Scientific research progress | Yang Tianming group made progress in the security of artificial intelligence in the brain -like algorithm
Author:The Chinese Academy of Science Time:2022.08.09
Background
Artificial intelligence can be seen everywhere in daily life. Whether it is face unlocking or autonomous driving, it is inseparable from automatic recognition techniques for people, vehicles, traffic signs and other objects. Once artificial intelligence is wrong, it will cause the inconvenience of users, and the severe consequences may cause serious consequences such as the destruction of the car. As a result, ensuring the security of algorithms is a very important part of AI research. At present, the common confrontation attack algorithm can be attacked for artificial neural networks. By adding some difficult noise on the picture or voice information, AI has a completely wrong judgment.
When animals and humans make decisions, although there may be many noise in sensory stimuli, the brain can exclude various interference and eventually make reasonable choices. Drift diffusion models in cognitive neuroscience (Figure 1, DRIFT-Diffusion Model, DDM) quantitative description of this process: The brain made the final decision when it reaches a certain threshold by accumulating evidence of interference. A large number of psychological physical experiments have found that the behavior of people and animals in the process of choice can be well explained by the DDM model. At the same time, neuron codes were found in the brain area such as the forehead and rear leaf in the brain and characterized the evidence accumulation process in the choice.
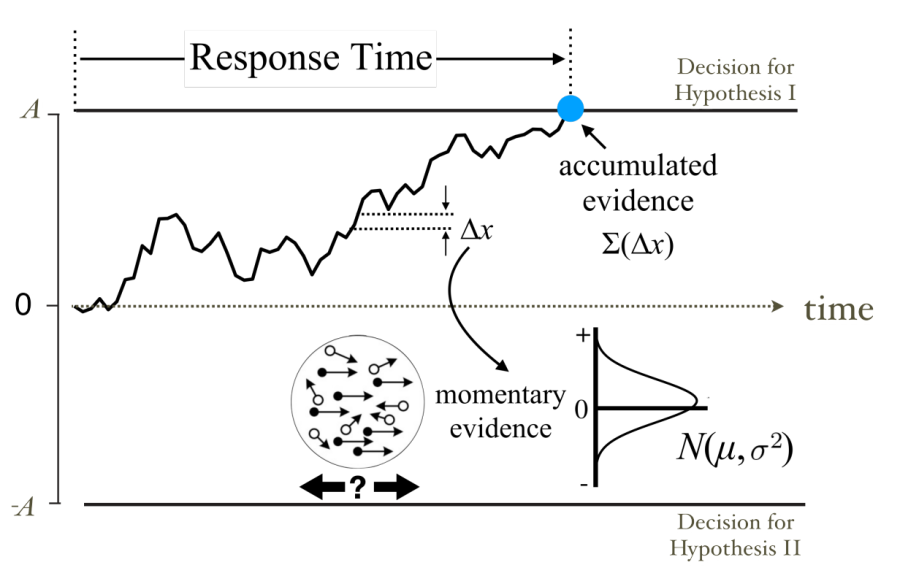
Figure 1: Drift diffusion model diagram. In a dilemma, at each moment, the model receives the signal of the noise containing a positive distribution as evidence. The model has accumulated evidence in time until the accumulated evidence reaches a pre -set threshold.
//
The Yang Tianming research team of the Institute of Innovation of Brain Science and Intelligent Technology (Institute of Neuroscience) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (Institute of Neuroscience) conducted a long -term and in -depth study of the neuromatical mechanism of the DDM model in the brain. The calculation principle performed in the middle. Inspired by this series of studies, the Yang Tianding research team designed a defense algorithm called Dropout-Based Drift-Diffusion Model (Figure 2) for artificial intelligence issues (Figure 2). The researchers first use the unit in the Dropout mechanism to simulate the synapses between neurons. This artificially introduced additional defensive noise can improve the accuracy of the attack classification when AI is attacked. The larger the introduction of the noise, the more you can "cover" those attack noise, which makes the attack failure. However, a large noise will also make the output of AI more random, and the accuracy will decline. Therefore, the researchers further introduced the DDM mechanism to accumulate AI on random output as evidence, and set the threshold to judge to remove the interference of noise and improve the accuracy of classification.

Figure 2: (left) The process of choice in the biological brain. (Right) The choice process in DDDM.
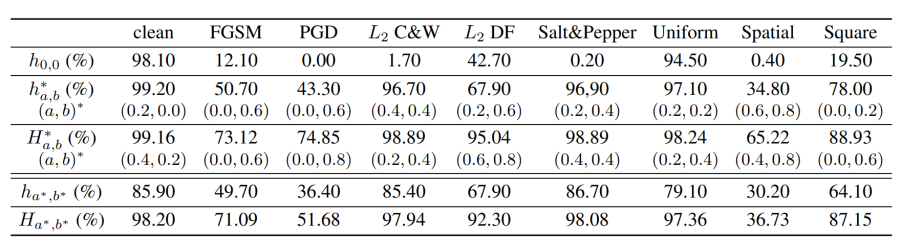
Researchers conducted experiments under the three scenarios of images, audio, and text, which verified the effectiveness of DDDM during defense attacks and the generality of different data modes and different attack methods. In the most important image classification task, researchers used eight different methods to attack a handwritten number of convolutional neural network classifiers. DDDM has greatly restored the classification accuracy under all attacks, and the accuracy of the four attacks can be restored to more than 98%(Table 1). In the experiment of the CIFAR-10 picture dataset, IMDB movie review data set and SpeechCommands voice instruction data set, DDDM also successfully improved the accuracy of classification after attack.

The DDDM model can also be adjusted dynamically to adjust the time required for the choice. When the amplitude of the attack noise gradually increases, the difficulty of choice becomes greater. At this time, DDDM maintained the accuracy of the classification at a high level by extending the decision -making time. This behavior is similar to animals and humans, and can maintain a certain accuracy rate by regulating the time required to make decisions when facing different difficulties.
The study fully shows that the DDDM model inspired by the brain's choice mechanism is a universal brain algorithm framework that can resist against attacks in a multi -mode and multi -task scenario. The model does not depend on pre -training for specific attacks, and can make choices in terms of time and accuracy as needed.
The study was completed by Chen Xiyuan, a doctoral student, and post-doctoral Li Xingyu under the guidance of Researchers Yang Tianding and Researcher Zhou Yi. It has been included in the 2022 International Artificial Intelligence Joint Conference papers (IJCAI-20122). This work was funded by the Ministry of Science and Technology, the Chinese Academy of Sciences, and Shanghai.
- END -
Qingdao played the "combination boxing" of the industrial Internet to benefit enterprises

Qingdao Daily/Guanhai News, June 16th. In recent years, under the wave of digital ...
Wind Observation 丨 Target "Northern E -sports Capital", how does Qingdao become the winners from pioneers?

Fengkou Finance reporter Lu HuaA young and open city, encountered a trendy and fas...