"Another loneliness", will the oversized cities lack vegetables?
Author:Poster news Time:2022.09.03

"I don't know if it will be missing, but if you don't stock up, you will not be solid." On September 1, Shenzhen and Chengdu upgraded the epidemic prevention and control measures at the same time. As soon as the news came out, the first reaction of some citizens in the two places was "grabbing vegetables".
The crowded supermarkets and farmers' markets are "shifted" freezers and shelves, citizens who grab vegetables in various poses, and similar pictures can be seen everywhere on various social platforms. Subsequently, the official media of the two places released news, saying that the vegetables were sufficient and there was no need to hoard.
In fact, under the influence of the epidemic, in the face of possible "difficulty in buying vegetables", many large cities have had a boom in vegetables. Just as food security is not only an economic issue, but also an important issue of people's livelihood and political issues. The "vegetable basket" security is the same.
In today's social media, all kinds of vegetables and meat have been filled with shelves, leaving a question worth thinking about — will the large cities lack vegetables?
Spontaneous
To answer this question, the first thing to pay attention to is is whether the large cities can provide sufficient dishes to meet the local needs as much as possible, and to meet the local needs nearby?
In the agricultural field, "self -sufficiency" is generally used to describe the capabilities of cities. An article "Farmers Daily" states that in a few more, the self -sufficiency rate of vegetables is to "use it for me" or "for me"; it is not me to buy on the market, nor the supply of my foreign base base. Instead, you must be "born in Sri Lanka, growing in Sri Lanka"; as long as I want to eat, this part of the material can be produced, transported, and provided.
Can they maintain sufficient vegetable self -sufficiency rate for industrial structure adjustments earlier and agricultural proportion. Let's take a look at the two cities that "grabbing vegetables" this time.
Look at Chengdu first. Historically, Sichuan Chengdu has superior geographical conditions and outstanding urban advantages. It has always been known as "Tianfu Grain", while Chengdu is the core area of "Tianfu Grain".
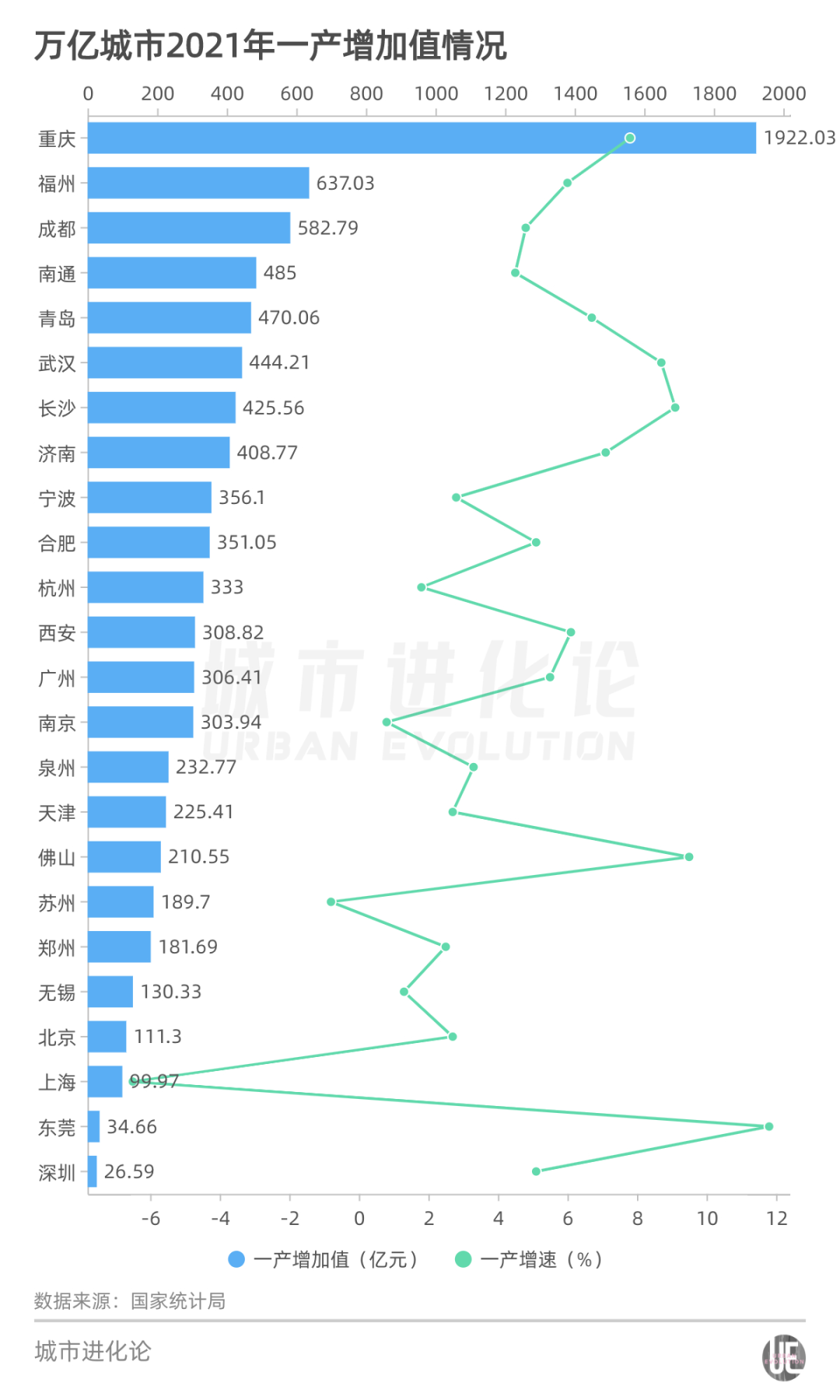
From the perspective of the three industrial structures, in 2021, the added value of Chengdu's yield was 58.279 billion yuan, second only to Chongqing and Fuzhou in the trillion club cities. Urban modern agriculture has also been an important part of the Chengdu industrial system.
In Chengdu, agriculture has not been "optimized". On the contrary, while ensuring the supply of local agricultural products (6.030, -0.02, -0.33%) of local agricultural products in Chengdu, a large number of products are also shipped to the country as an advantageous product.
Vegetables are one of them. Yesterday, in the face of the concerns of "lack of vegetables", the county -level Pengzhou Agricultural and Rural Bureau under the jurisdiction of Chengdu disclosed to the media that the city's current vegetable area is about 60,000 acres, with a mature period of nearly 20,000 acres, and about 600 tons of daily production.

Picture source: Xinhua News Agency
This also allowed Pengzhou to be seen again -Pengzhou is the main "South Caipan North Caipan" and winter and spring vegetable production bases. It is also the largest vegetable trading center in the Southwest. Pengzhou's annual total vegetable output is sold outside the province.
Under the support of Pengzhou, data showed that in 2020, the area of vegetable broadcasting in Chengdu was stable at about 2.6 million mu, the output was stable at about 6 million tons, and the self -sufficiency rate of leaf vegetables reached 100%.
Shenzhen is like the "opposite" of Chengdu. With an area of 48.1%of the construction area, which accounted for the forefront of Shenzhen in the country, the value -added of the yield in 2021 was only 2.659 billion yuan, ranking at the end of the trillion -dollar city. This means that Shenzhen does not have vegetable supply conditions like Chengdu.
But looking at the entire Guangdong, there are multiple agricultural cities in the northwest of Guangdong. Not only the vegetable bases such as Zhanjiang and Qingyuan are "escorting" in the Greater Bay Area, including Shenzhen, but also a large vegetable planting market as a provincial capital. Vegetable production is second only to Zhanjiang in the province. 100.6%.
Earlier, the "Southern Rural Daily" had statistics that based on the production of vegetable production in the first quarter of this year, Guangdong's vegetables were basically self -sufficient.
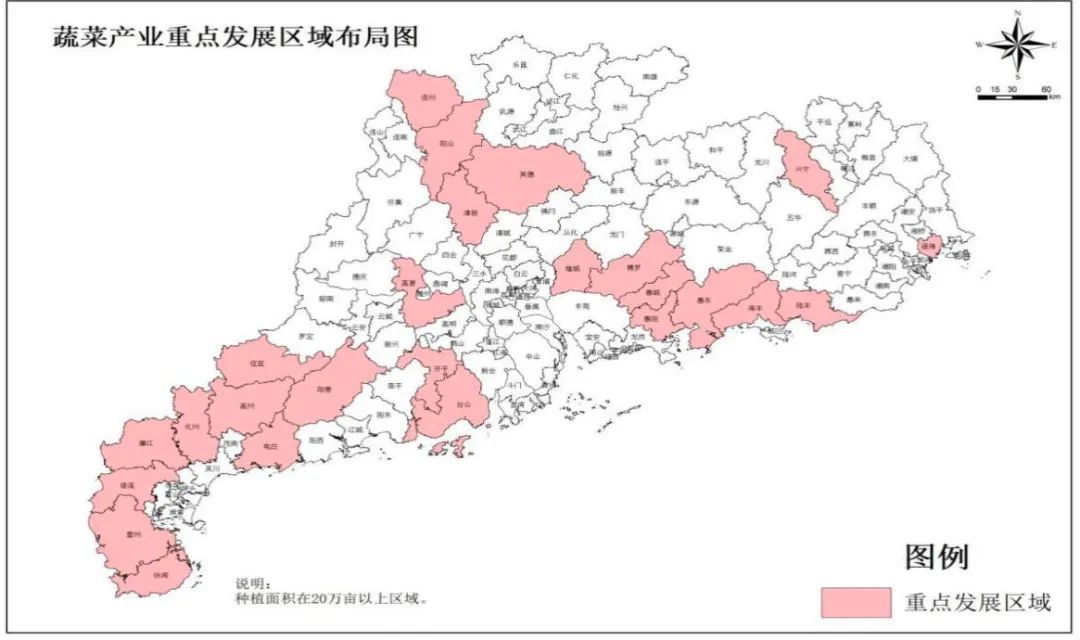
Image source: "Guangdong Province Promoting Agricultural and Rural Modernization" Fourteenth Five -Year Plan "
Profit and loss
Do all the oversized cities have such a powerful backing?
According to the latest statistics of the Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs, in late July this year, the country's vegetable area was 10.413 million mu, an increase of 3.85 million acres, and the output was 29.59 million tons, an increase of 1.42 million tons.
Look at the situation of different provinces. Vegetable production data released by the National Bureau of Statistics last year showed that there were more than 50 million tons of vegetable output in 5 provinces across the country.
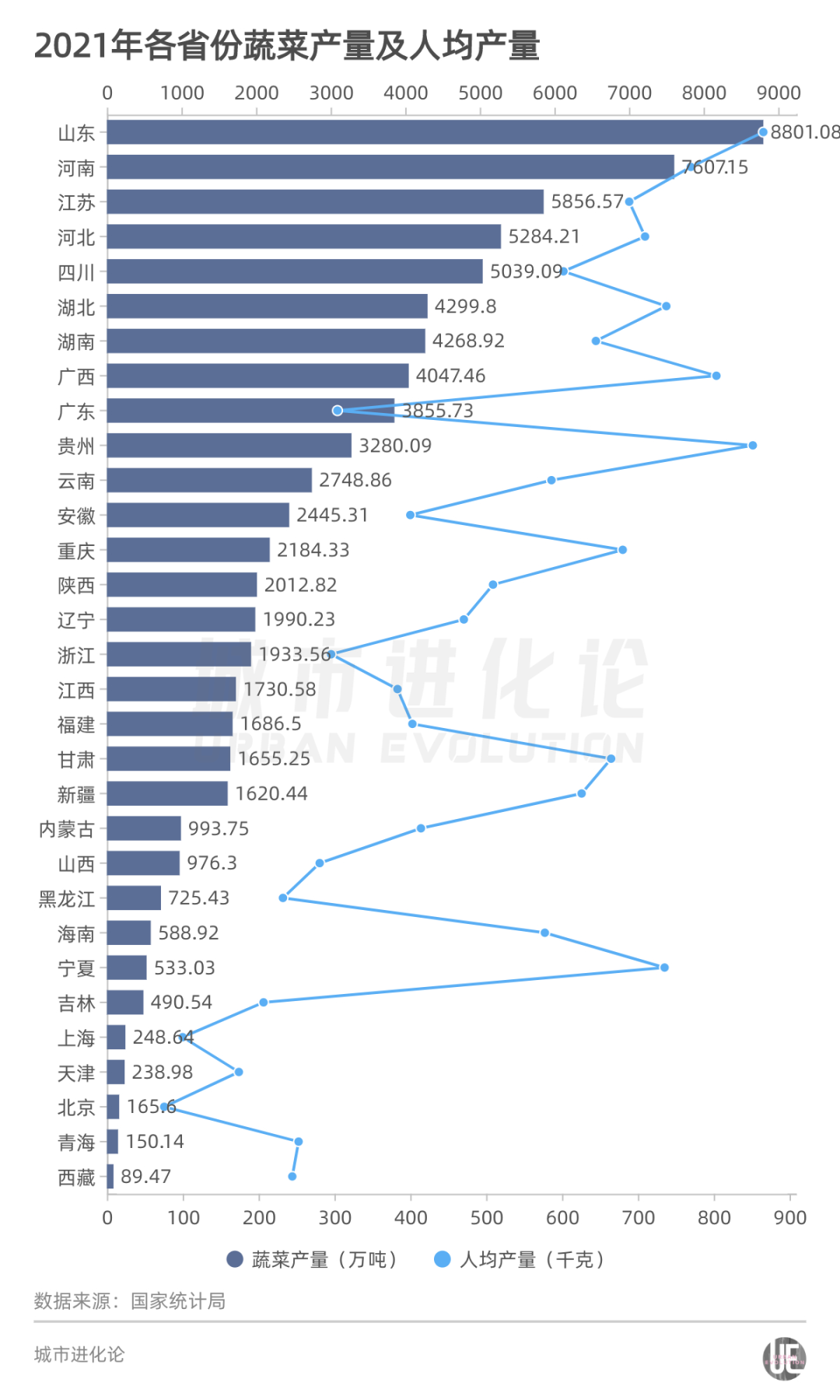
Among them, Shandong ranked first in the country with 88.018 million tons, followed by Henan output of 76.071 million tons, Jiangsu 58.565 million tons, Hebei 52.842 million tons, and Sichuan 50.390 million tons.
Among the 7 large cities, the total vegetable output of vegetables in Chengdu, Guangzhou, and Shenzhen is ranked among the top ten in the country.
Chongqing's total vegetable production ranks 13th, but the per capita vegetable output is the highest among 7 large cities, with 680.05 kg. In addition, the three municipalities in Beijing, Shanghai, and Tianjin, the total vegetable output and per capita output rankings are relatively backward.
It depends not only on production, but also consumption.
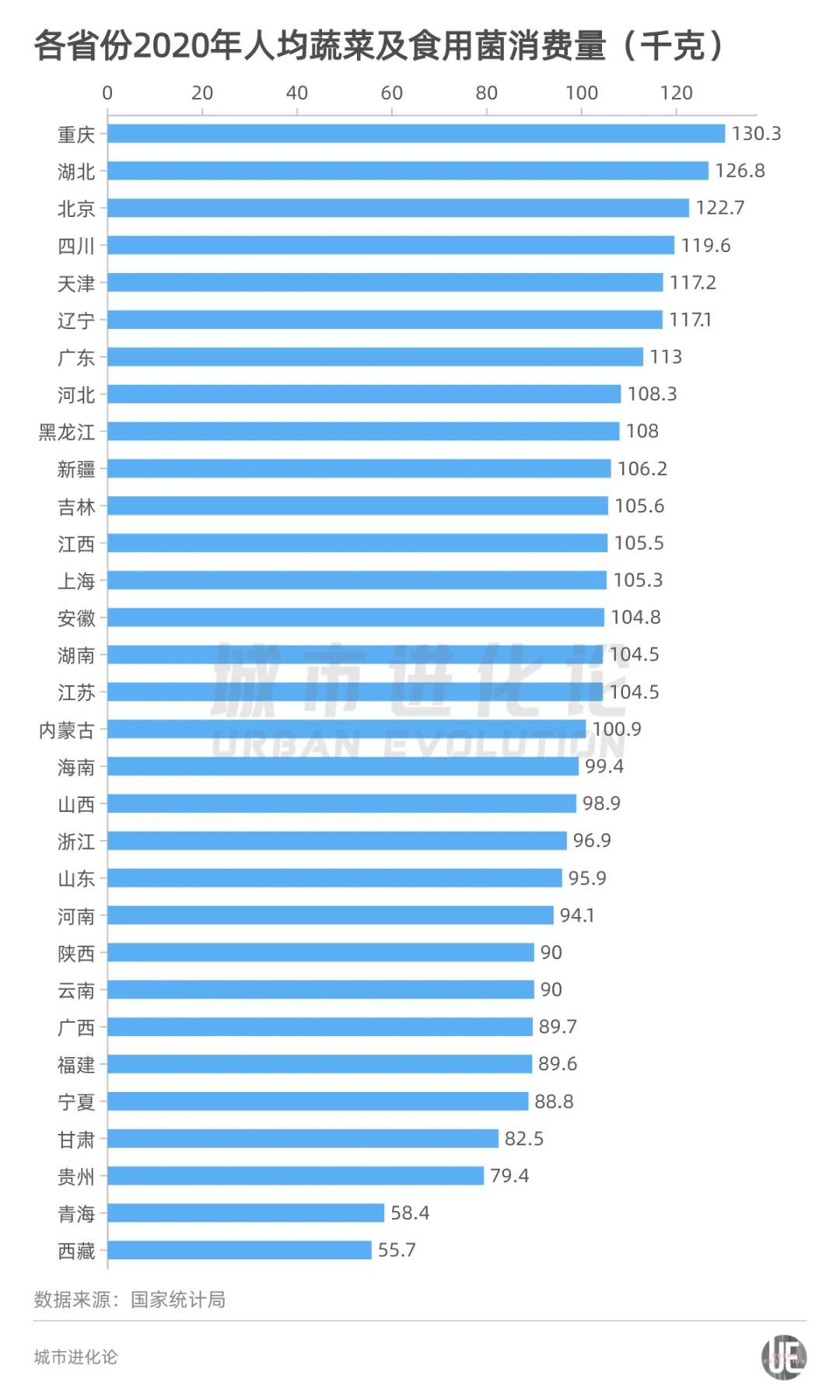
From the 2020 data released by the National Bureau of Statistics (the data of 2021 has not been announced in 2021), the five provinces with the highest per capita consumption per capita in vegetables and edible fungus are Chongqing, Hubei, Beijing, Sichuan, Tianjin, all of which exceeded 117 kg.
Exactly, can the output of vegetables in various places meet the consumer demand of many people?
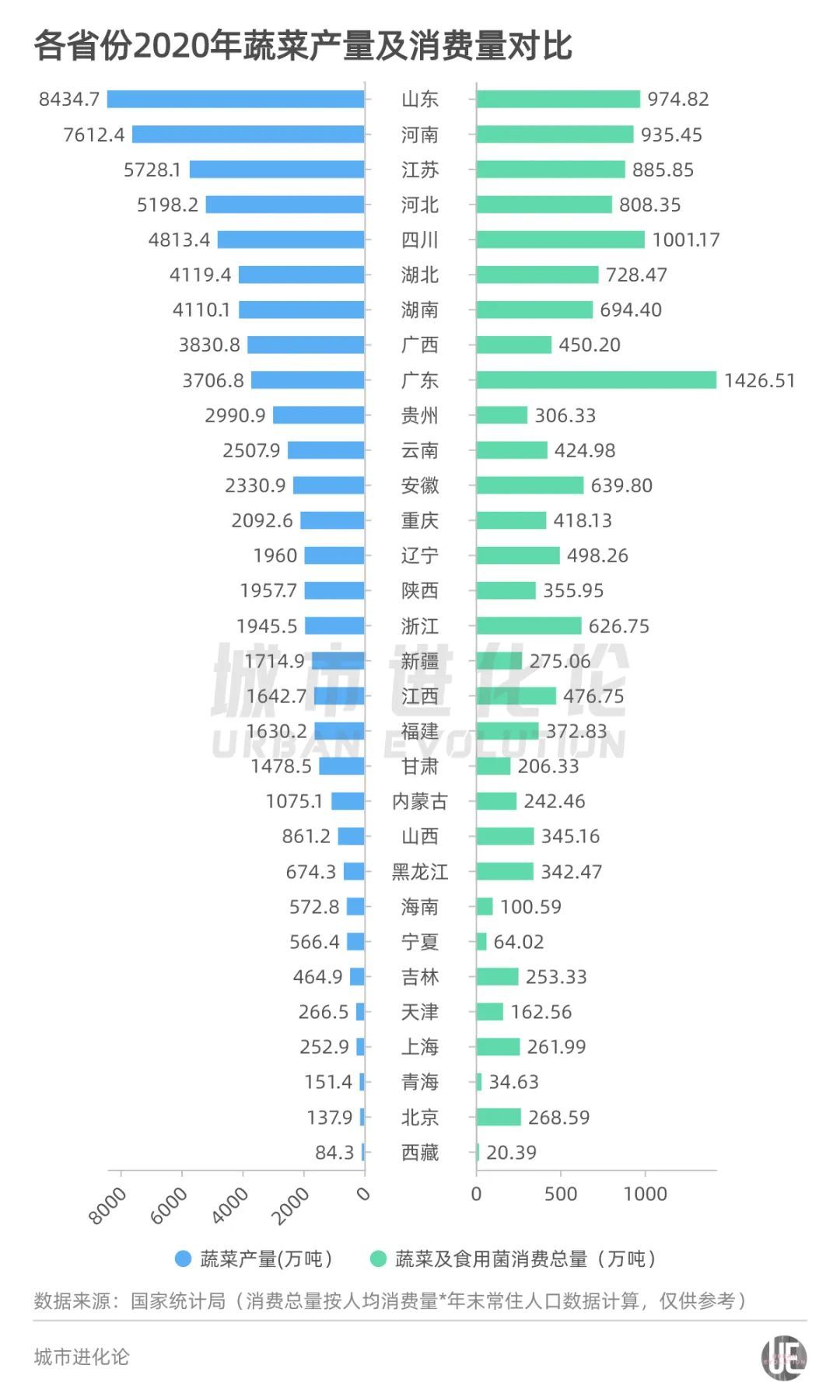
If the consumption of the per capita vegetables and edible fungi per capita by the National Bureau of Statistics' 2020 is multiplied by the total population at the end of the year, the total consumption of each province is calculated, and the total output of vegetables in various places can be found. The output of vegetables in the province is much higher than its consumption, and the "vegetable basket" can be described as full. On this basis, conditions per large cities are also trying to improve the self -sufficiency rate of vegetables.
In 2010, the self -sufficiency rate of vegetables in many large and medium -sized cities across the country did not exceed 30%. In this regard, the State Council has issued the "Notice on Further Promoting Vegetable production guarantee market supply and basically stable prices", which requires stability and improved its self -sufficiency in large cities, "especially large cities with a population of more than one million in urban areas."
Today, the self -sufficiency rate of Shanghai's vegetables and green leafy vegetables has remained at about 40%and 80%for many years; the self -sufficiency rate of Guangzhou vegetables has reached 100%per year; Beijing's self -sufficiency rate has gradually increased from 10%in 2010 to 2021 to 2021. 15%.
Circulation
Of course, oversized cities may not be able to pull the self -sufficiency rate of vegetables to 100%like Guangzhou. In special cases, there may also be a situation of insufficient vegetable supply. In this case, is there sufficient response measures?
In fact, for the sudden "grabbing", Chengdu and Shenzhen also took the initiative to deal with the problem of insufficient supply of vegetables. According to reports, a number of guarantees for enterprises in Chengdu to increase vegetable allocation channels, such as additional goods from vegetable bases such as Kunming and Shandong to Chengdu; Shenzhen's largest "vegetable basket" company also chooses to increase inventory, and the source of vegetables is also Yunnan and Guangdong. And Shandong.
Picture source: Xinhua News Agency

From the data point of view, Shandong is indeed a well -deserved vegetable planting province. But the large output is not enough to show the competitiveness of Shandong vegetables -behind it, it is a complete set of vegetable circulation supply chains.
Financial writer Qin Shuo once went to Shouguang, the "Chinese Vegetable Hometown" in Shandong, and found that agricultural products in some places were sold in Beijing and could not be sold. Go to the dividend of one -stop services in the large market. "
Specifically, the "one -stop service" contains all aspects of the upstream and downstream of the vegetable industry chain. In local media reports, Shouguang is a highland of vegetable information, prices, marketing, logistics, storage and processing. It is not only the largest vegetable distribution center in the country, but also price formation centers, information exchange centers and logistics distribution centers. On average, 8526 kg of Shouguang vegetables are sold at home and abroad every minute.
Improving circulation capabilities is also an important part of the "vegetable basket" project that has been promoted since 1988. At that time, it was precisely because of the improvement of food consumption and structural changes in the improvement of living standards that the "vegetable basket" project must solve the tension of various types of non -staple food supply, which was concentrated in cities, especially large and medium -sized cities. From increasing the self -sufficiency production terminal to the increasing circulation end of supply safety, the supply level of urban by -products is finally enhanced.
Right now, a sound circulation system has basically taken shape for the demand for vegetables in large cities. Data show that by 2020, the agricultural and sideline product market has become the circulation of agricultural and sideline products in urban and rural areas across the country, covering all large and medium -sized cities, and more than 80%of fresh agricultural and sideline products are provided through the wholesale market. Usually, the larger the cities are, the larger the size of the city. The higher the gravity.
For large cities in different geographical locations, vegetable channels that are across the country have also provided important supplements. According to the "National Vegetable Industry Development Plan (2011 ~ 2020)", my country's vegetable production areas are specifically divided into six major areas of South China, Yangtze River, Southwest District, Northwest District, Northeast District, Huanghuaihai and Bohai Rim. There are different types and time. Through the South Caipan North Transport and North Caipan South Transport mechanism, it enriches the "vegetable basket" in each city citizen.
In general, it is difficult for oversized cities to have a completely "lack of vegetables", and an important premise is to ensure the smooth flow of logistics.
Zhang Jing, an associate researcher at the Institute of Agricultural Information of the Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, previously pointed out in an interview that local vegetables' reduction or transportation interruption will not affect the supply of vegetables in large cities. It must be guaranteed to provide residents' "vegetable baskets" and must be urban vegetables and the city's own supply capacity. "At this stage, we discuss the self -sufficiency of vegetables in big cities, and a preset condition is 'emergency'."
It is worth noting that this year's Central Document No. 1 clearly stated that "stabilizing the amount of vegetable land in large and medium -sized cities, vigorously promoting the construction of vegetables in northern facilities and South Cai Bei Transport Bases, and improving vegetable emergency supply capacity."
- END -
Yunnan Min University organized a series of "Lanmei" series of activities 2022

Yunnan Net News (Reporter Han Chengyuan Liu Ziyu Bi Yi Qian Gao Yimeng) On June 15...
Human Resources Control of internal control of public hospitals

Human ResourcesPublic hospitals should design an effective internal control mechan...