding a life signal has always been an important scientific goal for Mars detection tasks. In the Research on Mars 'Life Signal, in addition to the Mars' position detection, many of the natural existence on the earth provided new ideas for studying Mars life with similar characteristics (called Mars environment) with similar characteristics (called Mars environment). The research on life of Earth Mars' extreme environment has important guiding significance for evaluating Mars's livable potential and searching for the life signals that Mars may save.
The Chaidama Basin is located in the north of the Qinghai -Tibet Plateau in my country. It is one of the most drought and the highest altitude in the world. Due to the rise of the Qinghai -Tibet Plateau, the climate of the Chaidama Basin has changed drastically since the update of the world, and it has gradually evolved from the original huge lake to the desert with extremely drought, high ultraviolet radiation, and large temperature difference between day and night. Today, the droughtness of the Chaidama Basin has gradually increased from the southeast to the northwest. Its environment can be compared to the environment from the late Martian Nooyan to the early Western period. In addition, the Chaidama Basin has developed a lot of Mars -like landforms similar to the characteristics of Mars landforms, such as punching grooves, accumulation fans, mudslides, Yadan, polygonal landforms, etc. Studying the Microbial diversity and adaptation mechanism of the Chaidama Basin helps to better understand the survival strategies of the Earth's life tolerance to extreme environment, whether the past and current celestial biology of Mars may have the scientific issues such as life.
The Ministry of Planets and Planets Magnetic Farm and Livioral Discipline Group of the Earth and Planet Physics Institute, Liu Li, and researcher Lin Wei, a mentor Lin Wei, in combination with the team of Professor Li Yiliang of the University of Hong Kong. The surface soil microorganisms conducted a systematic research (Figure 1), which improved the traditional method of extraction of soil microorganisms DNA, and achieved a sufficient amount of DNA from the low bi quantity samples of the Chaidama Basin to conduct group studies. On this basis, comprehensive use of molecular ecology and macroine groups, etc., have studied the community diversity and their main physiological metabolism characteristics of microorganisms in the surface of the area on the surface of the area. The gates (Actinobacteria) and Protobacteria are dominant groups. At the same time, ancient bacteria such as EuryArchaeota and Crenarchaeota were also found (Figure 2). The samples in the northwest of the basin and the microbial abundance and community diversity in samples in the southeast region are different, revealing that soil water content and organic carbon are important environmental factors affecting microbial abundance and diversity.
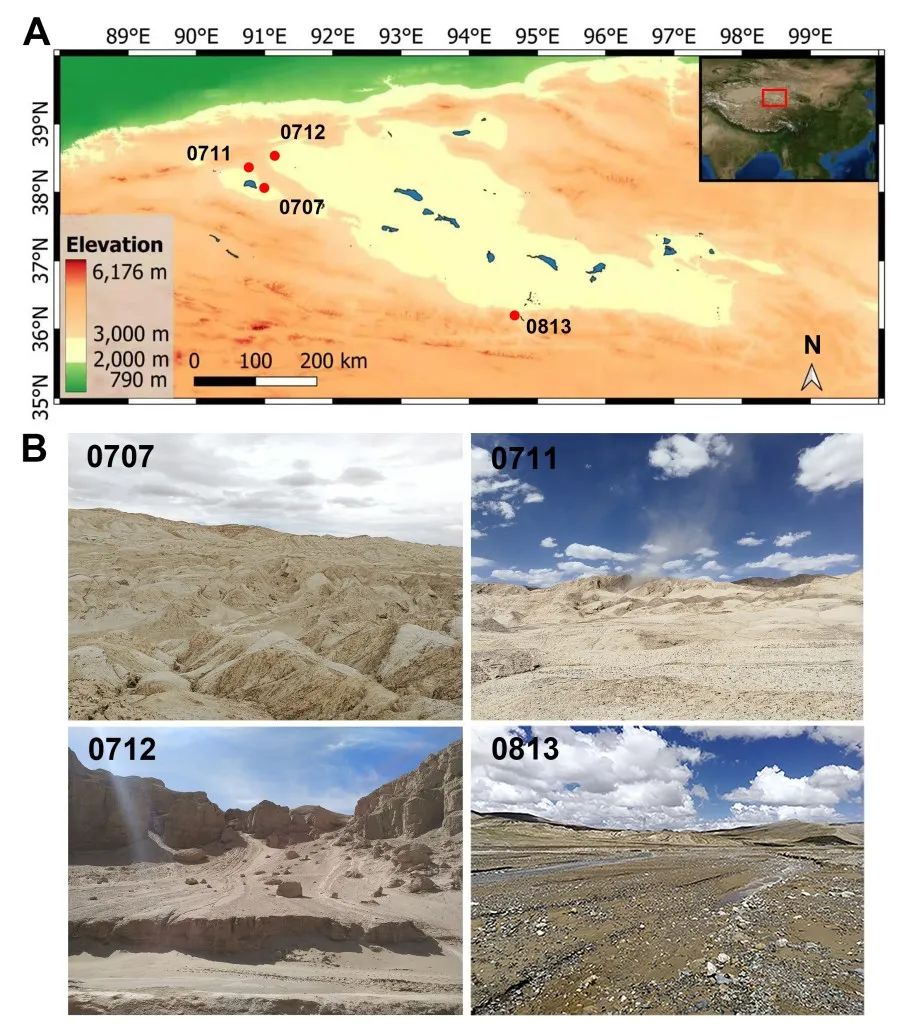
Figure 1 The sampling location of the Shidama Basin
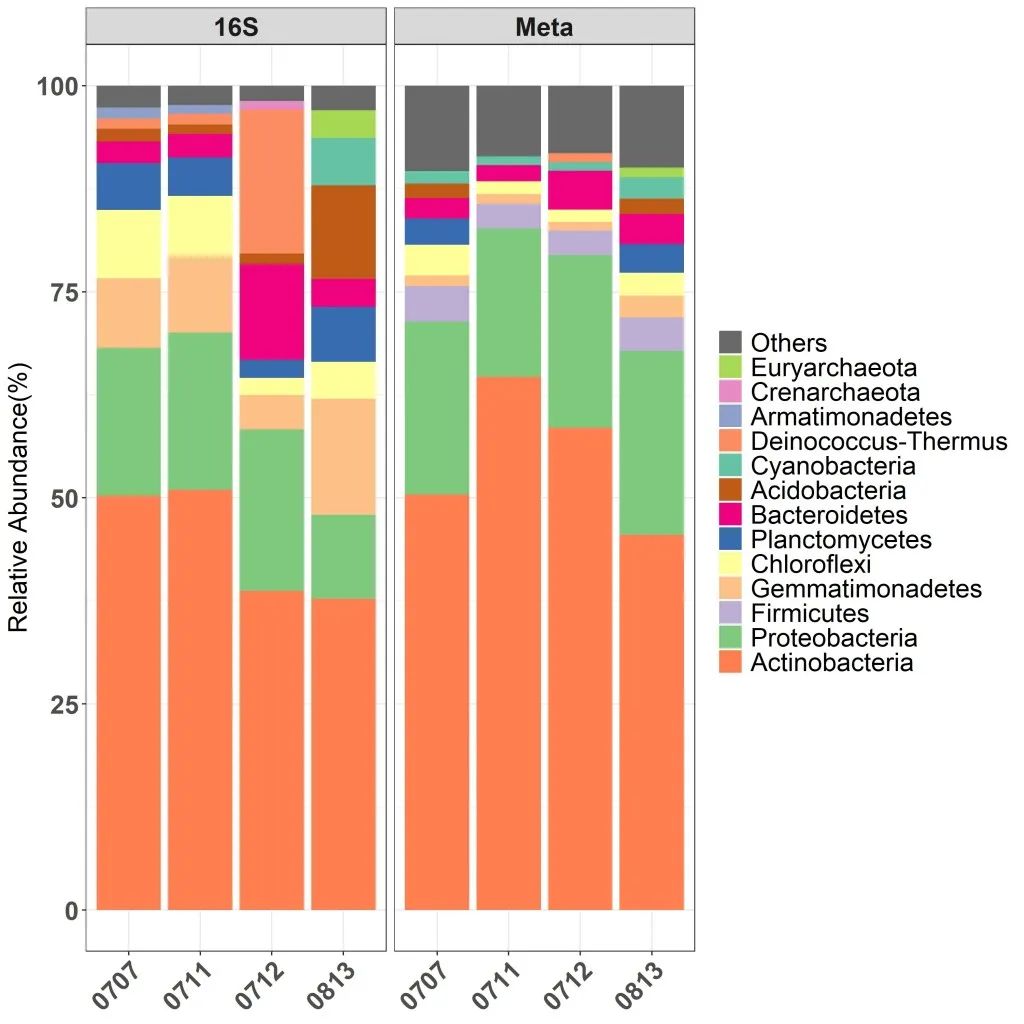
Figure 2 Based on the main microbial category and relative abundance of the Shibalmu Basin on the representative regional surface of the Temoduma Basin discovered by the 16S RRNA gene (left) and the macroscopic group (right) studies
Further studies have found that the surface soil microorganisms of the Chaidama basin may be able to obtain the energy required for survival by absorbing trace gases (such as CO, H2, CO2, etc.) in the environment (Figure 3). These microorganisms also found genes that may participate in repairing DNA damage and responding to environmental temperature fluctuations, indicating that DNA repair and protein protection may be important mechanisms for microorganisms to respond to extreme environmental conditions such as high -ultraviolet radiation and temperature drama of the Chaidama basin (Figure Picture 3).
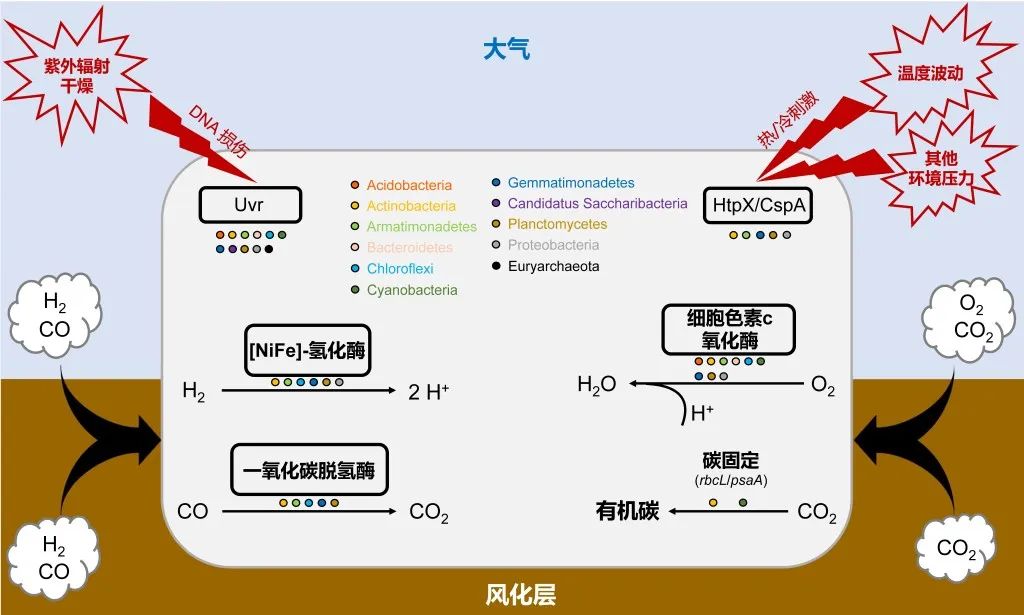
Figure 3 The adaptation mechanism model of the Mars -class Mars -like Extreme Environmental surface soil microorganisms
Studies revealed the diversity of community diversity and its main adaptation mechanisms in the Chandam Basin Mars 'extreme environment, and provided a reference for in -depth understanding of the possibility of the early life of Mars and the detection of Mars' life signals.
成果近期发表于国际学术期刊Environmental Microbiology Reports(刘立,刘海韵,张文斯,陈妍,申建勋,李一良,潘永信,林巍*. Microbial diversity and adaptive strategies in the Mars-like Qaidam Basin, North Tibetan Plateau CHINA [J]. Environmental Microbiology Reports, 2022. Doi: 10.111/1758-2229.13111). Studies were jointly funded by the Chinese Academy of Sciences, the National Natural Science Foundation of China, and the Institute of Geoscience and Geophysics of the Chinese Academy of Sciences.

Beautiful editor: Chen Feifei
School pair: Wanpeng
- END -
How to generate heavy elements and try to overthrow the gravity?
How to fill the earth with gold and other precious metals in the collision of neut...
The demand is wide and the growth rate is not diminished. The wave of cloud computing is running forward

Edit | Yu BinProduced | Chaoqi.com Yu See ColumnUnder the leadership and promotion...