Musk enlarged tricks, mobile cars will be connected to the star chain, how is the spectrum competition?
Author:Galaxy Aerospace Roaming Guide Time:2022.08.27
The following article comes from the Satellite Internet Hundred People Conference, the author Dr. Hou.

On the morning of August 26th, Beijing time, Musk sent a Twitter, and the official announcement of the second -generation "Starlink" satellite to be launched next year can connect to the phone directly. In addition, he responded on Twitter about whether these connections could be used with Tesla's electric vehicles. It is reported that these cars are currently connected to the ATT LTE network. According to Musk, the answer is yes.
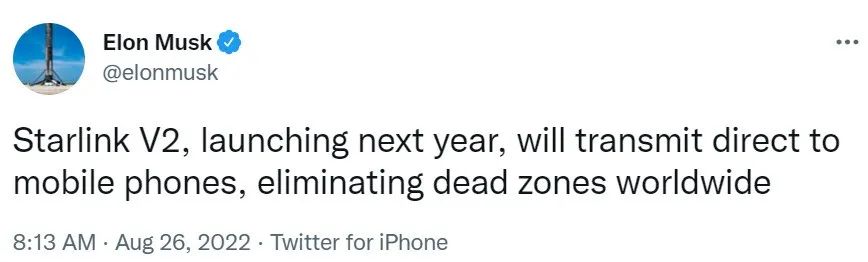
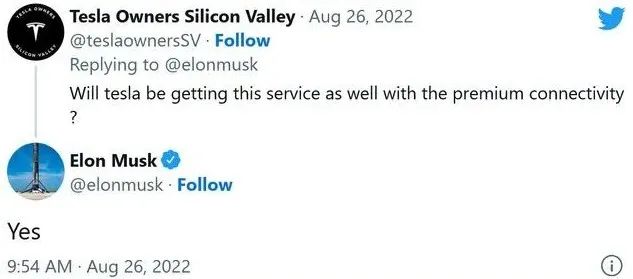
The picture comes from: Musk's personal Twitter
At the same time, recently, according to foreign media reports, SpaceX has reached strategic cooperation with US telecommunications operator T-Mobile, and the two parties will jointly explore the integration of ground communication and satellite communication. T-Mobile CEO said that it will establish a technical alliance with SpaceX, and the cooperation will end the deadlock in the mobile field. Musk introduced at the event that even if all the mobile phone signal towers were paralyzed, the new service of SpaceX's "Star Chain" satellite could work normally.

Photo is derived from: SPACEX official Twitter
Earlier, on July 28, Space News also released a news that "SpaceX requests the FCC to allow the use of 2GHz bands to" enhance 'its satellite mobile service ". This news is common and unusual.
It is common to say that it has not disclosed the specific details of the next generation of services provided by the "Star Chain" program. It is unusual, because the S frequency band is the world's only IMT (International Mobile Telecommunications, International Mobile Communications) satellites and IMT grounds can be used. It is also an important target band in 5GNTN. It is also the best candidate for direct mobile phones. Frequency band.
The "Star Chain" satellite currently uses KU and KA frequency bands. In the future, there are also Q/V frequency bands. These frequency bands are limited by terminal antenna size and link budget, and ITU's landing power restrictions. With satellites. The S frequency band is one of the best frequency bands of the direct -connected satellite on the mobile phone. There are mainly the following reasons:
01
The frequency of the S frequency band is low and the terminal uses omnidirectional or semi -directional antenna. It is easy to adopt the air interface of the ground network.
02
The S frequency band is a frequency band that can be used by satellite and ground mobile communication. It has 3GPP standard support;
03
The S frequency band is allocated according to the FDD, which is suitable for both ground channel environment and satellite channel environment.
So, what is the current deployment of satellites and ground systems in the S frequency band? Is there still room for development? Let's sort it.
1. The S frequency band is the only frequency band that can be used in the world's only IMT satellite and IMT ground.
The resolution of the ITU "Radio Rules" 122 determined that the core frequency band of the IMT was 1885-2025MHz and 2110-2200MHz, with a total of 230MHz bandwidth. The satellite part can also be used for the ground IMT business. It is specifically used for satellite business or the ground IMT business depends on the competent departments of various countries. In 2017, 3GPP defined the S-frequency band (1980-2010MHz/2170-2200MHz) with IMT Channel 1 (1920-2010MHz/2220-2200MHz) as IMT65 channel.
In July 2022, 3GPP announced that the 5GR17 standard frozen, which marked the completion of the third standard version of 5G. 5G R17 expands the network coverage scene from the ground to non -ground (NTN). Among them, the most important frequency band of the satellite part is the S frequency band.

2. The deployment of the satellite mobile communication system in the S frequency band
At present, the development of the satellite business using this band is: North America, Europe, China and Japan. (1) North America
North America first used this band to build a satellite mobile communication system. The ICOG1 satellite launched in 2008 and the Terrestar-1 satellite launched in 2009 were all used in this band, and they all covered North America. The two systems use the 20MHz bandwidth of this band, and the frequency division sharing method is used for each system 10MHz. Among them, ICOG1 uses 2010-2020MHz/2180-2190MHz, Terrestar-1 uses 2000-2010MHz/2190-2200MHz. The US Echostar acquired the United States ICO and Terrestar in 2011.
(2) EU
In 2009, the European Commission issued a decision, that is, 2009/449/EC decided to divide the S frequency band in half and authorize to Inmarsat and Solaris Mobile 15MHz resources each. Inmarsat's S-frequency band load is carried on the Hellassat-3 of the Hellas satellite company in Greece and launched on June 28, 2017. The effective load of the S -frequency band provides enhanced mobile services throughout Europe through the ground LTE hybrid network.
Solaris Mobile was originally a joint venture of SES and EUTELSAT. It was acquired by Echostar in 2014 and changed its name to Echo Star Mobile. It launched the Echostar-Band satellite on June 8, 2017 to provide satellite mobile services for Europe.
(3) Japan
QZSS is a satellite positioning system in Japan, mainly consisting of 3 "quasi -ceiling" track (QZO) and 1 static orbit satellite. There is a security confirmation service in QZS, which uses 2000-2005MHz/2190-2195MHz band. This service can only be used in Japan and its coastal areas.
Third, S frequency band constellation plan

At present, three satellite companies in the United States, Australia and Russia plans to deploy global constellations.
(1) omnispace
Omnispace was established in 2012. Its goal is to build a constellation so that various mobile smart devices can roam between honeycomb and satellite networks. Omnispace constellation originated from ICOGLOBAL, with 12 medium -orbital satellites (10355km). Two orthogonal mid -circuit planes have 5 satellites and 1 spare star on each orbit plane.
ICOGLOBAL launched a satellite in 2001 before bankruptcy. Omnispace acquired ICOGLOBAL NGSO assets and owned this ICO-F2 satellite. In addition to the acquisition and ICOGLOBAL NGSO assets, Omnispace also declared Omnispacef2 network data through Papua New Guinea. Its constellation configuration and frequency are the same as the ICO system. The user link uses the S frequency band. On April 9, 2020, Omnispace announced that it ordered two prototype satellites from Thales Alenia Space.
(2) SIRION
Sirion Global is an Australian satellite operator. On April 10, 2012, the Sirion-1 satellite mobile constellation was declared from Australia. There were 56 satellites, of which 28 satellites were located at 4 orbit at the height of 2000km. The orbital inclination angle is 89 °; the other 28 satellites are located at 7 orbital surfaces at the height of 650km, 4 satellites per track, and the orbital inclination angle is 96 °. On October 25, 2019, Echostar announced that its subsidiary Echostar Global LLC has acquired Sirion Global. Echostar has ordered two tiny S-band satellites from the Tyvak Nano-Satellite Systems to launch a low-earth orbit constellation program with the Sirion-1 satellite network data.
(3) GONETS
Gonets (messenger) include three generations of satellites: Gonets-D1, GONETS-M, and future Gonets-M1. The GoneTS-M1 uses S frequency bands and plans to deploy from 2024. There are 24 satellites of the constellation, 4 orbit surfaces, 6 satellites per track, a rail height of 1500km, and an orbital inclination of 82.5 °.
Fourth, the S -frequency band already has a country and region with ground IMT applications

FCC authorized the frequency band to ground mobile services on December 17, 2012, called AWS-4 (Advanced Wireless Services) and shares the frequency of satellite business. Dish company Dish, a US company, who has recently argued AWS-4 spectrum permits in KU (12GHz) frequency band. The European aviation network co-constructed by Inmarsat and German Telecom adopts the European CGC (Complementary Group Component) rules. It is an integrated S-Band system. The "sky" part is the mobile communication satellite, and the "ground" part is the ground 4G/LTE network. Satellite and ground network adopt the same S-Band frequency to serve the European airspace's civil aviation passenger aircraft. In addition, more than 20 countries in South America and the Caribbean region, the Philippines in Asia and Bangladesh, Ukraine in Europe, Nigeria in Africa, and other countries have used some frequency of the S -frequency band to ground mobile business. Vietnam and South Korea have clearly stated that the entire S -band will be used for ground mobile business.
Although the competition in the S frequency band is fierce, most countries and regions around the world have no actual application in this section. In the frequency plan of various countries, it can be a ground business or a satellite business. SpaceX's application S frequency band still has a lot of room for development in the world. What kind of business will SpaceX use the S frequency band? Can the direct -connected satellite be successful? let us wait and see.
- END -
Binzhou Mobile fully do a good job of supporting the communication along Huang

On August 5th, Deputy Mayor Bi Zhiwei went to the Paper Fang to control the guidan...
[Humanities Tour] "Super Moon" rises on the pyramid

On the evening of July 13, Cairo, Super Moon appeared again in the night sky. T...