What happened to the asteroid that made the dinosaurs extinct?
Author:Astronomy online Time:2022.08.18
It disappeared 66 million years ago.
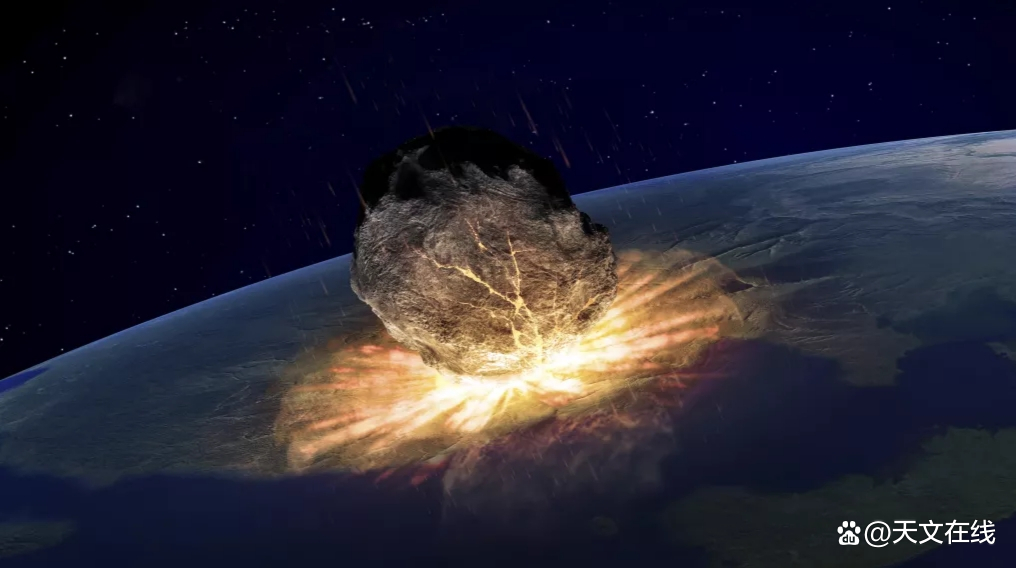

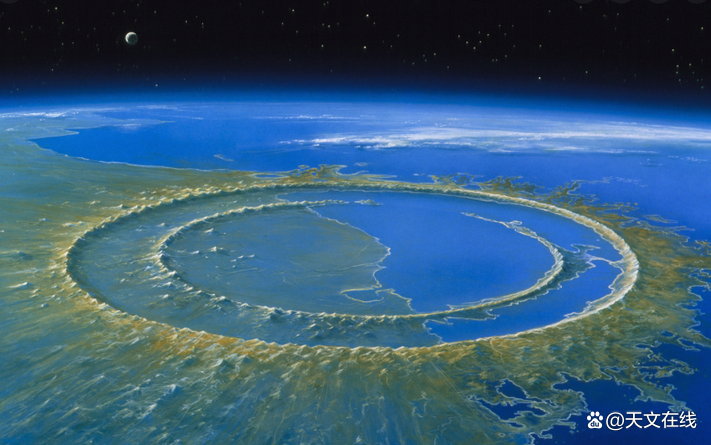
A artist describes a little asteroid about the extinction of dinosaurs, leaving a 124 -mile -wide crater on the surface of the earth. (Index: Andrzej Wojcicki Via Getty Images))
Hidden under the Water Bay of Mexico, Hick Surubo pit marked 66 million years ago asteroid hitting the earth's impact site. The result of this catastrophic event was the fifth large -scale extinction, 80%of all animal types, including non -bird dinosaurs.

But when the asteroid hit the earth, what happened?
After studying Hick Suruber and the world's geography, scientists made up for the bad day and what happened in the next year.
According to a study published in natural communication in 2020, before the asteroid impact, it had prepared the slaughter and hit the earth from the most destroying all angle. This asteroid is about 7.5 miles (12 kilometers) in diameter and a speed of about 27,000 miles per hour (43,000 kilometers per hour). Saine Gurik, a professor at the Institute of Earth Physics, said that he was the leader of the research. More importantly, the asteroid hit the earth about 60 degrees on the horizontal line. This angle can be completely destroyed, because it sprays a large amount of dust and gas -soluble gel into the atmosphere.
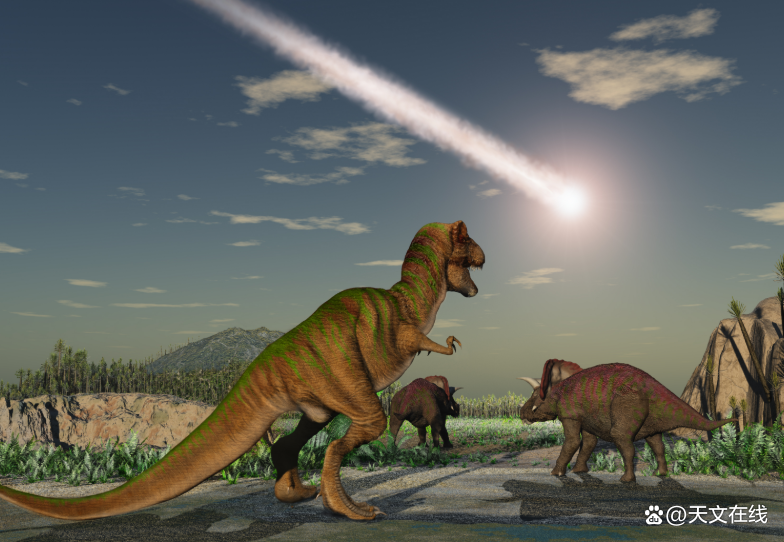

Gurik pointed out that his colleagues' evidence in this area can support the simulation of impact from this angle, including the asymmetric structure of the crater, the position of the mantle rock of the upturned (upward), and the unique in the rock core collected from the area. The sedimentary sequence, especially in the rock core, does not have a unique type of rock called evaporation rocks, such as stone salt and gypsum.

Gurik's team estimates that the impact will evaporate the evaporation, which will discharge 325 billion tons of sulfur and 435 billion tons of carbon dioxide into the atmosphere in the form of sulfur gas solution.
A study published in the magazine of "Natural Earth Science" in 2014 showed that the substances that were thrown into the atmosphere were mainly composed of crushed rocks and sulfate droplets. These substances came from sea -phase rocks rich in sulfate, known as hard plaster gypsum. , Evaporate during the asteroid impact. This cloud consisting of micro -substances forms a layer of coverage around the planet, reducing solar calories and light entering the earth. The long -term cooling generated has completely changed the climate of the earth. A study published in the magazine of Earth Physics Research in 2016 found that the average temperature in tropical regions dropped sharply from 81 Vargment (27 degrees Celsius) to 41 Varicidity (5 degrees Celsius). As the incident sun darken, the photosynthesis weakened, the foundation of land and marine food chains collapsed, and dinosaurs and many other animals fell.

At the same time, research in 2014 found that sulfuric acid in the air caused fatal acid rain after several days after the impact, killing countless marine animals living in the upper part of the ocean and lakes and rivers.
The impact also triggered a large -scale tsunami, the shallow water wave spread on the earth's ocean. According to the model research, the waves were originally a height of nearly 1 mile (1.5 kilometers) and a speed of 89 miles per hour (143 kilometers/h). 4 meters). More importantly, the sediment records around Louisiana preserved evidence of deposits from huge waves. The 3D earthquake survey of Louisiana geology showed that the 52 -foot (16 -meter) high -symmetrical giant wave pointed to the Bay of Mexico.

Raging fire
After the impact, the gravel and ashes flowed back to the surface, which also triggered a series of wildfires. The researchers compared it to the grilled chicken to lit the dry match. Additional smoke and ashes may be the cause of the cooling cover, which further reduces the sunlight.
When a geological scientist checks the rock formation, it is easy to see when the asteroid impacts; a milestone research published in the magazine in Science in 1980 found that it can be traced back to the end of the Baiji period of 66 million years ago around the world. There is a thin layer of clay in the rock.种 is a rare element on the earth, but it is common in space rocks. However, although other spectacular events such as wild fire and tsunami attracted people's imagination, Gurik believed that it was more important to change the earth's atmosphere, and the terrible corpse cloth led to more than ten years of cooling.
He said: "The only way to create a big extinction is to mess up things that affect the entire earth. Here, you have direct evidence to prove this."
By: Stacy Kishh
Fy: Fu Mo
If there is related content infringement, please contact the author to delete after the work is released
Reprinted, please obtain authorization, and pay attention to maintaining integrity and indicating the source
- END -
Shanhai Cooperation Wenzhou Institute of Technology Taishun Research Institute unveiled
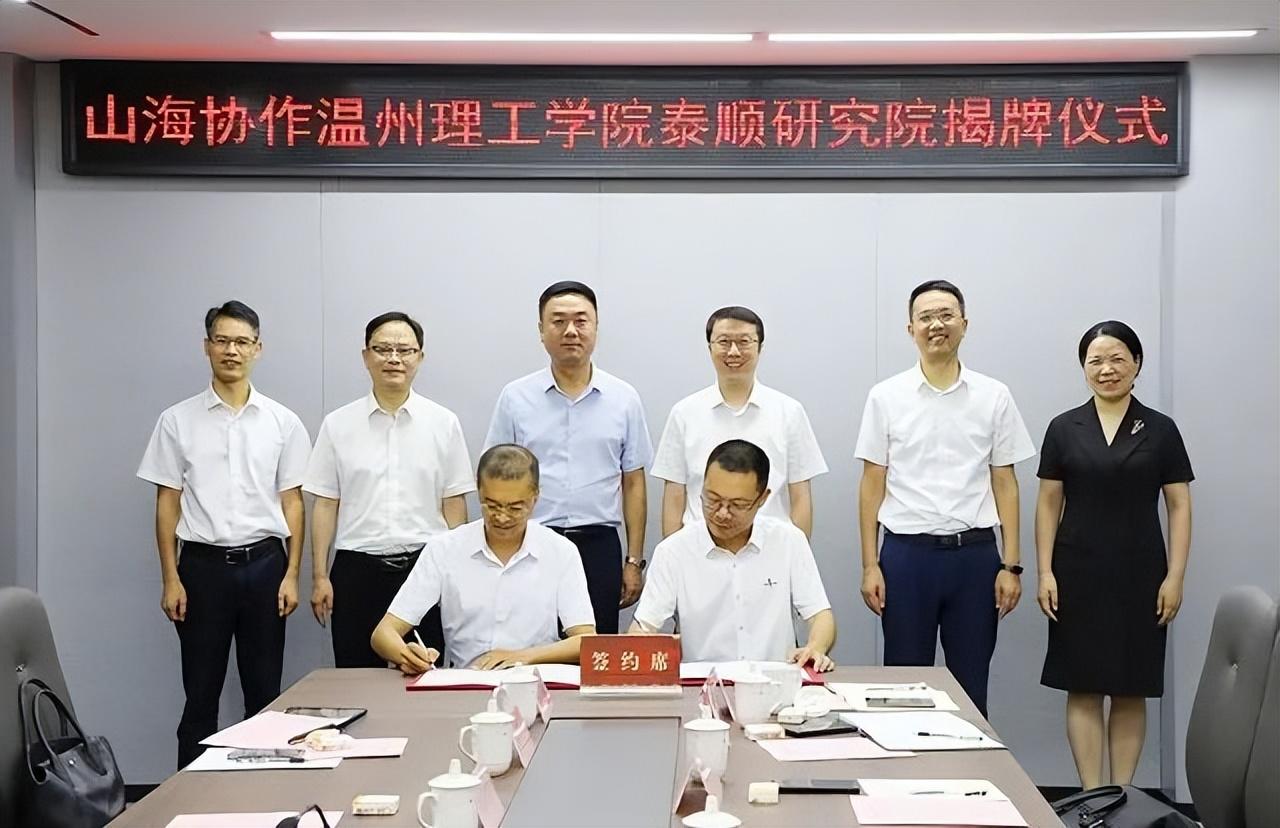

On August 8th, the unveiling ceremony of the Shanhai Association of Wenzhou Associ...
The most technology!The freshman admission notice of Zhejiang University is made with Maogu
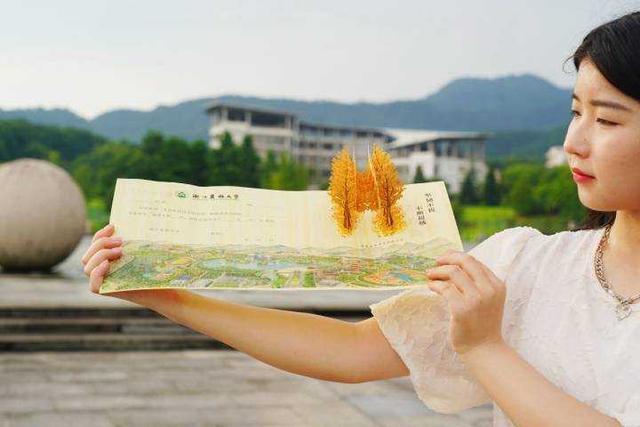

Recently, Zhejiang Agricultural and Forestry University announced the 2022 Most Sc...