"Artificial intelligence, is it necessary to be like humans?"
Author:Institute of Physics of the Ch Time:2022.08.10
Will the machine think? Can artificial intelligence be as smart as humans? A latest study shows that artificial intelligence may be done.
In a non -language Turing test, the research team led by Professor Agnieszka Wykowska, the Italian Technology Research Institute, found that the Behavioral Variability can blur the difference between people and machines, that is, it can help the robot look more like more like more like a more like a robot. Humanity. Specifically, their artificial intelligence programs simulated the behavior variants of human response time when playing games related to human teammates to match shapes and colors, and passed non -language Twenty tests. The relevant research papers are published on the scientific journal Science Robotics, " The research team stated that this work can provide guidance for future robot design and give robots a similar human behavior that human beings can perceive.
Regarding this study, Lin Xueping University's cognitive system professor Tom Ziemke and post -doctoral researcher SAM Thellman believe that the research results "blur the difference between people and machines" and make it very much for people's scientific understanding of human society. Valuable contribution.
However, "human similarity is not necessarily the ideal goal of artificial intelligence and robotics technology development, making it may not be like humans may be a more wise approach like humans."
Through Turing test
In 1950, Alan Turing, the "Father of Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence", proposed a test method to determine whether the machine has intelligent testing, that is, Turing test. The key idea of Turing test is that the complex issues of machine thinking and intelligence possibilities can test whether humans can distinguish whether they are verifying with another person or interaction with a machine. Today, Turing test is used by scientists to evaluate what kind of behavior characteristics should be achieved on artificial intelligence to make it impossible for humans to distinguish between computer programs and human behavior.人工智能先驱司马贺(Herbert Simon)就曾表示:“如果程序表现出的行为类似于人类表现出来的,那我们就称它们是智能的。” 类似地,Elaine Rich 将人工智能定义为“研究如何Let computers do things that are now better. " Non -language Turing test is a form of Turing test. For artificial intelligence, it is not easy to pass non -language Twenty tests, because they are not as skilled as humans in terms of testing and distinguishing between other people (objects). So, can a human robot be tested by non -language Tu Ling to reflect human characteristics in its physical behavior? In non -language Twenty tests, the research team tries to figure out whether artificial intelligence can be used to change the reaction time in the range similar to human behavior mutation, which is regarded as humans. To do this, they arranged humans and robots in a room with different colors and shapes on a screen.

Figure | Robot and humans perform tasks together. (Source: This paper)
When the shape or color changes, the participants press the button, and the robot responds to this signal by clicking the opposite color or shape displayed on the screen.
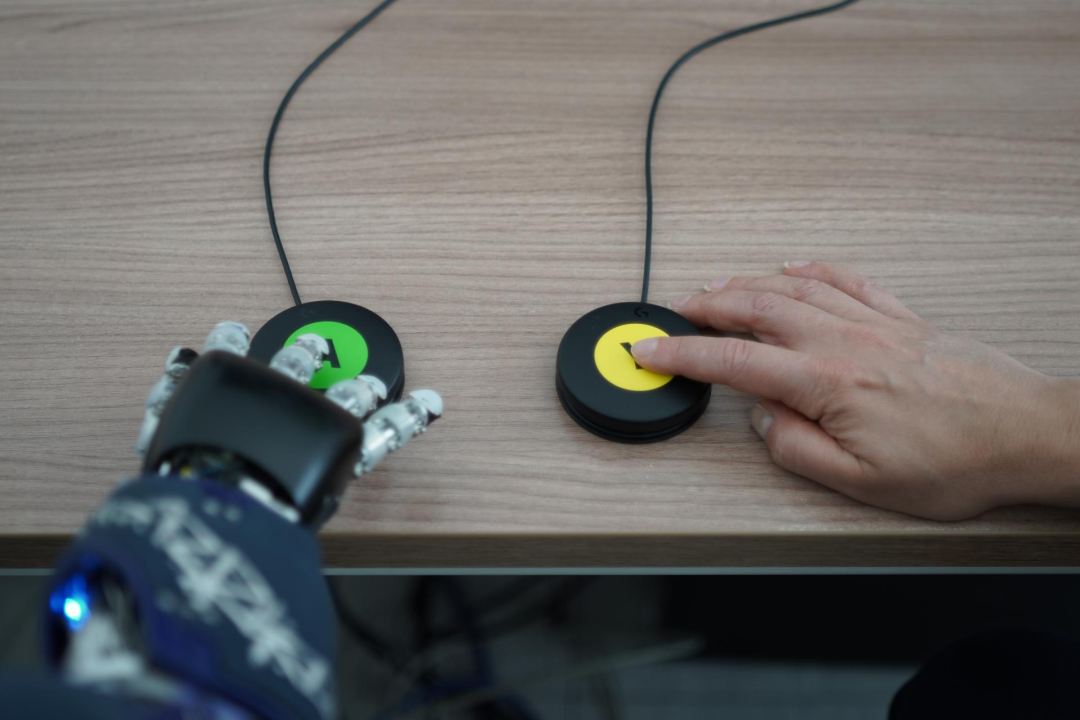

Figure | Press the button to respond (Source: This paper)
During the test, robots are sometimes remotely controlled by human beings, and sometimes artificial intelligence controls that are imitated by trained imitation behavior.
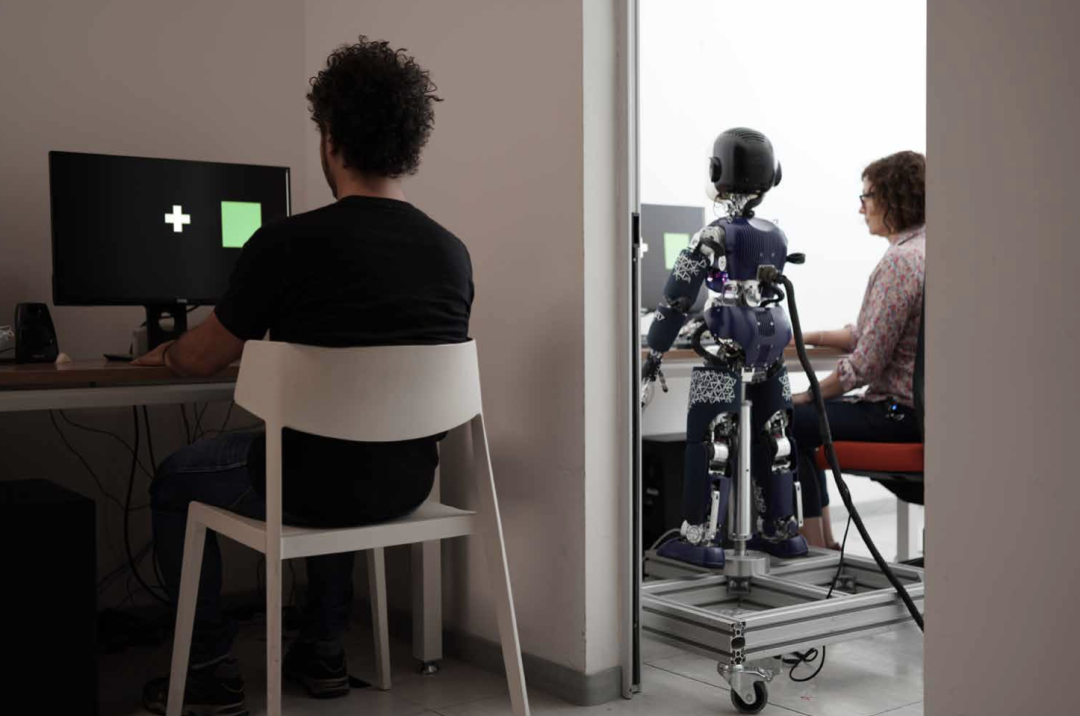

Figure | Participants are required to judge whether the robot behavior is pre -programmed or controlled by humans. (Source: This paper)
The results show that participants can easily distinguish when the robot is operated by another person.
However, when the robot is operated by artificial intelligence, the probability of the participants is more than 50%.
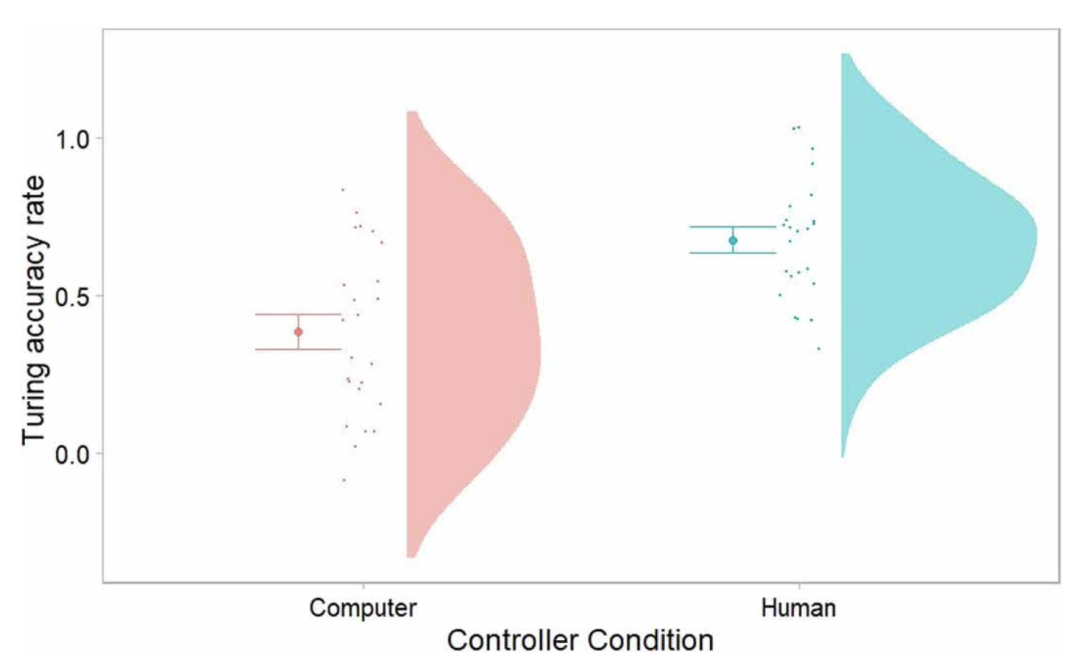
Figure | The average accuracy of Turing test. (Source: This paper)
This means that their artificial intelligence has passed non -language Tu Ling test. However, researchers also said that the variability of human behavior may be only a necessary and inadequate condition for non -language Twenty testing by physical artificial intelligence, because it can also be manifested in the human environment.
Is artificial intelligence, is it necessary to be like humans?
For a long time, artificial intelligence research has always regarded human similarity as the goal and measurement standards. Studies by the Wykowska team proved that behavior variability may be used to make robots more like humans. ZIEMKE et al., It is believed that it may be a more wise approach to make artificial intelligence like humans, and explains the two cases of autonomous cars and chat robots.
For example, when you are preparing to pass through the crossway on the road, you can see that a car is approaching you. From a distance, you may not be able to judge whether it is a autonomous car, so you can only judge based on the car behavior of the car to judge the behavior of the car. Essence
(Source: pixabay)
However, even if you see someone sitting in front of the steering wheel, you are not sure whether this person is actively controlling the vehicle or just monitoring the driving operation of the vehicle. "This has a very important impact on traffic safety. If you can't show other people to other people in the autonomous driving mode, it may cause unsafe human -machine interaction."
Maybe some people will say that ideal, you don't need to know if a car is autonomous, because in the long run, autonomous cars may be better than humans. However, at present, people's trust in autonomous vehicles is not enough. Chat robots are closer to the real scene of Turing's initial testing. Many companies use chat robots in their online customer services, and the dialogue topics and interaction methods are relatively limited. In this case, chat robots are usually more or less different from humans.
(Source: pixabay)
So, the question comes. Should companies tell customers the non -human identity of the chat robot? Once told, consumers often cause negative reactions, such as decline in trust. As described in the above case, although from the perspective of engineering, human behavior may be an impressive achievement, but the uninterrupted human machines bring obvious psychology, ethics, and legal issues. Essence On the one hand, people who interact with these systems must know the nature of the content they interact to avoid deception. Taking chat robots as an example, California California has formulated chat robot information disclosure law since 2018. It is clear that disclosure is a strict requirement. On the other hand, there are more examples that cannot be distinguished than chat robots and human customer service. For example, when it comes to autonomous driving, the interaction between autonomous vehicles and other road users does not have the same clear starting point and end point. They are usually not one -to -one, and they have certain real -time constraints. Therefore, the question is when and how to convey the identity and ability of autonomous vehicles. In addition, fully automated cars may take decades to appear. Therefore, in the foreseeable future, mixed transportation and part of different degrees of automation may become a reality. There have been many research on what external interfaces may be needed to communicate with people. However, people who are able to cope with disadvantaged people such as children and disabled people can actually know very little about children and disabled. Therefore, the general rules mentioned above, that is, "people who interact with such a system must be informed of the nature of the interactive object", may only follow in a clearer situation. Similarly, this contradiction is also reflected in the discussion of social robotics research: given that human beings tend to integrated human state and give them similar attributes, many researchers aim to make robots more like humans in appearance and behavior. They can interact more or less like humans. However, some people believe that robots should be easily recognized as machines to avoid excessive anthropomorphic attributes and unrealistic expectations. "Therefore, the more wise approach may be to make the robot less like humans with these discoveries." In the early days of artificial intelligence, imitating human beings may be a common goal in the industry, "but in artificial intelligence, it has become part of people's daily life part of people's daily life. Today, at least we need to think about what direction to achieve artificial intelligence similar to human beings. "
Reference link:
https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/scirobotics.abo1241
https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/scirobotics.add0641
Reprinted content only represents the author's point of view
Does not represent the position of the Institute of Physics of the Chinese Academy of Sciences
If you need to reprint, please contact the original public account
Source: academic headline
Edit: Just_iu
- END -
After watching "Lone Moon", don't look at where the moon comes from?

How is the moon formed?The most mainstream hypothesis is the Big Crane Paragraph. ...
Science | Three responsible persons in the flood prevention of small reservoirs: How do you know how to perform his duties and responsibilities?

The number of small reservoirs in my country and a large number of disease insuran...