Satellite "carbon measurement": it is easy to go to the sky, it is difficult to land | 36 carbon focus
Author:36 氪 Time:2022.08.17

During the short period of storage, in the field of carbon satellite, the national team has enough to serve as the main force. But commercial satellite companies are essential.

Wen | Yuan Silai
Edit | Su Jianxun
Source | 36 carbon (ID: carbon_36kr)
Cover Source | Vision China
After the "double carbon" goal is confirmed, all walks of life have a strong demand for carbon reduction. The first step in solving this demand is to know "where is carbon", that is, the monitoring and collection of carbon data.
Calculating the carbon emissions of an enterprise can be operated. However, if a industrial park, a city, or even a country can be calculated, the difficulty will be greater.
The industry is trying to solve this problem with satellites.
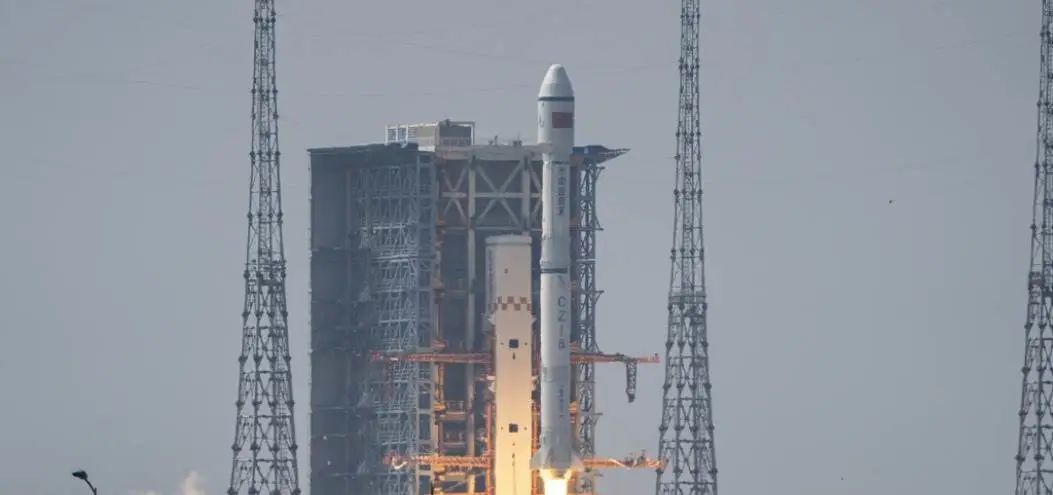
On August 4, the Long March No. 4 of the Rockets sent the carbon monitoring satellite "Jumang" into space. This remote sensing satellite can observe the height of the forest vegetation, area, and chlorophyll fluorescence emitted by plants. Through these elements, forest carbon exchange can be calculated, that is, "the amount of carbon dioxide absorbed and stored in the forest vegetation".
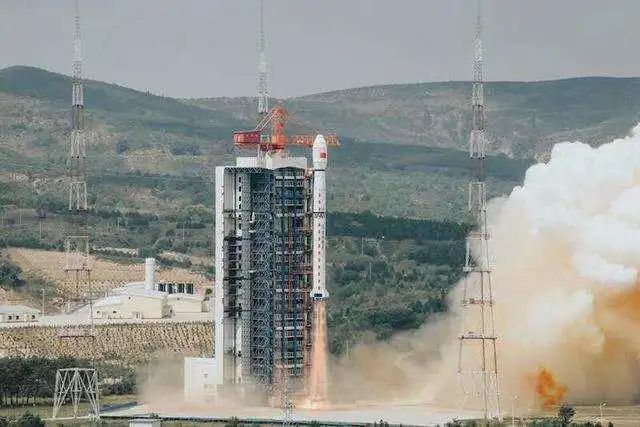

Sentence Mang's launch site. Picture from China Youth Daily
In the past, the forestry bureau had to find out forest carbon exchange, and could only use extremely "primitive" monitoring methods: forest investigators went deep into the mountain forest, measured the height of each tree and the trees of the trees in turn, and then calculated the carbon exchange. This measurement data update is not timely, usually once a quarterly update.
After the carbon neutralization became a global hot spot, carbon trading rises, and the requirements for data frequency and quantity are high. And human life carbon emissions are changing rapidly, such as a Google search will generate 0.2g of carbon emissions. The data updated once every three or four months cannot meet the fast -changing trading market.
Satellite observations have also become a relatively mature solution. Many domestic data companies currently track carbon exchange and use satellite data from overseas. The "Juman" is one of the few domestic satellites that are positioned as "carbon detection", which can give more targeted information, and it is also an important step for domestic carbon exchange monitoring to enter the era of remote sensing.

How to monitor carbon exchange in Jumang?
Carbon monitoring satellites are not new, and the detection technology used by Jumang has already matured.
In the past few years, China alone has launched more than one carbon monitoring satellite. In 2016, China launched the first carbon dioxide satellite to monitor carbon dioxide. In April of this year, the Long March 4th B launched a atmospheric environment monitoring satellite to monitor the concentration of carbon dioxide concentration in laser.
Earlier, there were many greenhouse gas observation satellites in space. In 2009, Japan launched the first greenhouse gas concentration monitoring satellite GOSAT. In 2014, NASA launched the "Rail Carbon Observation 2" (OCO-2) to observe how El Nino and other phenomena affect the carbon dioxide concentration.
The monitoring of the "Juman" is more segmented, and the design is biased towards measuring forest carbon exchange. It uses laser+optical cameras. On the one hand, laser laser is launched, reflected through ground objects, and calculating the height of the forest. On the one hand, it can detect unsally visible light such as infrared and ultraviolet rays from five angles to draw a three -dimensional vegetation distribution. See the growth of forest.
In addition, the "Sentel Mang" also has a detector and imaginger that can measure forest photosynthesis and PM2.5 values. These designs focus on observing forest scenes. Through the diameter of the height and tree, the researchers can calculate how much carbon per tree is stored, and then know the carbon exchange of the whole film forest.
However, carbon exchange will also be affected by other natural conditions, such as diseases and insect pests, which are difficult to reflect through laser. The additional spectral camera can detect unsightly light, and healthy forests have higher reflection rates to invisible light, so this camera can detect whether the forest grows lush and has diseases and insect pests.
Moreover, the spectrum camera can also depict the terrain. Generally, because there is less human intervention, the vegetation can save more carbon, and the carbon exchange is naturally higher. The slope can naturally calculate carbon exchange more accurately.
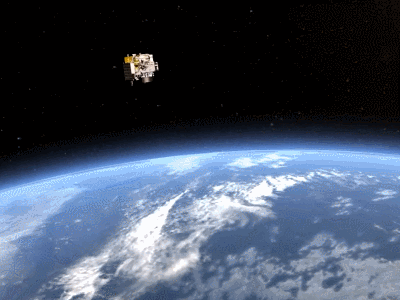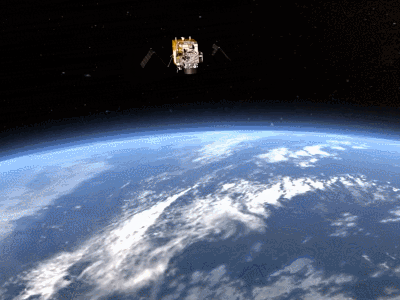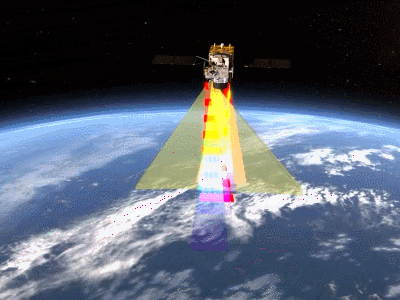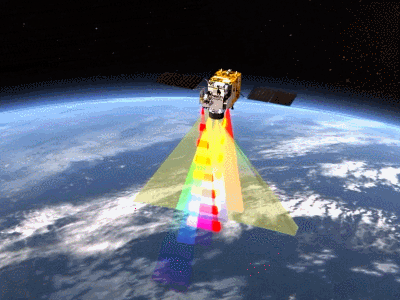
Satellite work signaling animation (the moving picture comes from the Fifth Academy of Aviation)
However, although the satellites have been on the sky, there are still several key indicators that have not yet been made public, including width and re -visits cycle. These are also the most concerned indicators for commercial data companies. Commercial use.
(Note: "width" refers to the one -time detection ground width of the satellite. Update frequency and information amount.)
Bai Chunyu, CEO of Planet Data, a carbon data solution provider, told 36 carbon that customers who purchased carbon data for carbon transactions are very concerned whether they can monitor and analyze the carbon assets of transactions according to demand, such as the overall changes in China's forest carbon exchange in China in the past three months Happening. This requires satellite -supported data countermeasure software to quickly process various needs, but there are very few domestic commercial companies in China. Even if such data is fully disclosed, it is difficult to apply quickly.
The commercial remote sensing data of domestic carbon trading reference relies on overseas. Even if the data of the sentence is disclosed, the number of carbon monitoring satellites currently launched in the world is difficult to meet the update needs. "Data insufficient" is a major problem that remote sensing carbon data analysis companies will encounter.

Unsolved data anxiety
In the past, carbon data was mainly monitored by ground monitoring. For example, 31 greenhouse gas global atmosphere observation stations coordinated by the World Meteorological Organization. However, these sites can only monitor land climate and cannot monitor the ocean. Satellite remote sensing monitoring can make up for regrets.
Europe, Japan, the United States, and Canada have successively launched satellites that observe carbon dioxide concentrations, which is of great significance for research on national level research. For example, American research institutions can already measure the operation and emissions of specific coal -fired power plants. The Institute of Atmospheric Physics of the Chinese Academy of Sciences also made a global carbon flux data set through "China Carbon Satellite" data. However, the number of remote sensing satellites that China can be used for commercialization is not high. Compared to NASA, European Air Bureau, and even the Japanese Astronomical Bureau, the public data of China's remote sensing satellites, regardless of quantity, quality, or easy access, the gap is not small.
"Even if there is an advanced satellite, I want to make precise measurement for global carbon exchange, and only rely on one orbit to serve, and there is no way to solve the problem overall. We hope that professional people can do professional things, such as business, such as business The work of space can be handed over to commercial companies. "Bai Chunyu said.
In fact, there have been successful cases for commercial aerospace companies to participate in carbon monitoring. For example, the Canadian satellite company GHGSAT launched three greenhouse gas monitoring satellites, and they also have their own data management platform Spectra. GHGSAT customers include Shell Petroleum, Chevron, and Daidal Energy. Investors are no shortage of petroleum giants such as Saudi Arabia and Exxon Mobil.
The painter's virtual GHGSAT satellite picture, copyright belongs to UTIAS-SFL

In fact, as far as the national team is concerned, the hardware and aerospace technology of Chinese satellites is enough to be better than the world. However, after the information collected by satellites, how to quickly process information and take out carbon exchange data needed by ordinary commercial customers is a more important issue.
According to Bai Chunyu, these processing should be uniformly designed before the satellite and the docking with potential customers, instead of analyzing after the obtained by the satellite information.
However, data users of the national team satellites are often national scientific research units. Their demand is mainly aimed at more macro global changes research or national needs at the national level. Even after getting such data, the space application company that can be performed is very limited.
Of course, relying on the underlying spectrometry information of overseas, as long as there is an analytical ability, some companies can make carbon emissions and carbon exchange data. However, the development of carbon trading is a dynamic process. At present, the global carbon trading market has grown rapidly. In 2021, the total global carbon market transaction volume increased 1.6 times compared with 2020 to 760 billion euros.
After various countries participate in carbon neutralization, the frequency and amount of carbon transactions will increase. With the maturity of the financial market, the demand for carbon emissions and carbon exchange data will only be more hungry.
The market must always be full of vitality after countless participants cooperate. Because of the participation of commercial companies, the industry can grow rapidly. In particular, carbon neutral and this area involving global money and resource flow cannot be relying on several giant companies or institutions to provide all needs.
In the field of carbon satellites, the national team has enough to serve as the main force. But commercial satellite companies are essential. When various countries and companies have reached the era of carbon data, a large number of commercial satellite companies and data companies can ultimately meet their needs.
36 The official public account of its subsidiary


I sincerely recommend you to follow


Let's "share




Satellite "carbon measurement": it is easy to go to the sky, it is difficult to land
- END -
Kancai | Swipe your face and eat, cooking meals ... AL restaurant is really wisdom or a gimmick

Robotic cooking, calculating calories when ordering ... There is a AI cafeteria in...
Chinese mobile phones continue to innovate, and the full screen will further, leading mobile phone innovation

It is reported that mobile phone companies have developed a new front camera techn...