Does the Big Bang of the Universe exist?Where does everything come from?
Author:Institute of Physics of the Ch Time:2022.08.30
Original: Brian Koberlein
Translation: Li Xiaochuan
School translation: He Yongqiang Cao Lei Tu Tianyu
Arrangement: Wang Zhajun
Backstage: Hu Yongzheng Li Ziqi Li Mingchen
Original link:
https://www.UniversetODAY.com/157264/the-latest-ebb-observations-disprove-the-big-but-theterestIn/57264

""
Important in advance: The theory of the Big Bang has not been overturned. The recent observation results of James Wob telescope did not deny the theory of Big Bang, which is not consistent with the conclusions claimed by some popular articles.
However, the latest observation data also unveiled the strange and unexpected side of the universe. If you want to learn more, then read it ~
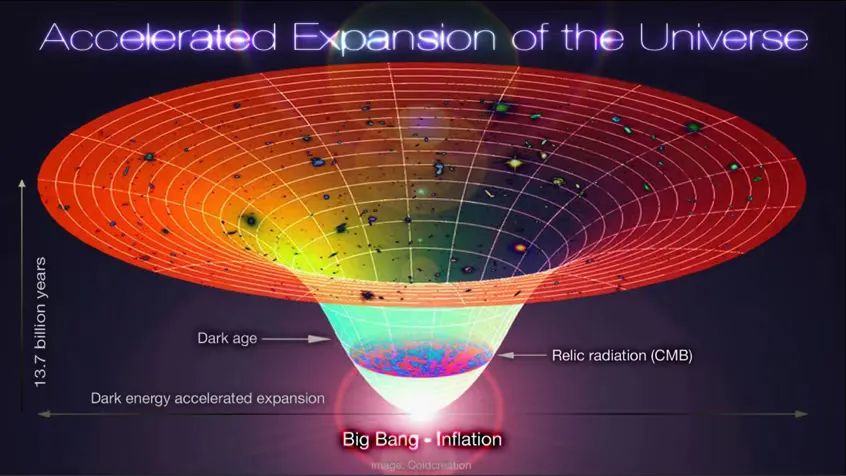
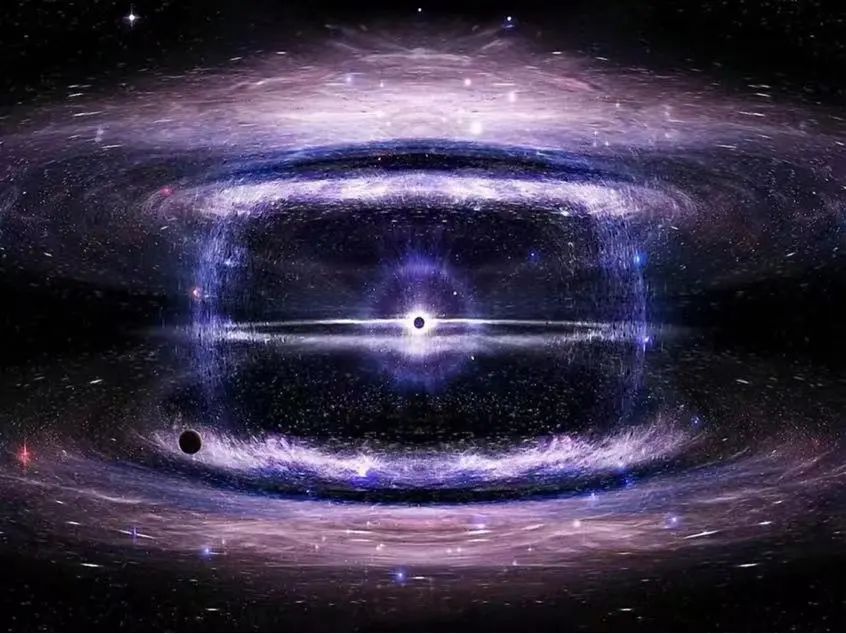
Illustration λcBR universe, the expansion process from the Big Bang of the Universe
Photo source: Alex Mittelmann/ColDCreation
Let's take a look at where the rumors come from. How is Webb's latest observation data be considered to be able to deny the Big Bang?
In fact, as early as a few years ago, the Hubble telescope gave the same type of data. We usually believe that the evidence of the Big Bang theory always revolves around the following two facts: First, the farther the galaxy moves higher. Second, the universe is full of the cosmic microwave background radiation. The former shows that the universe is constantly expanding, and the latter shows that the early universe was in a state with extremely high temperature and extremely density. These two are two of the "three pillars" that support the theory of Big Bang, and the other "pillar" is the relative abundance of the elements of the primitive universe.
However, these observations found that it is only the basis of the Big Bang model. We created a standardized cosmic model -the LCDM model, which is a universe opened by the explosion, full of material, dark matter, and dark energy. From the acceleration of the universe to the formation of the galaxy, everything is in line with this model. The model also predicted other observation trials, which we could further verify its authenticity. Those rumors appeared.
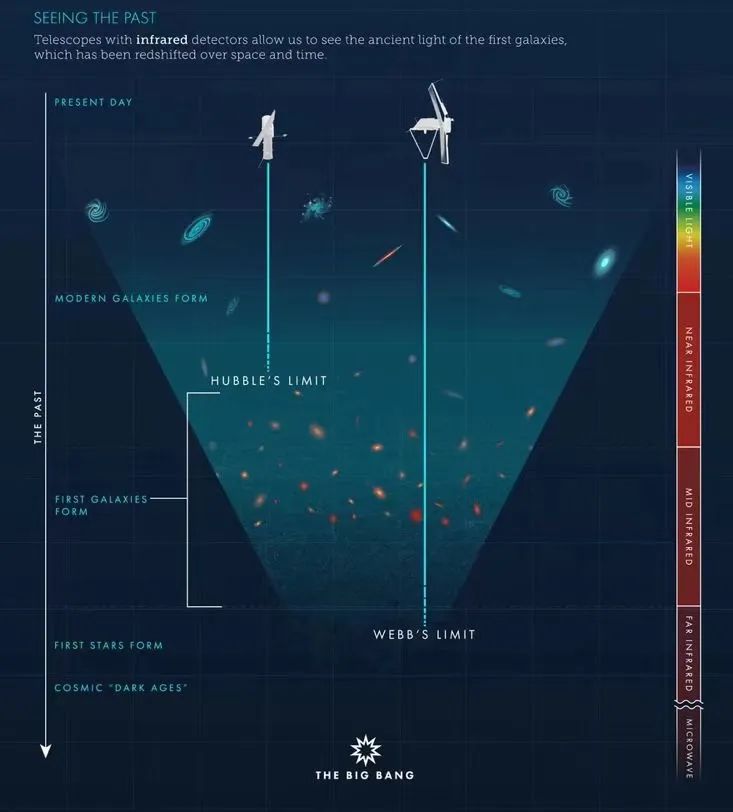
Tip of Weibu and Hubble observation distance comparison, Zuo Huber Youbbu
Picture source: NASA, ESA, Leah Hustak (STSCI)
One of the observations mentioned above is the Toman surface brightness test. The test was proposed by Toman in the 1930s to compare the visual brightness and diameter of the galaxy, and the ratio of brightness and size is the surface brightness. Generally, the larger the galaxy, the brighter it, so the surface brightness of each galaxy should be roughly the same. The galaxy far away is darker and the diameter is smaller, so the surface brightness should be similar. The Toman test shows that in a static universe that does not expand, the surface brightness of all galaxies is the same, which has nothing to do with observation distance.
However, the facts are opposite. What we observe is that the surface brightness of the far galaxy is lower than that of a higher galaxy, and the decrease in the brightness value and the red shift value are proportional. Perhaps you think that this confirms that the distant galaxies are accelerating from us, but not. If that's the case, red shift and increased distance will have a superposition and darker effect. The Toman test believes that in the expansion universe, the surface brightness will be inversely proportional to the red shift and distance, and we only observe the effect of red shift.
Some people use this discovery to propose a static cosmic theory -light will lose energy over time and lose energy. This is the so -called fatigue light hypothesis. This theory is loved by opponents of the Big Bang theory. If the universe is static and the light will be spontaneous and energy, then what the Toman trial shows the facts we observe: the big bang does not exist.
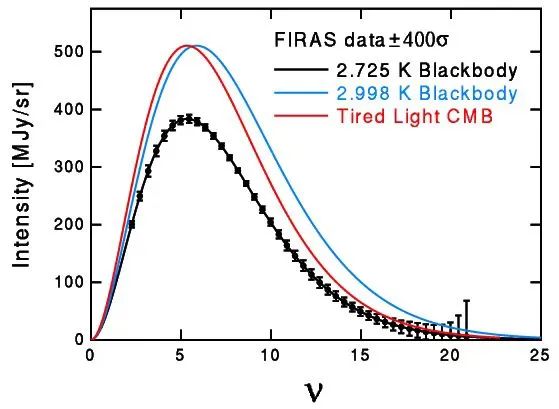
Cosmic microwave background radiation icon, denying fatigue optical hypothesis
Picture source: NED WRIGHT
Eric Lerner is a critic of a Big Bang theory. He published a popular book "Big Bang never happened". Back to 2014, Eric Lerner and others published a paper explaining the aforementioned view, which caused a series of articles on the mass media that did not happen. His hand. In 2014, the observation data of the Hubble Telescope conforms to Lerner's point of view, and the latest Webu data is the same. However, the data of Hubble and Weiban also supported the LCDM model.
The phenomenon of red shift confirms that the galaxy is accelerating from us, which is a typical error. The distant galaxy has not accelerated in the universe. It is the expansion of the space of the universe itself, making the distance between galaxies greater and more obvious. There is a subtle difference between the two concepts, which means that the red shift of the galaxy is generated by the universe, not the relative speed. This also shows that the distant galaxy looks bigger than in the static universe. These galaxies are actually distant and small, but the expansion of the space becomes bigger. Therefore, the surface brightness will only be proportional to the red.
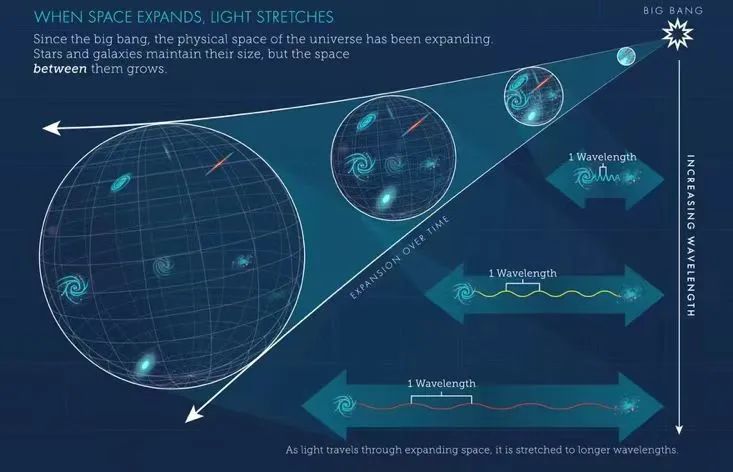
The red shift of the universe is not caused by the Doppler effect
Picture source: NASA, ESA, Leah Hustak (StsCl)
Of course, we know that "fatigue optical hypothesis" is wrong, because the background of the universe microwave. In a static fatigue light universe, the "original fireball" (one of the models of the big bang hypothesis) in the early stage of the Big Bang will not have any calories. The distant galaxy will appear vaguely (the facts prove that this is not the case); the supernova in the distance will not be observed later because of the expansion of the universe (the fact is not the case). The only model that can conform to all observation evidence is the Big Bang, so Lerner's theory was overturned early. Back to now, the Wabbu Telescope does observe some unusual phenomena. The most significant one is that we have discovered more unexpected galaxies and remote galaxies. This will lead us to revolutionary changes on the basis of existing models. The current understanding is that after the Big Bang, the universe entered a "Dark Age". During the period, the last beam of light of the universe was annihilated, and the original stars and galaxies had not formed at that time. The accuracy of the Wabbu telescope can be observed that some of the initial galaxies formed by the "Dark Age" just ended. Everyone thinks that the number of first -generation galaxies is less and not as mature as the subsequent galaxies. However, the observation of the Webb Tengnic Mirror discovered that the first -generation galaxies with high red shifts were not only a large number, but also quite mature.
This is the data that astronomers are looking forward to, and the mystery is heavy and unexpected. It is for this reason that we wanted to build a Weibu telescope at the beginning. At this point, everything is clear, the big bang theory is not wrong, but our assumptions about the Big Bang may not be true.
Editor in charge: Huang Jing
Mufu New Media Editorial Department
IC 5146: Cocoon Nebula
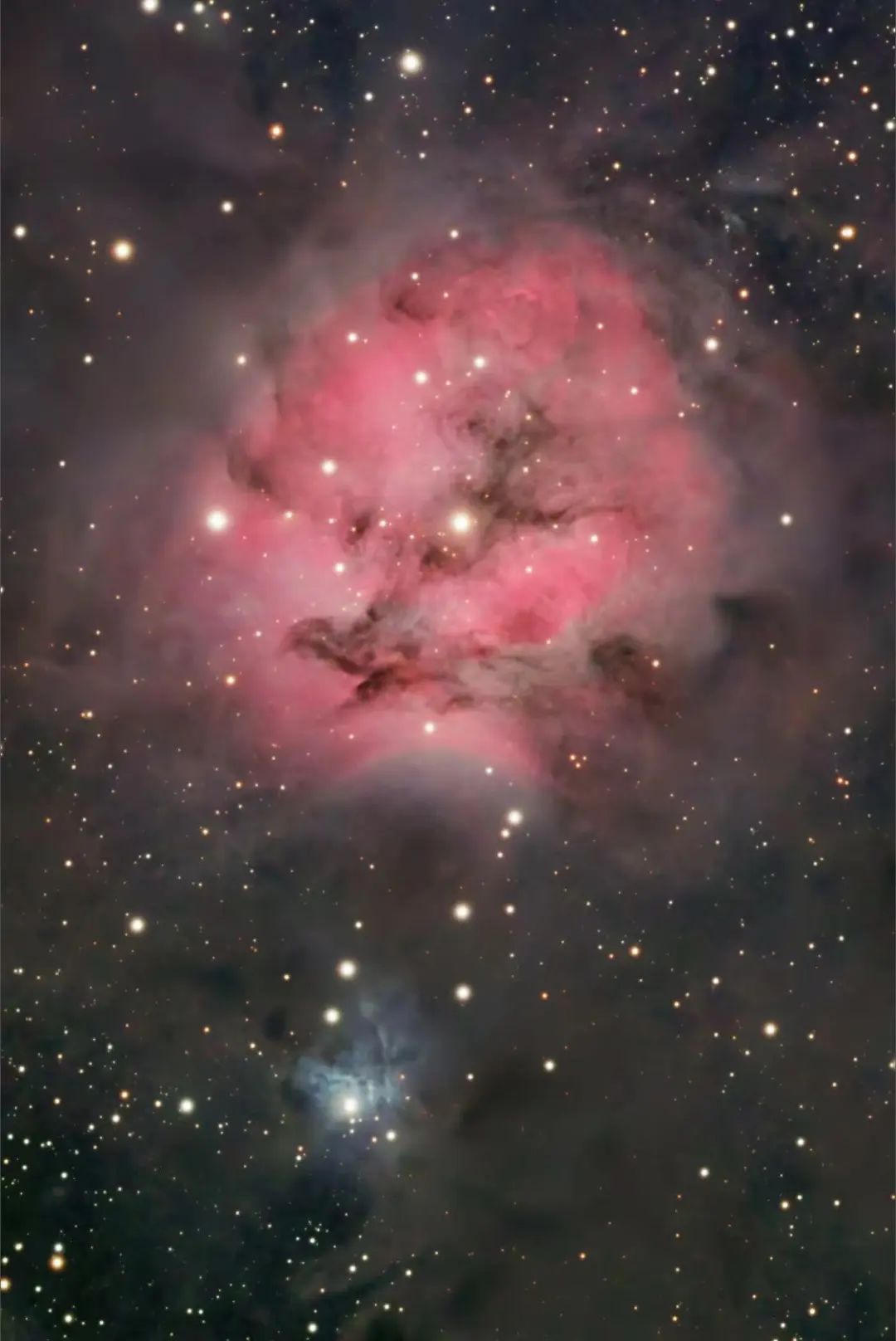

Picture source: NASA
Reprinted content only represents the author's point of view
Does not represent the position of the Institute of Physics of the Chinese Academy of Sciences
If you need to reprint, please contact the original public account
Source: Murator Astronomy
Edit: lychee jelly
- END -
[In Zhi Ai Jianhui Hui Hui Huan] Electronic business license is "too convenient" and inserted into technology wings "Demonstration Office"

Huiminrong Media News I did not expect that the electronic business license was so...
There are only 200 mature individuals: the unique Guizhou golden monkeys in Guizhou are extremely endangered
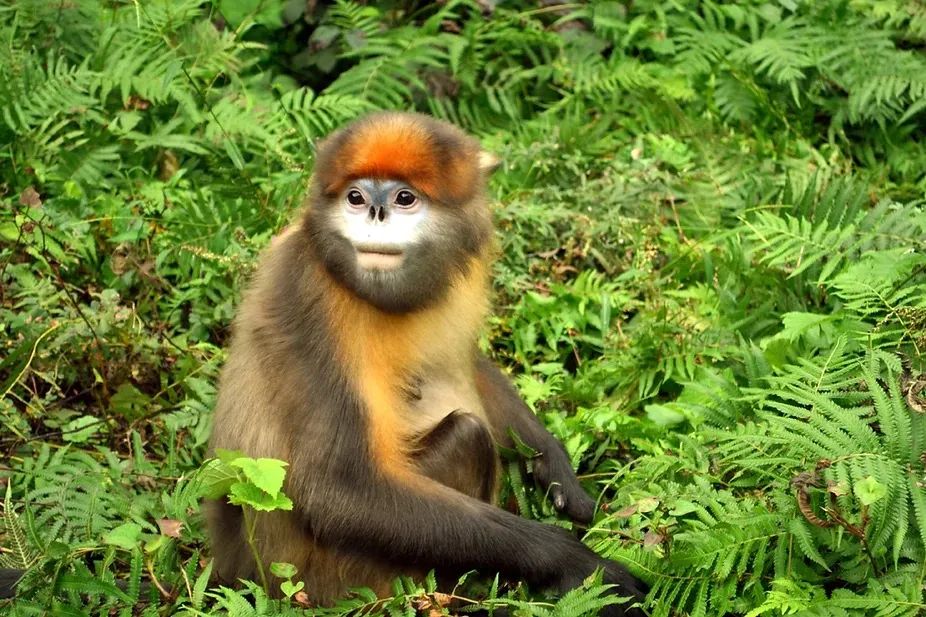

Suddenly I found that IUCN rose to the bearing monkey to extremely endangered, and...