They manufacture 20%oxygen on the earth, but now they are dead
Author:High Energy Institute of the C Time:2022.07.21
The following article comes from WeChat public account: Global Science, author Global Science
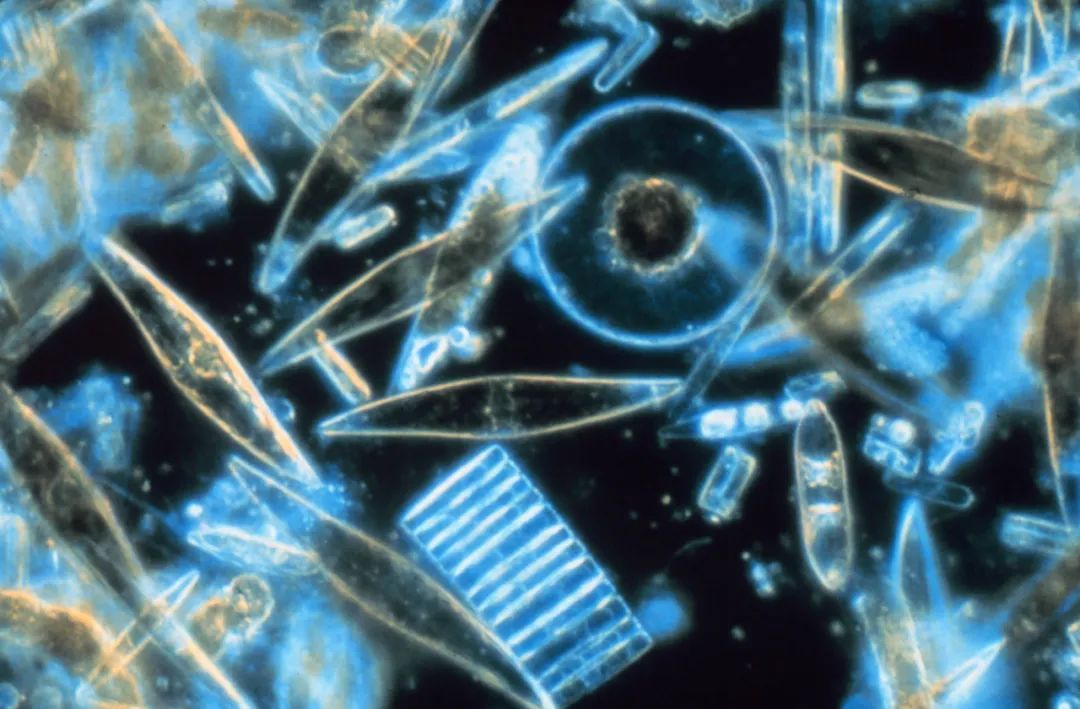
The round, long, square, and square in the picture are diatom (picture source: gordon T. Taylor, Stony Brook University/Public Domain)
There are 2037 words in this article. It is expected to read 5 minutes and inhale about 6.5 liters of oxygen.
Written article | Two Seven Seven
Review | Wang Yu
For most lives on the earth, you have to breathe oxygen if you want to survive. Most of our breathing oxygen is produced by biology -such as the photosynthesis of plants. But the most important oxygen producer is not the trees we are familiar with, but the tiny creatures in the water. One of the most important categories is diatom.
The diatom is a very small single -cell algae, most of which are only a few microns to tens of microns, and a few can be put down on one pin. But if you use a microscope to observe these small creatures, you will definitely be shocked by their delicate appearance -in fact, these exquisite structures you see are diatomic cell walls, also known as its "silicon shell".
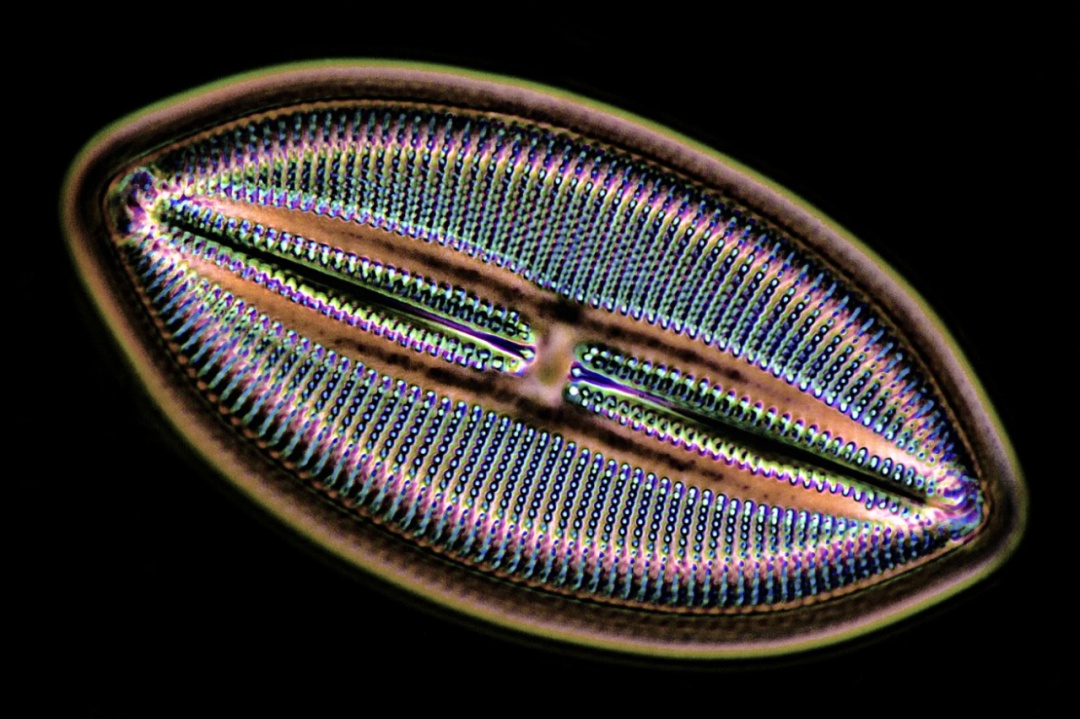
1500 times the diatom case under the microscope (picture source: Massimo Brizzi/Wikipedia)
Different from plants or animals, diatom cell walls are made of silicon dioxide. It is precisely the same as the ingredients of Opal (a gem) component. Similar to Opal's color change, the cell wall of diatoms will also show gorgeous structural colors.
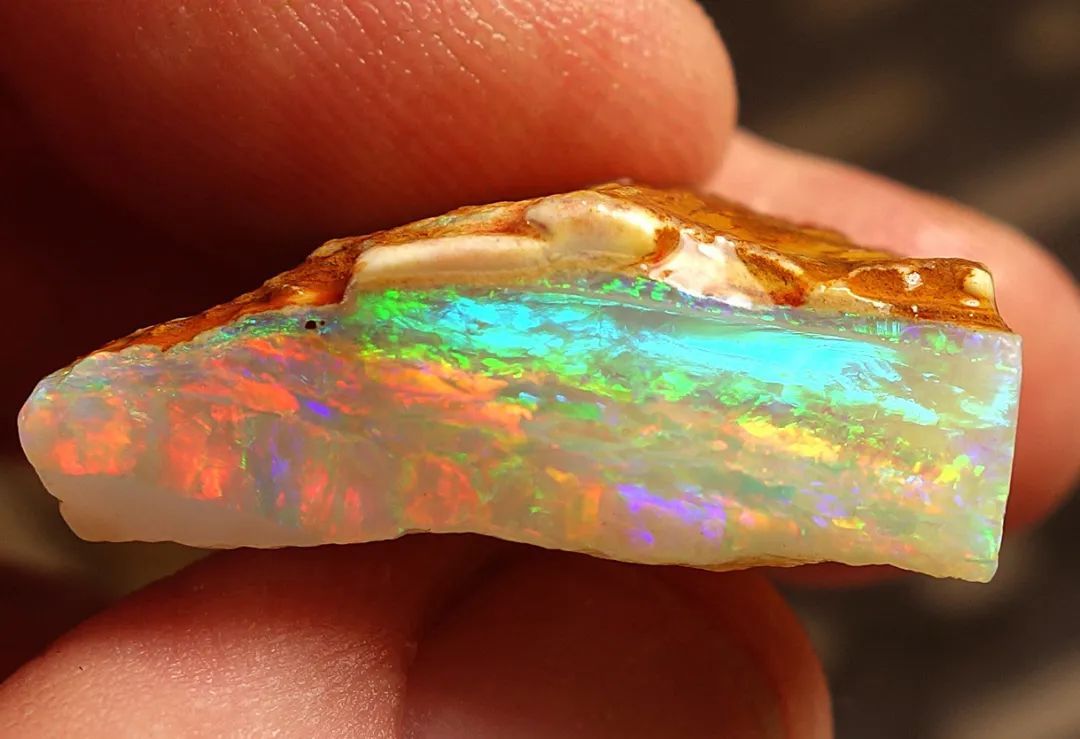

The transformation on the surface of Opal (picture source: dpulitzer)
Such a hard shell has made the diatoms the absolute winner on the earth. The known diatoms have exceeded 20,000. They are distributed in the ocean, rivers, and lakes that are distributed around the world. You can even be in a hot spring or The diatom figure was found in the South Ocean.
Such a wide range of distribution also brings huge productivity. According to estimates, among the air in your breathing, an average of 20%to 30%oxygen is produced by diatoms. This number even far exceeds the tropical rain forest known as the "lung of the earth". While producing oxygen, diatoms are also absorbing a large amount of carbon dioxide in the environment and stored it deep in the ocean.
"Diatom is one of the most important plankton in the ocean," Jan Tauch, a marine biologist at Geomar Hamhitz Marine Research Center, explained his strong interest in diatom, "their Any change may lead to a significant change in the marine food network, and it will even change the ability of the ocean as a carbon exchange to absorb carbon dioxide. "
Acidification
What we all know is that climate change is threatening the marine ecology. The dissolving carbon dioxide in the atmosphere will increase the acidity of the seawater. For those marine creatures with carbonate shells (mainly calcium carbonate), this is almost equal to the disaster of extinguishing: in the acidified seawater, the process of building calcium carbonate shells will consume more energy; if Seawater acidification intensifies, the concentration of carbonate is too low, and their carbonate shells may even be dissolved -this is the disaster that corals and shellfish in many regions are experiencing.

With the intensification of seawater acidification, the carbonate shells of many marine life are being threatened (picture source: noAA)
However, for diatom, the story of climate change is much more complicated. Many studies believe that diatom theory has the ability to resist the acidification of seawater, and may even gain benefits from climate change. On the one hand, as a microorganism that can perform photosynthesis, when the carbon dioxide dissolved in seawater increases, diatoms are more likely to absorb carbon dioxide and increase the rate of photosynthesis. On the other hand, the acidic environment can reduce the dissolution rate of silicon dioxide, so diatoms can save their own "silicon cottages" more effort.
The problem is that these are only theoretical speculations. Even single -cell algae has a very complicated life system. If you want to know that diatoms are more specific and possible under climate change, further research needs to be studied. Recent
Silicon in short supply
For many plankton in the ocean, the concentration of main nutrients (such as nitrogen or iron) determines their distribution. But the diatoms are more "valued" silicon in the seawater.
The silicate in the seawater is generally unsaturated, so the shell of the diatom is actually easily eroded and dissolved by the seawater. When the diatom is alive, it will secrete a layer of organic coating on the outside of the shell to provide protection. However, when diatom dies, this layer of protective coating will be unlocked by bacteria. In the process of falling along gravity to the depths of the ocean, the silicon in the shell was also released into the seawater of the "along the way", which also made up for the silicon consumed by diatoms in the surface seawater to a certain extent.
In this way, the diatom itself plays the role of "biological pump". Like the pump, the silicon in the seawater is transported from the surface to the deeper, and then the global marine circulation is transported back to the surface of the ocean to provide the next batch of diatoms.
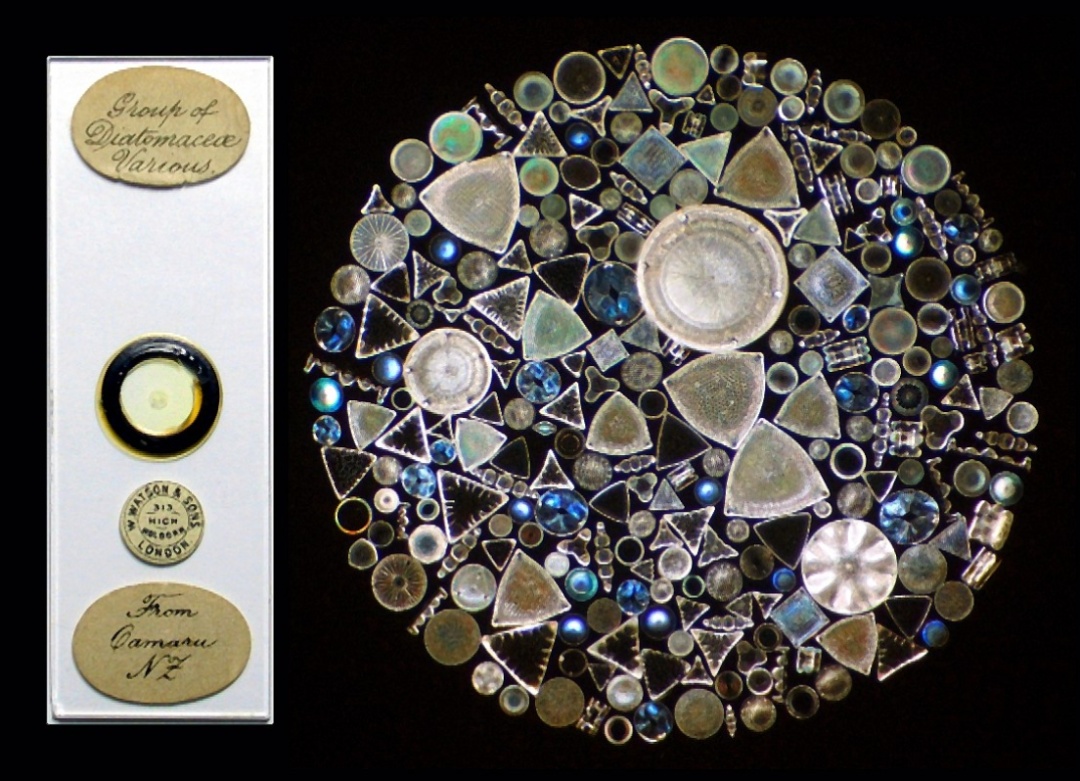

The diatom of the microscope is shining like a gem (picture source: Watson & Sons)
In order to simulate the changes in the marine environment under the climate change, Taohel's research team adopted the method of encirclement experiments: they separated a piece of seawater in 5 pieces of the ocean, and maintained a normal seawater cycle through artificial pumps. This is like intercepting 5 huge test tubes in the ocean. Researchers can enter carbon dioxide of different concentrations to the test tube to simulate the ocean acidification scene of different degrees. Researchers simulated the degree of seawater acidification of medium emission scenarios (RCP 6.0) and high emissions (RCP 6.0) and high emission scenarios (no measures to control carbon emissions at all). The ratio increased by 17%on average. In other words, in the more sour seawater, more silicon shells fall into the sediment without dissolving into the seawater.
Dominico card of diatom
Further model research brings greater concerns. The distribution of silicon in seawater is mainly affected by the two factors of "diatom pump" and marine circulation transportation. However, in the situation of severe acidification of seawater, the dissolution of the shell slows down, and more diatoms are directly sinking into the bottom of the sea, and it cannot be deposited there for a long time. Obviously, the ocean circulation cannot make up for this vacancy, so the diatoms that grow later cannot get enough silicon to make their own shell.
Seawater acidification will lead to a significant decrease in the concentration of silicate in the surface seawater (red represents increase, blue represents decrease, picture source: original paper)
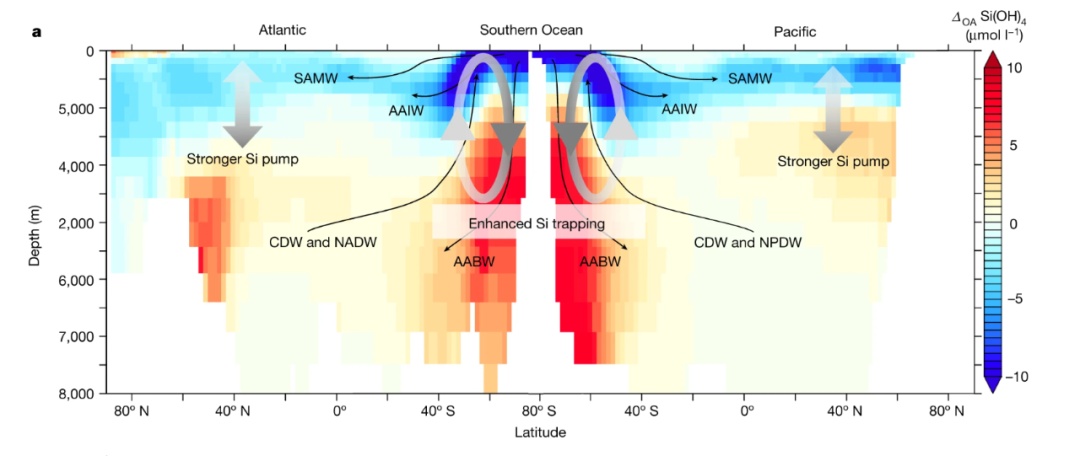
The simulation results show that in high emission scenarios, the silicate concentration in the ocean surface layer in 2200 will decrease by about 27%, which will directly lead to a decrease in the number of diatoms by 26%. If such a large number of junior producers are lost, other lives on the earth will be greatly affected.
In the dissertation, researchers are even more worried about "the consequences of ecosystem functions and carbon cycles are more difficult to evaluate", and the current data does not discuss the Domino brand effect on other consumers on the biological chain.
Image source: Howard Lynk
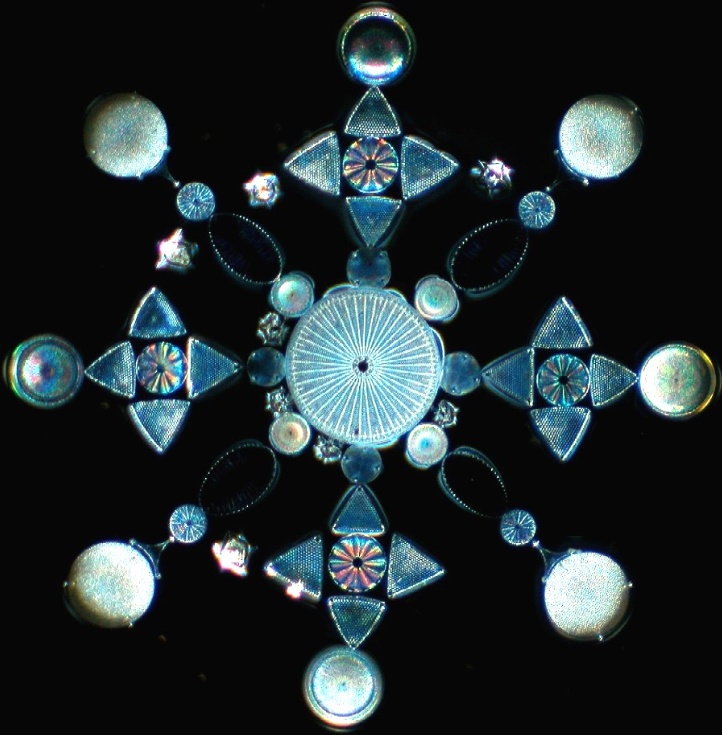

But in any case, the results of this study warned us how the feedback mechanisms that have not been noticed in the earth system will change our predictions on the environment and biological changes -we still do not know enough about our planet and the form of life in it is How to interact.
For Tauchl, this discovery is a sad surprise: "This surprise reminds us repeatedly that if we do not quickly and decisively deal with climate change, we will face irreparable risks."
Friendly reminder: you can breathe during reading
Related thesis:
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articleS/pmc5516106/
https://www.nature.com/articleS/S41586-022-04687-0#Ref-CR1212
https://onlineelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1111/j.1529-8817.2010.00919.x.x
https://esajournals.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1002/ecy.2765?saml_referrerrrrr
——End —————
This article is authorized to reprint from WeChat public account: Global Science Author: Global Science
Reprinted content only represents the author's point of view
It does not represent the high energy office of the Chinese Academy of Sciences
Edit: Xianyu
- END -
State Administration of Radio, Film and Television speaks!Such channels will be basically shut down!
On June 21, the website of the State Administration of Radio, Film and Television issued a opinion on further accelerating the development of high -definition ultra -high -definition TVs, which pointe
The market value is reduced by 10 billion US dollars!Growth is weak and the net loss expands, and the prospects of graffiti are geometry?

Text/Yang JianyongIt benefits the global wave of intelligence, and the unicorn on ...