Six countries scientists jointly launched the "Unprepared Research Protection Plan"
Author:Return Time:2022.08.16
Protein is an important alien of life, participating in all important parts of the body. It is the material foundation of life and the main undertaking of life activities. It can be said without exaggeration that there is no life without protein. People have never stopped the research on protein, but they are also protein, but different types of attention is different. So far, most protein studies are concentrated on some limited proteins. As a result, popular proteins are becoming more and more well -known. The unpopular protein biological function is still known. In the long run, the huge "gap" between known function protein and unprepared protein began to appear slowly. Therefore, paying attention to the study of unbuctulatory protein, narrowing the cognitive gap between different types of proteins, and solving the problem of non -exit of annotations. It can be said that the arrows are on the string, which is imperative.
This year, Georg Kustatscher and other six countries such as the six countries jointly launched a survey called the "Protein Program for Inaudible Research" and published two important articles on the Nature Methods and Nature Biotechnology, calling on the academic community to unite systematically without representing a systematic connection. The protein and the protein of known functions are reduced, and the annotation gap between the two is to lay the foundation for detailed mechanism research.


How will this plan be carried out? How many unknown surprises will it bring us? This article compiles on the basis of not changing the original text. It is hoped that more researchers and scientists can respond to these appeals, decrypt the unknown unknown and "dark matter" protein, and expand the boundaries of human perception of biological macromium.
Original title: "Six Kingdoms scientists jointly launched the" Unsubinable Research Protein Plan ", Nature's two major subsidiaries follow the" Dark Material "Study of the Protein Group"
Compilation | Ji Shi
Responsible | Li Xiaowei
1 Protein research status quo
Scientists pay attention to different proteins. The most popular protein in the human protein group is P53. On average, there are two documents published by P53 as the research object every day. At the same time, thousands of other human protein biological functions have not been studied. In the research of the functional representation of the human protein group, 95%of the published works are focusing on 5,000 human proteins that have been fully studied. The sequencing of the human genome is considered the key to reducing this prejudice, but even after the genome sequence is disclosed for ten years, 75%of the published works still only pay attention to the genes that have been studied before the genome drawing. In fact, since the release of human genome sequences, this annotations of this annotation (Annotion inquality) have almost doubled.
Non -exitability hinders the advancement of biomedicine. Research on related mechanisms between genetic diseases is usually concentrated on the widely known protein (Figure 1). At the same time, many unswerving proteins -related proteins related to disease have not undergone functional research. For example, many protein functions involved in rare diseases (uncomfortable), we know very little about them. In addition, common diseases such as neurological disorders and cancer are caused by many rare genetic mutations in different genes. It is worth noting that as of 2015, 330 (18%) of the 1,878 genes that were proliferated to a human cell system had not yet been characterized. This deviation extends to about 3,000 proteins that are currently expected to do drug research: currently only 5-10%of the potential target proteins can be used as the target of the FDA (US Food and Drug Administration) approved drugs.
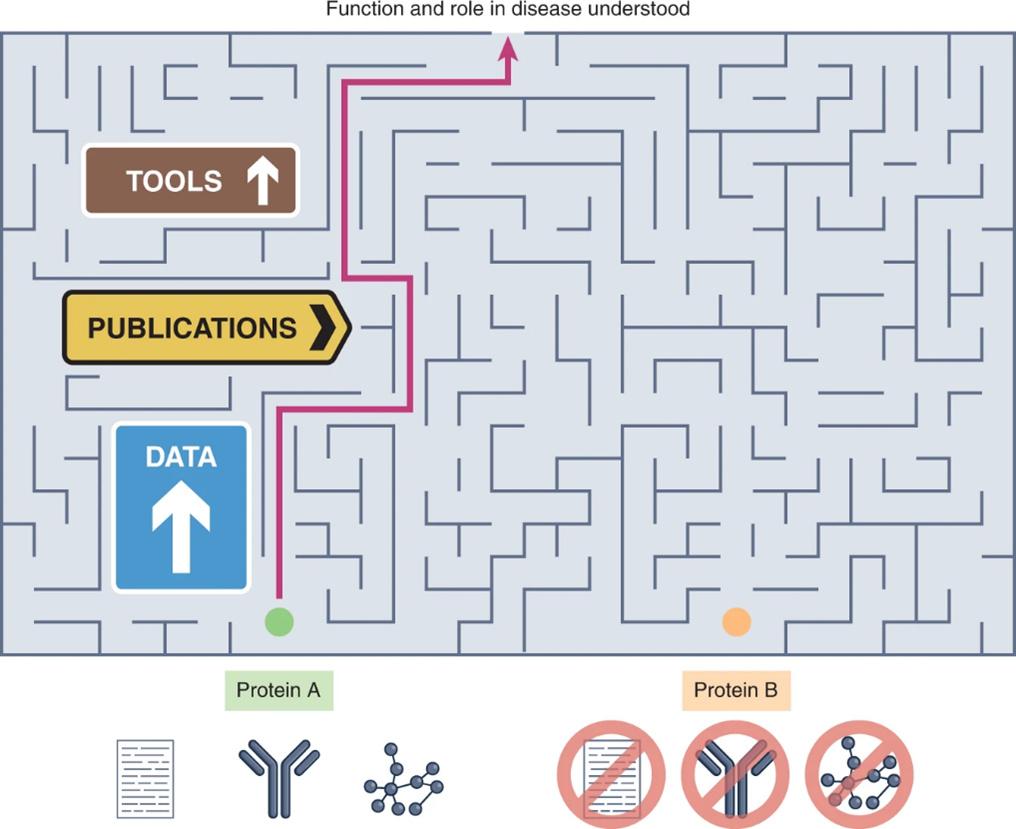
Figure 1 Protein annotations have hindered the progress of biomedicine. The number of previous documents, data, and tools determines whether the protein research problem is easy to propose and solve. This deepen the annotation deviation and also make the problem that has not fully studied protein.
2
The origin of protein annotations
The reasons for protein annotation deviations are multiple aspects, and some are practical reasons. For example, experimental tools such as antibodies, plasmids or carefully created reference data have strongly promoted people to choose to study those proteins that have been fully studied. The number of literature on protein is also related to its basic biology and biochemical characteristics, such as protein size, abundance, hydrophobicity, and the sensitivity of its genes to mutations. In fact, so far, 1,899 (9.6%) of the 19,733 personal protein coding genes lack the reliable support of protein groups, and some of them may constitute genome injection errors.
In addition, one of the significant common features that are not fully studied is that the molecular weight is extremely small: 40%of the most annotated protein in Swissprot is less than 15 kda. In addition, the "small protein" library that is currently known to be fully studied may be just the tip of the iceberg, because we have just begun to discover the "alternative protein" group. These protein genes were previously considered to be non -encoding areas.
Other causes of protein annotations may reflect the prejudice of the research system. For example, people usually think that there are many research proteins that are more important in function. Scientists are usually more willing to explore the problems that have been studied in detail. In addition to the need to avoid risks in the application of funds and peer review systems, the large -scale research field can also increase the attraction and increase the opportunity to publish articles in high -influential journals. The paradigm that supports the existing paradigm rather than the new ideas has also slowed down the overall scientific progress. Some of the conditions for laboratory research are also important reasons. The contradiction is that these restrictions may be that the standardization of the laboratory conditions may make the study more repeated results. For example, under standard laboratory training conditions, about 20%of the lack of winemaking genes will produce a dead phenotype. However, when cultivation space expands, 97%of genes are essential for the best growth under at least one condition. This problem is more complicated for multi -cell biology with special cell types; some tissues or cell types are more research than other tissue or cell types.
Finally, protein annotation deviation reflects that people pay more attention to the research of assumption driving rather than problem -driven, and it is difficult to propose a molecular function of non -table protein mechanism. The philosopher Francis Bacon was once considered the "father of scientific methods". He believes that experiments should not be driven by assumptions to avoid the prejudice of observers. Therefore, some people have proposed that strict data -driven methods can help reduce protein annotations.
3 Accelerate drug discovery for drugs that have not fully studied protein
From the perspective of drug discovery, those measures that improve our understanding of protein-small molecules interaction, such as structural genomics alliances, enzyme function plans, clarifying the pharmaceutical genome plan, and open targets. Fundamental progress is gained in the study of protein. In this case, "functional characterization" usually indicates the molecular characteristics of special -related proteins that are specially related to drug development, such as its structure, ligand, chemical probe, and associated with disease. The focus is on the protein family that is convenient for pharmacological research, such as ion channels, g protein coupling and kinases. But with the development of new methods (such as Protacs), the definition of medicinal proteins is developing over time.
4 How to use a functional protein group to solve the problem of non -existence of comments?
It is necessary to distinguish two different types of protein annotations: original research and "association" method. Original research on new biological functions is essential. It involves many detailed mechanism research, which is time -consuming and spending great. For researchers, to be committed to such a work, the protein studied must have a certain level of basic annotation. Otherwise, its functional assumptions will lack the foundation. The "functional correlation" annotation can provide the foundation that lacks the lack of knowledge transfer, thereby linking the previously unprepared protein to the protein and its biological functions that have been fully studied.
The protein group method is particularly suitable for revealing functional associations in large scale. This includes technologies that identify protein-protein interaction, to identify the methods of compassion for protein regulation, and how to reveal which protein sharing sub-cell space (specifically Figure 2). For example, before the antibody -based protein group identified hundreds of additional central protein, people believe that most centered proteins have been identified.
Although the protein group based on mass spectrometry has not yet reached the gene coverage of the genome method, it may be particularly useful to observe the protein directly when the function of the study (protein coding) genes. For example, compared to MRNA, the role of protein is particularly significant in capturing functional relationships. Based on protein -based analysis, it also has the potential to distinguish the form of protein, that is, a single molecular form that is expressed by protein. Among them, editing and post -translation modification have significantly increased the functional diversity of protein groups. Protein forms may need to use protein groups that are from top or bottom or from from middle or down. The volume of protein groups is rapidly increasing, and there are already ways to record hundreds of protein groups on a single mass spectrometer every day.
However, it is unlikely that protein annotations are unprepared to completely solve through large -scale methods. The first step to work hard to solve the deviation of protein annotation may be systematically provided the necessary minimum data basis for individual researchers who targeting related experiments, such as using mass spectrometer to identify protein-protein and protein-protein-protein-protein-protein-compound interaction Bioplex and Hu.map projects; use antibodies to attribute human protein to human protein maps (Human Protein Atlas) with different tissues and sub-cells; and the NEXT-CP50 project that is designed to signs 50 kinds of non-protein through protein groups to signs 50 kinds of non-fully study protein projects Wait.
Figure 2. Reveal the protein group method associated between different proteins: mass spectrometry (MS) and antibody -based methods, to identify the interaction between different proteins (PPI) Different from deviations, each method has advantages and disadvantages. The above is the key technology in recent years. It is worth noting that there are various intangible spectrum methods that can also reveal the connection between different proteins. Including binary analysis, such as Y2H, Lumier, genetic interaction screening, and metabolic feature analysis. 5 How to increase the role of functional protein group in mechanism research?
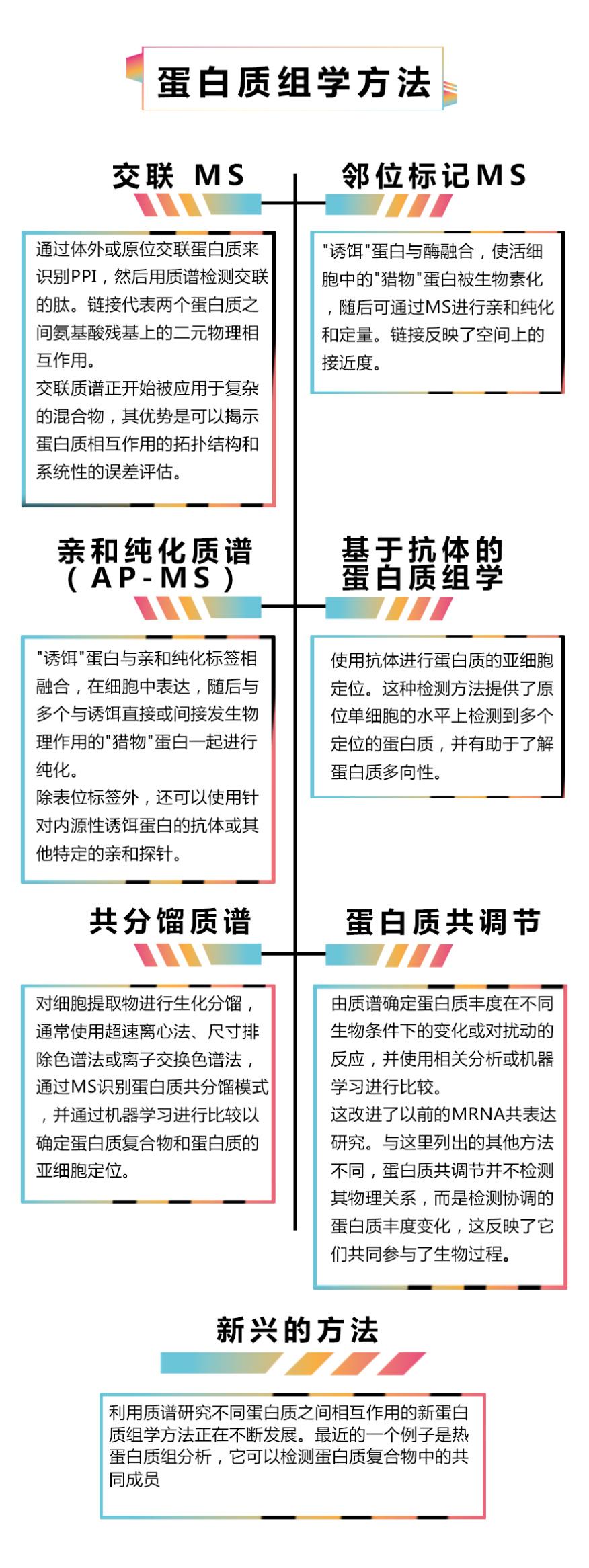
Biologists can view molecular networks through various powerful and convenient resources, including Intact, BIOGRID, NDEX, and String. Although these resources are easy to obtain, the annotation deviation is increasing. There may be many reasons: maybe cell biologists do not understand these comments portals, or they may lack trust, or insufficient annotations and insufficient integration of different comments.
Cell biologists may still have doubts about data relying on large -scale projects. In fact, processing errors in statistical methods are unique advantages of large -scale methods. Although errors are unavoidable, the severity is the key parameter of understanding the reliability of the result. One example of the calculation error detection rate (FDR) in functional protein group is the cross -linking mass spectrometry method. Similarly, the conventional calculation method of all mass spectrometer protein identification also needs to calculate the FDR. In addition, the statistical framework in the space protein group is also developing, with a view to distributing protein to the sub -cell area.
In addition to expanding the amount of large -scale data available, new tools and technologies need to be developed to fill the systemic gaps left by the current method. Emerging functional protein groups have the method of cross -linked mass spectrometry, co -concentrated protein group, and research on dynamic sub -cell district rooms. At present, the predictive protein structure has achieved great success, and it may further improve the structure -based functional prediction, especially when the predicted structure can be confirmed by experiments such as the crosslinker. These technologies and other intracellular technologies are particularly worthy of attention, because many proteins need to be folded or assisted factor or post -translation modification assistance to operate normally. In addition, the protein group technology of single cells is becoming increasingly mature, and this technology can determine the heterogeneity between cells.
The last key challenge is to integrate different types of data across dimensions (time and space), which will maximize the synergies between different types of groups of data. For example, the integration of human protein diagrams and BIOPLEX data shows that the generation of cell hierarchical structure can reveal many new cell systems, and these systems cannot be detected by any data set alone. Such a computing tool can also accelerate the scientific development by providing data -driven assumptions, that is, researchers are expected to connect their data to learn big data from protein groups.
Even if the function of a protein has been well noted, there are more and more evidence that some proteins have the ability to perform other unrelated functions and are called "part -time" in the literature. Because the researchers assumed that "a protein has only one function", people do not find other functions for most proteins. Another advantage of the full -system combing of functional protein groups is that it can provide other functional notments of protein that can provide full research, and better understand which "part -time" of protein can do.
6 How to quantify the progress of functional characterization?
If you want to formulate a strategy to solve the non -exiterity of protein and optimize and evaluate it, you need to ensure that the information is reliable and sufficient. The evaluation function characteristics are by no means easy. To a large extent, this term itself has different meanings. "Protein function" can refer to biological eyes in the general sense of protein, such as which type of phenotype it, or which metabolism it belongs to, can also refer to how to understand the structure and mechanism of these functions in the molecular level, such as the structure and mechanism of the molecular level, such as the structure and mechanism of the molecular level, such as the structure and mechanism of the molecular level, such as Enzyme mechanism, etc.
There are many methods for determining protein annotations, including literary scores based on text mining, UNIPROT annotations scores, evaluation of Go coverage, and systems that classify them based on protein as a drug target. Each indicator captures or emphasizes the slightly different aspects in the existing annotations, and does not distinguish the original characteristics and functional associations. However, in order to systematically evaluate an annotation transfer system, it is necessary to conduct full quantitative research on it to avoid the error of Malanmara (based on a single, easy measurement target variable without considering a larger range and more difficult measurement factors Let's evaluate the progress of a complex goal).
7 How to avoid bias bias?
We believe that the protein group is a powerful tool for annotation gene functions, but the protein group method is also vulnerable to the influence of biochemical prejudice, such as the influence of protein abundance and solubility. Therefore, in order to systematically reduce the deviation of the entire genome annotation, it is necessary to optimize multiple functional protein groups separately and integrate its results together. We can also integrate protein group learning data with other groups of learning data. For example, the metabolic group can capture a complementary functional spectrum. Please note that combining protein groups with genetics, functional genetic or metabolic groups can greatly improve the efficiency of phenotype prediction.
However, no matter what method is adopted, the restrictive factor of the standard laboratory must be eliminated. The recent survey of multi -organism protein groups shows that more protein can be characterized by comparing protein groups, because a large amount of protein function can be retained during the evolution, and the retained protein is different in different organisms. Performance. Many groups of scientific technologies are combined with genome editors that can be directly applied to human cell research, which has caused people to worry that the research funding for non -human biological research may decline. Although detailed statistics show that these concerns may not be foundable at present. Research on extensive and diverse creatures not only discovered penicillin, GFP and CRISPR/Cas9, but also helps us capture the functional scores of the human protein group. 8 "Unpleasant Research Protein" plan
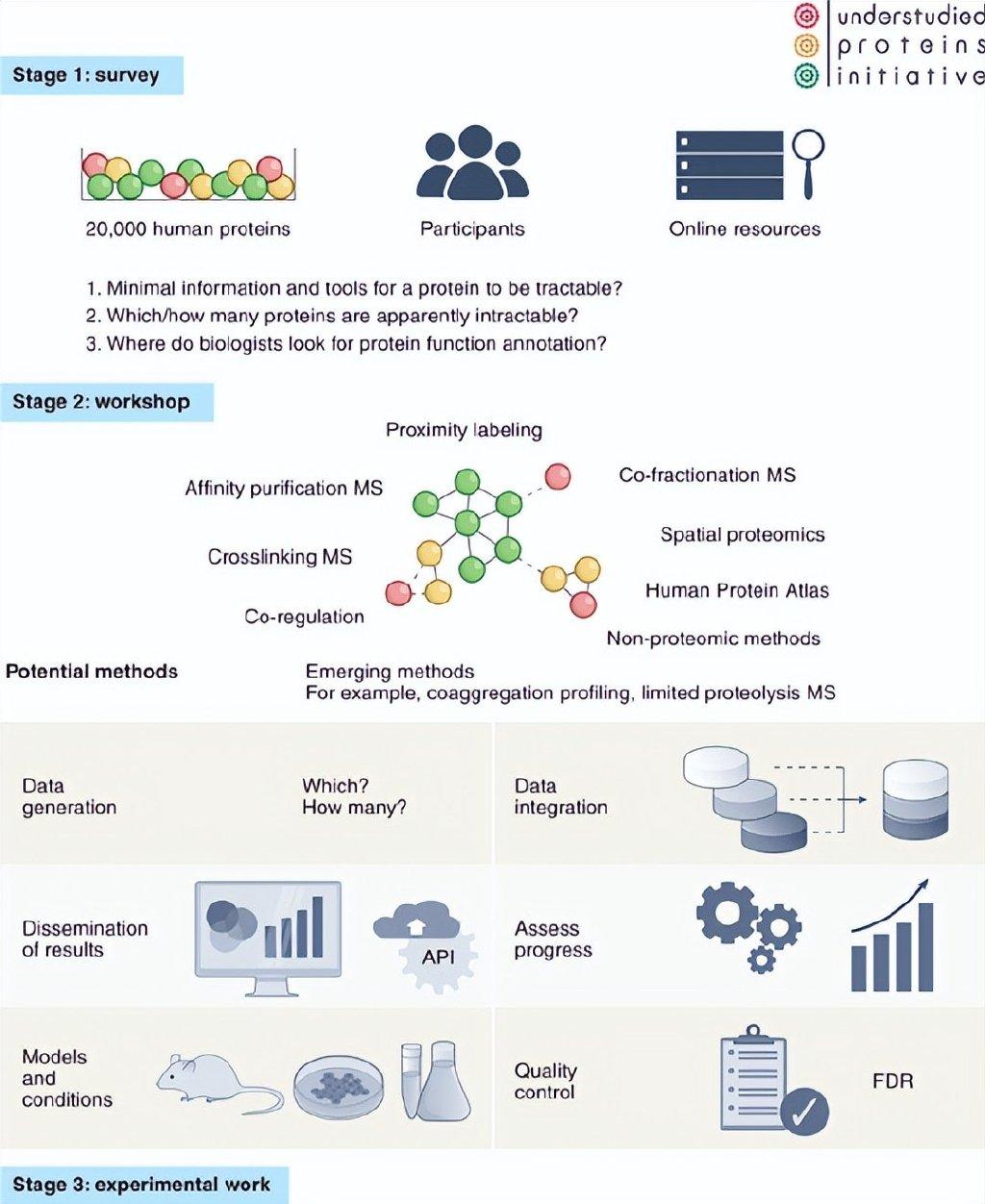
It is now when the annotations of the human genome and the protein group are not uniform (Figure 4). The "Unpleasant Research Protection Plan" will include a variety of different data generation methods, the development and integration framework, and providing comments to researchers through appropriate platforms. This project must not only solve technical problems, but also find the cause of the lack of genetic function, such as inaccurate growth conditions, a single point -point research, and over -concern for a small number of laboratory models with low genetic variability. The research on protein function extension may also promote the development of method science in functional protein groups and may extend it to other species.
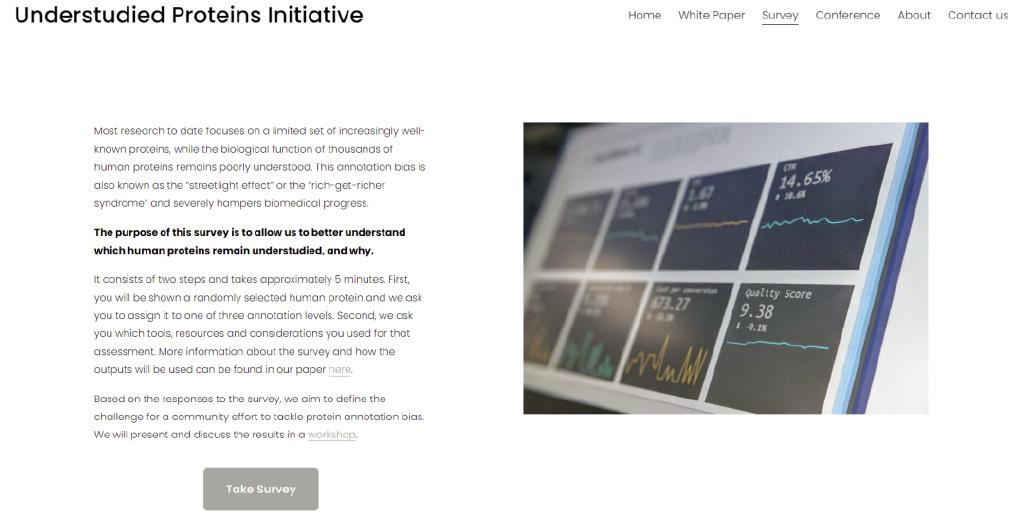
The first step must be clearly defined. If the role of functional protein groups is to promote the research on the mechanism that is not fully characterized by protein, then what are the most basic information required for scientists to start such work? This question can only be answered by scientists with a scientist of a single protein in the function of a single protein in the aspects of molecular and mechanism. In the end, the subjective judgment of laboratory scientists and auditors determined which proteins should be studied in detail. To understand these opinions, we recently launched a survey (https://undersStudiedProteins.org/survey). Scientific researchers can click the "Reading Original" at the end of the text and fill in the survey questionnaire.
Figure 3 "The protein plan that is not fully studied" survey screenshot (welcome all scientific researchers to click "Read the original text" at the end of the article, enter the page and click "Take Survey" to participate in the investigation)
In the second step, a team consisting of scientists interested in this field must be established. The plan is supported by the Wellcom Trust and will be started on the upcoming meeting (https://undersStudiedProteins.org/conference). The meeting will discuss the results of the above surveys, the impact of the goal of "unpleasant study of protein" and how to monitor the progress of these goals. This will help open discussions, such as which technologies or development can systematically release the potential of unspecified protein in current biomedical research? So as to promote more development in the field.
Figure 4. The roadmap of the "Protein" plan is not fully studied. The survey will help determine the challenges and goals of the plan. The seminar will bring together experts from the large -scale data industry to establish a planning framework covering six mobile fields. Finally, multiple laboratories will cooperate with experiments to solve the problem of not fully study protein through experiments.
Attachment: "The protein plan that has not been fully studied" and its scientific research units:
Georg Kustatscher: University of Edinburgh, Edinburgh, UKTom Collins: Wellcome Trust, London, UKAnne-Claude Gingras: University of Toronto, Toronto, Ontario, CanadaTiannan Guo: Westlake University, Hangzhou, ChinaHenning Hermjakob: EMBL-EBI, Cambridge, UKTrey Ideker: University of California San Diego, La Jolla, CA, USAKathryn S. Lilley: University of Cambridge, Cambridge, UKEmma Lundberg: KTH-Royal Institute of Technology, Stockholm, SwedenEdward M. Marcotte: University of Texas at Austin, Austin, TX, USAMarkus Ralser: Charité University Medicine, Berlin, Germany;Juri Rappsilber: Technische Universität Berlin, Berlin, Germany参考文献1. Kustatscher, G., Collins, T., Gingras, AC. et al. An open invitation to the Understudied Proteins Initiative. Nat biotechnol (2022). Https://doi.org/10.1038/s41587-022-01316-z z
2. Kustatscher, G., Collins, T., Gingras, AC. et al. Understudied proteins: opportunities and challenges for functional proteomics. Nat Methods (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41592-022-01454 -X
Special Note
1. Enter the "Boutique Column" at the bottom menu of the WeChat public account of the WeChat public account.
2. "Returne" provides a monthly retrieval article function. Pay attention to the public account and reply to the year+month for the four digits, such as "1903", you can obtain an index of articles in March 2019, and so on.
- END -
New Yellow River picture | China's first computing power conference is here. Why is it in Jinan?

New Yellow River Reporter: Huang MinEdit: Weekend
Building a "call security" defense line, there are more than one "security lock

Quietly planting the Trojan horse in the mobile phone, you can steal the other par...